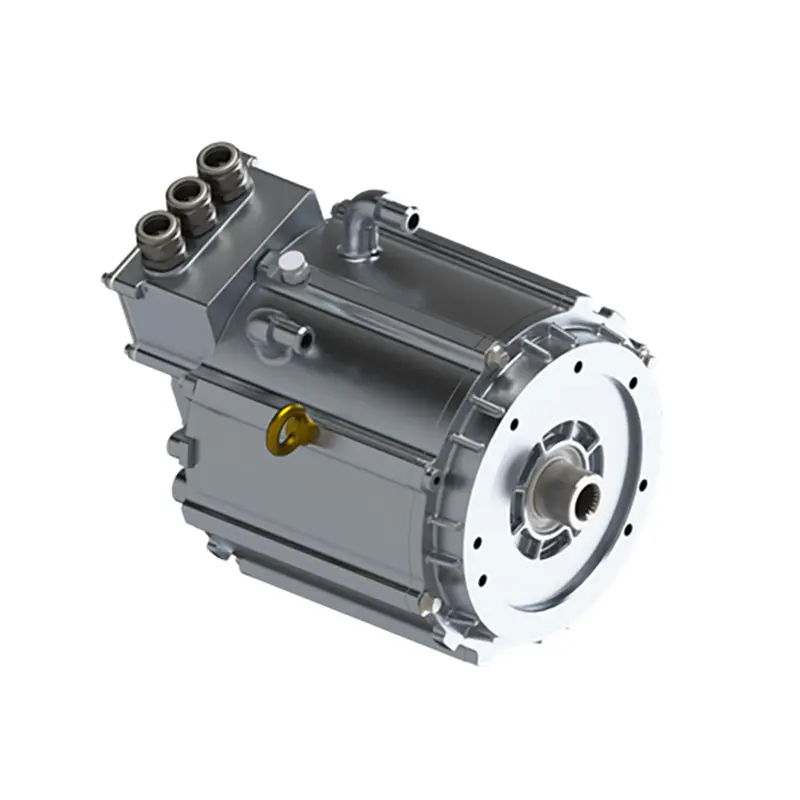
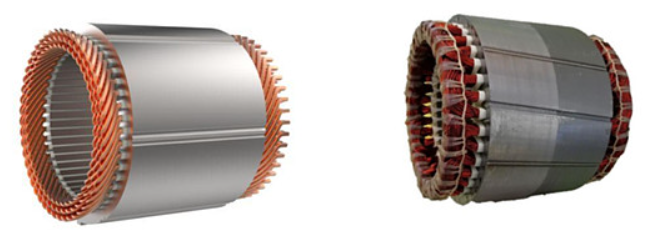
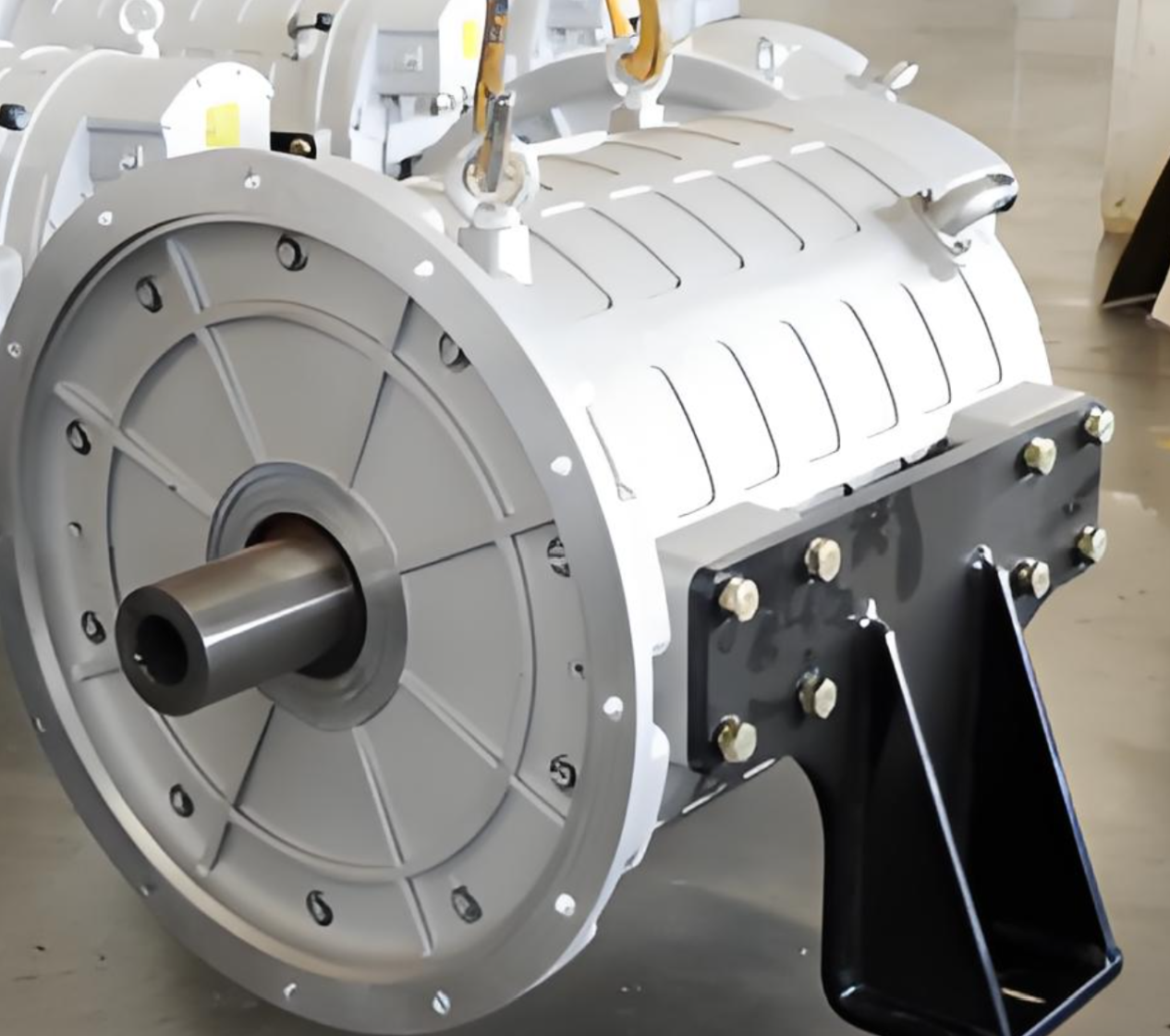
PUMBAA permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM ) for Electric vehicle Drive gen5 PML030
Characteristics of PUMBAA gen6 Electric Vehicle Drive PMSM Motor(Under development)
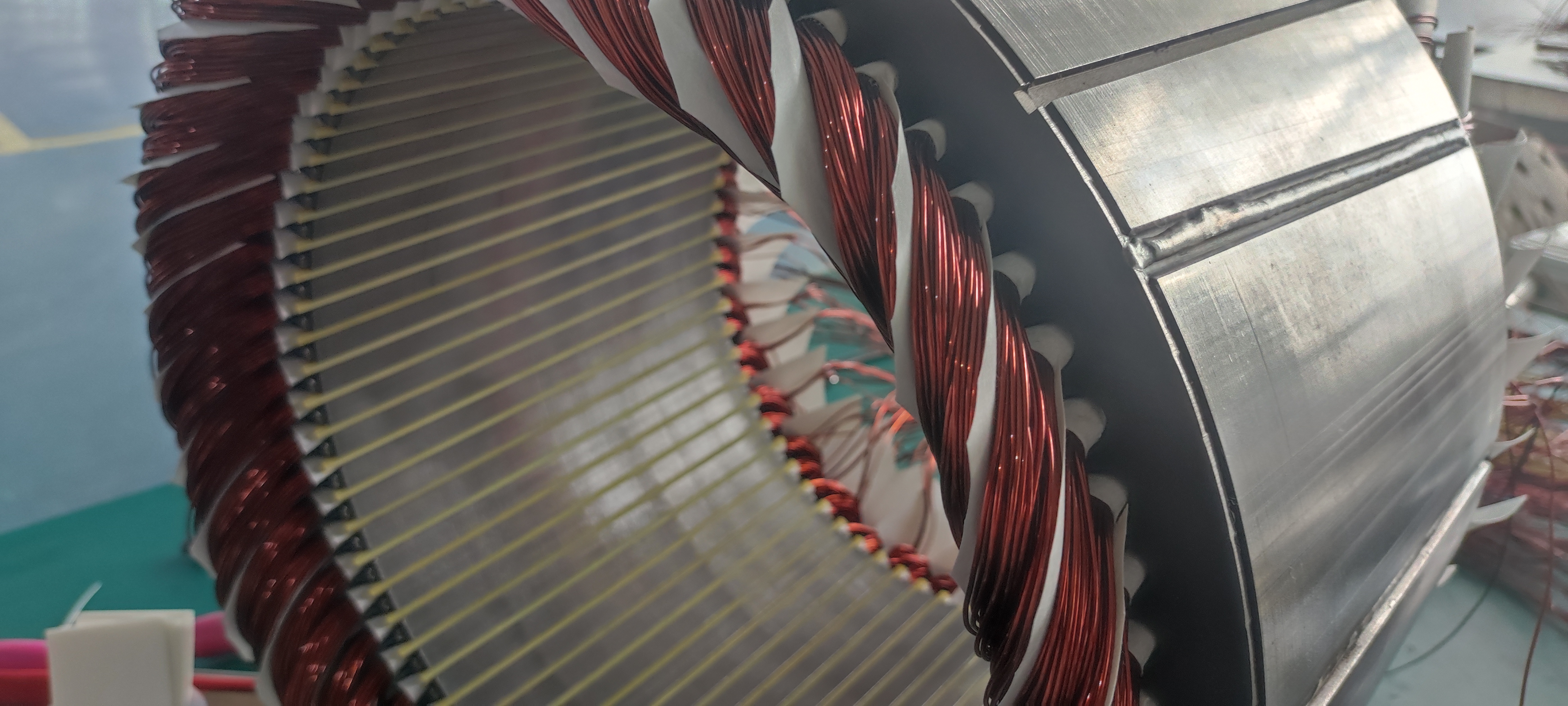
1. Flat wire motor
The winding form of the motor gradually transitions from round wire to flat wire, with high slot filling rate, short ends, high power density and strong heat dissipation capacity
2. High voltage insulation design
The motor adopts new insulating materials and processes to meet the high switching frequency requirements of SiC controllers for increasingly high-speed motors
3. High-speed and heavy-duty insulated bearings
The motor design uses insulated bearings, which can meet the design requirements of 24000RPM/min; And it can effectively inhibit the generation of electrical corrosion of bearings
4. Oil-cooled motor
The motor adopts a high-speed oil-cooled structure, which effectively reduces the rated power after the volume is reduced, which not only improves the efficiency, but also improves the service life of the system
5. Excellent NVH performance
The motor rotor adopts a segmented inclined pole structure, which effectively optimizes the NVH of the motor system
description2
Application of PMSM Motor

Minivans

Mini trucks
description2
What is Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor PMSM Motor?
PMSM motor is a type of AC synchronous motor whose magnetic field is excited by a permanent magnet that generates a sinusoidal reverse electromagnetic field. It contains the same rotor and stator as an induction motor, but the rotor uses permanent magnets to generate a magnetic field. As a result, there is no need to wrap magnetic field windings on the rotor. It is also known as a three-phase brushless permanent magnet sine wave motor.
Principle of PMSM motor
Compared with traditional motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors have high efficiency, brushless, fast speed, safety and high dynamic performance. It produces smooth torque and low noise, and is mainly used in high-speed applications such as robotics. It is a three-phase AC synchronous motor that operates synchronously with an external AC power source.
Instead of using windings, the rotor is fitted with permanent magnets to create a rotating magnetic field. With no DC power supply, these motors are very simple and inexpensive. It contains a stator mounted with 3 windings and a rotor mounted with permanent magnets to create magnetic field poles. Provide a three-phase input AC power to the stator and the operation will begin.

Permanent magnet synchronous motors work similarly to synchronous motors. It relies on a rotating magnetic field to generate an electromotive force at synchronous velocity. When the stator windings are energized by a three-phase power supply, a rotating magnetic field is generated between the air gaps.
Torque is generated when the rotor poles maintain a rotating magnetic field at a synchronous speed, and the rotor rotates continuously. Since these motors are not self-starting, it is necessary to provide a variable frequency power supply.
description2
Structure of the PMSM motor
Stator for PMSM motors:
As with normal AC induction motors, power is provided through the stator windings. PMSM stator windings are typically distributed over multiple slots to approximate a sinusoidal distribution, resulting in a reverse EMF waveform of the sinusoidal waveform.
Rotor of PMSM motors:
The structure of a permanent magnet synchronous motor is similar to that of a basic synchronous motor, with the only difference being the rotor. The rotor does not have any magnetic field windings, but permanent magnets are used to generate magnetic field poles. The permanent magnets used in PMSM are made up of samarium cobalt and dielectric, iron, and boron because of their high permeability.
The most widely used permanent magnet is ferron neodymium boron because of its low cost and easy availability. In this type, permanent magnets are mounted on the rotor. According to the installation method of the permanent magnet on the rotor, the structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be divided into two types.
If the magnet is mounted on the surface of the motor's rotor, the PMSM motor is called a Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet (SPM).
If the magnet is mounted inside the rotor, the PMSM motor is called an Interior Permanent Magnet (IPM). Motors with internal permanent magnet (IPM) rotors provide extremely high efficiency.

The structure of the PMSM motor
description2
PMSM control principle
description2
Advantages and disadvantages PMSM Motor
Advantages of PMSM Motor
PMSM has a strong overload capacity. The power density of PMSM is higher than that of induction motors.
Higher efficiency and smaller size compared to induction motors (permanent magnet motors are only one-third the size of most AC motors, which makes installation and maintenance easier).
PMSM is able to maintain full torque at low speeds.
PMSM motors use magnets to generate the rotor magnetic field instead of using the magnetized component of the stator current as in induction motors. These magnets consume almost no power, so unlike AC induction motors and excitation synchronous motors, the copper loss of the rotor is negligible.
Compared to induction motors, PMSM has low rotor electrical losses and less heat dissipation. In addition, since mechanical collectors and brushes do not need to be worn like induction motors, there is little friction and high durability.
PMSM is low maintenance, durable, and reliable. For brushless and mechanical switches, the cost of regular maintenance is greatly reduced, and the risk of sparks in special environments is eliminated.
PMSM motors operate at a higher power factor, which improves the power factor of the whole system. The increase in the power factor also reduces the voltage drop in the system and at the end of the motor.
Provides smooth torque and dynamic performance
Disadvantages of PMSM Motor
This type of motor is very expensive compared to induction motors.
Since it is not a self-starting motor, it is difficult to start.
We need a sophisticated control system to control the stator current.
In the realm of electric motors, the inverter brushless motor, often referred to as a BLDC inverter motor, plays a crucial role in modern applications. Both of these motor types utilize permanent magnets and rely on electronic commutation to operate efficiently. The BLDC inverter motor is designed to work seamlessly with inverter technology, converting direct current into alternating current to control motor speed and torque. This technology is closely related to Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM), as both utilize similar principles of operation. While the BLDC inverter motor typically emphasizes simplicity and cost-effectiveness, PMSM motors are known for their high precision and performance in demanding applications. Ultimately, the connection between these motor types highlights the advancements in electric motor technology, making them integral to various industrial and automotive applications.
description2