E-Axle for Trucks Driving the Future of Electric Commercial Vehicles
1.Introduction
The global transportation sector is undergoing a seismic shift as industries worldwide transition toward sustainable mobility. Among commercial vehicles, especially heavy-duty trucks, the need for cleaner, more efficient propulsion systems has never been more urgent. Governments are tightening emission regulations, logistics companies are under pressure to reduce carbon footprints, and technology is evolving to meet the new era of mobility. At the forefront of this transformation is the E-Axle—a cutting-edge technology redefining the performance and efficiency of electric trucks.
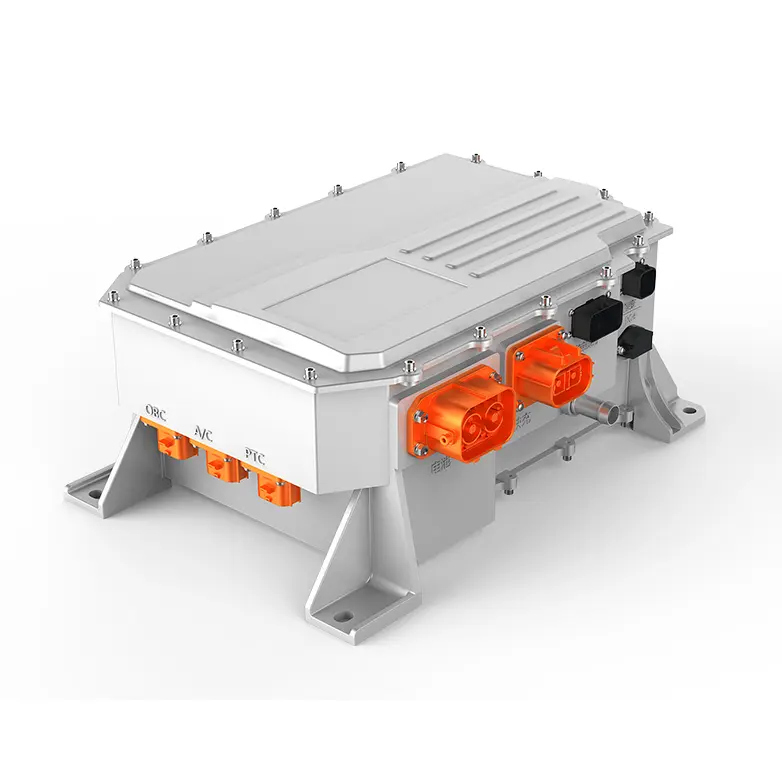
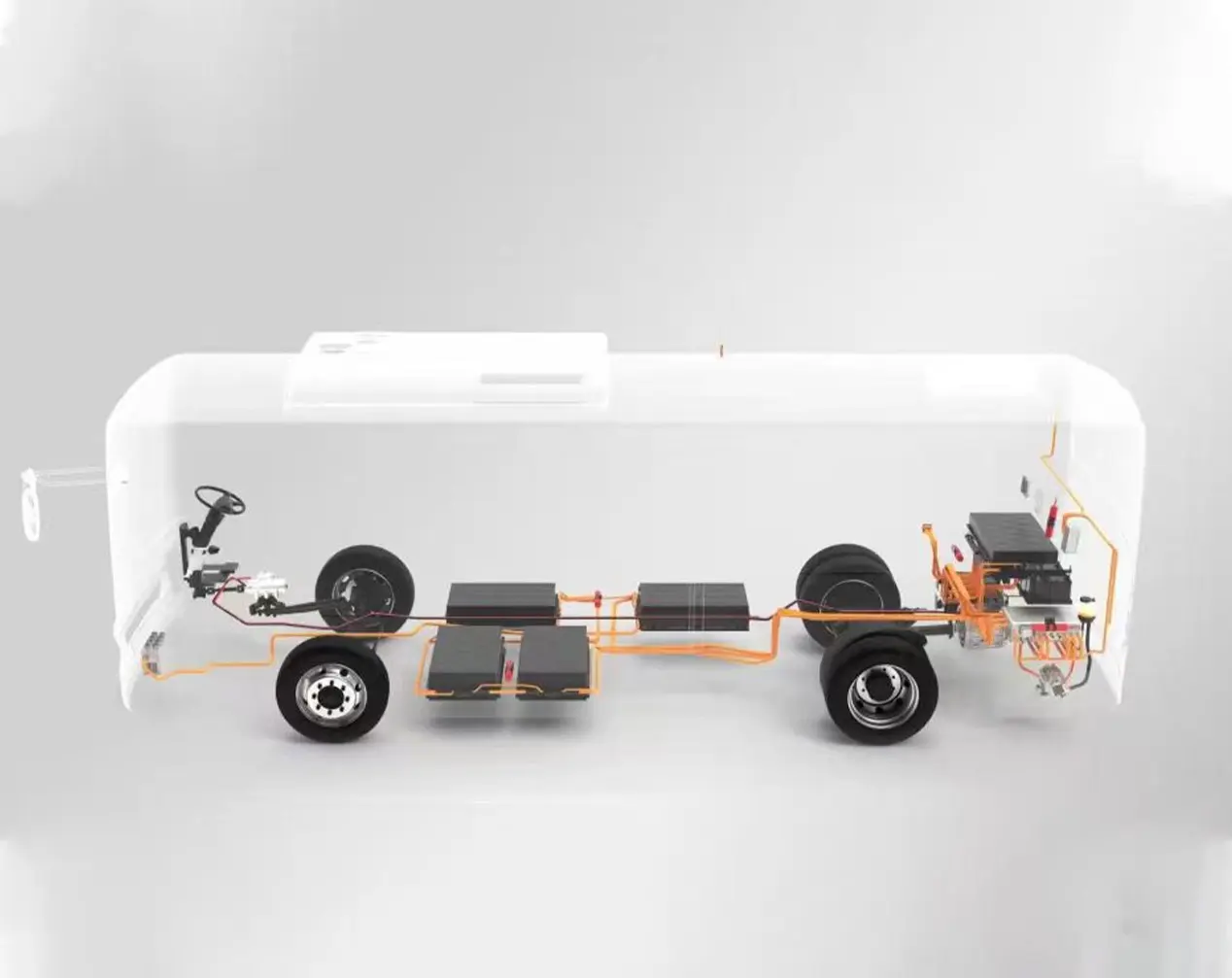
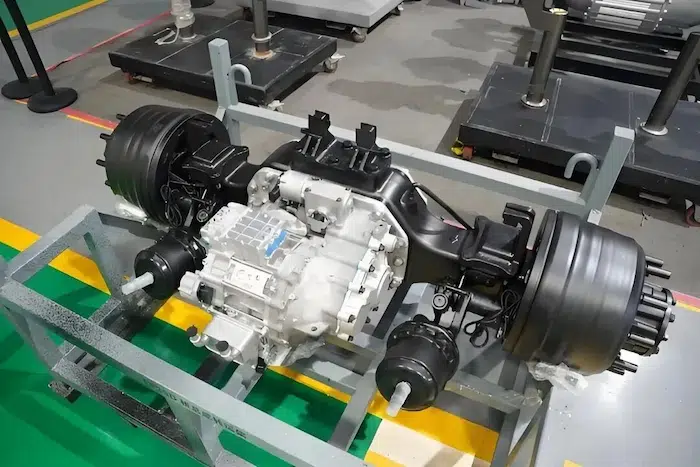
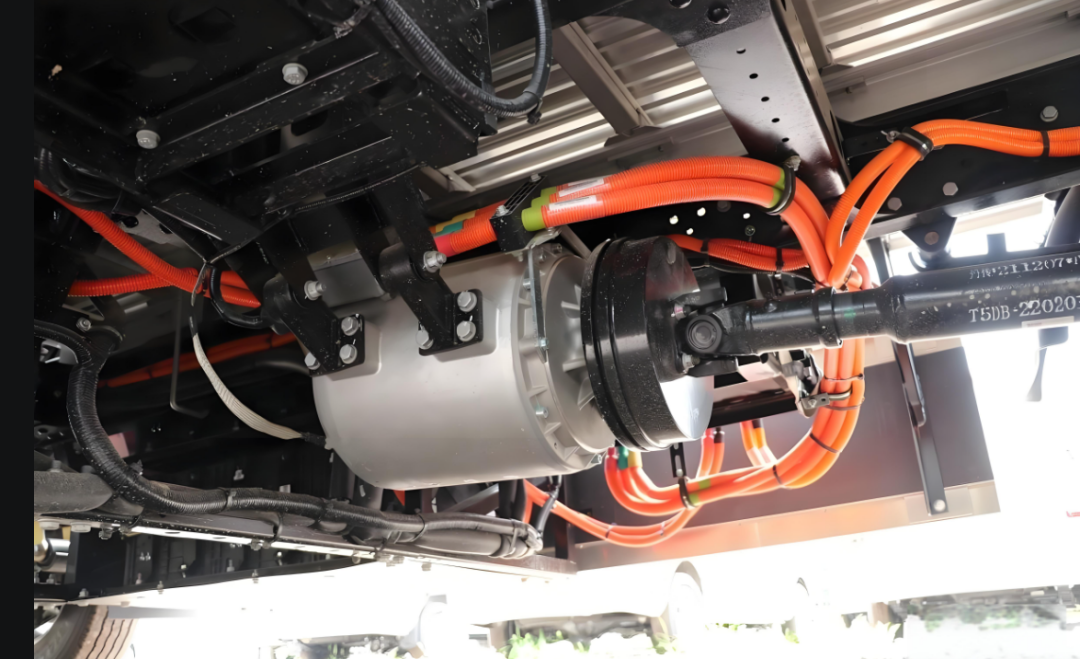
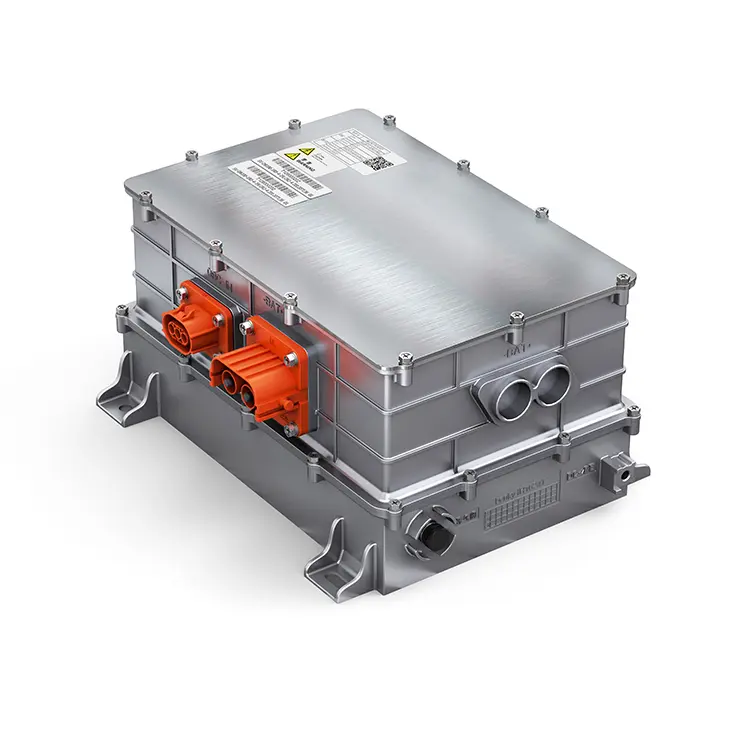
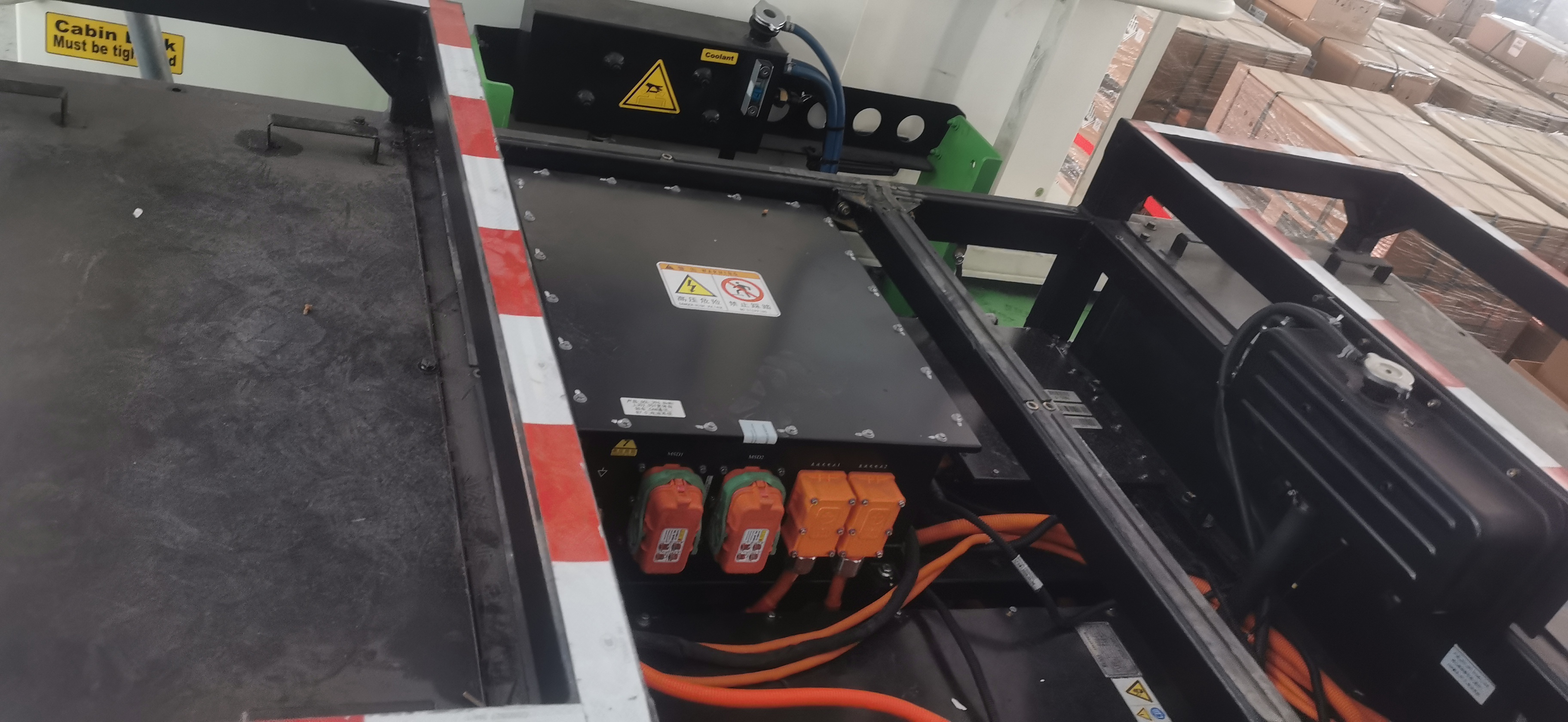
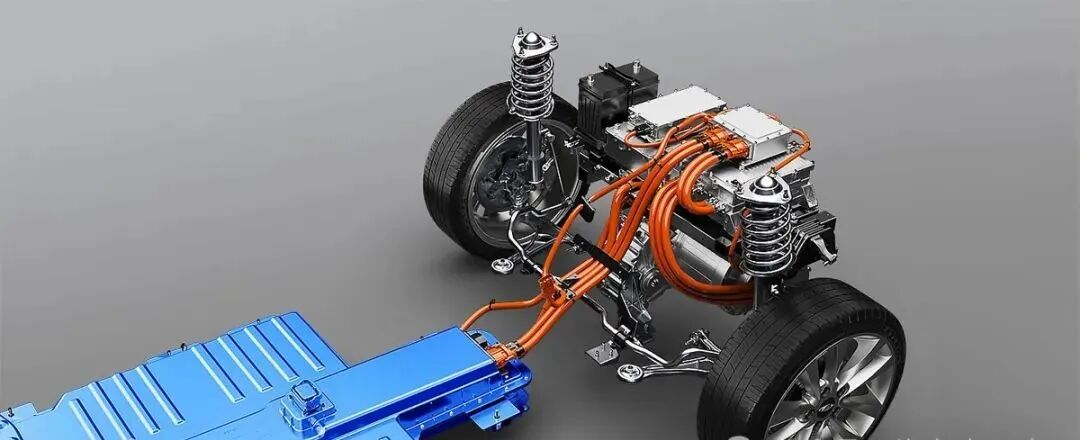
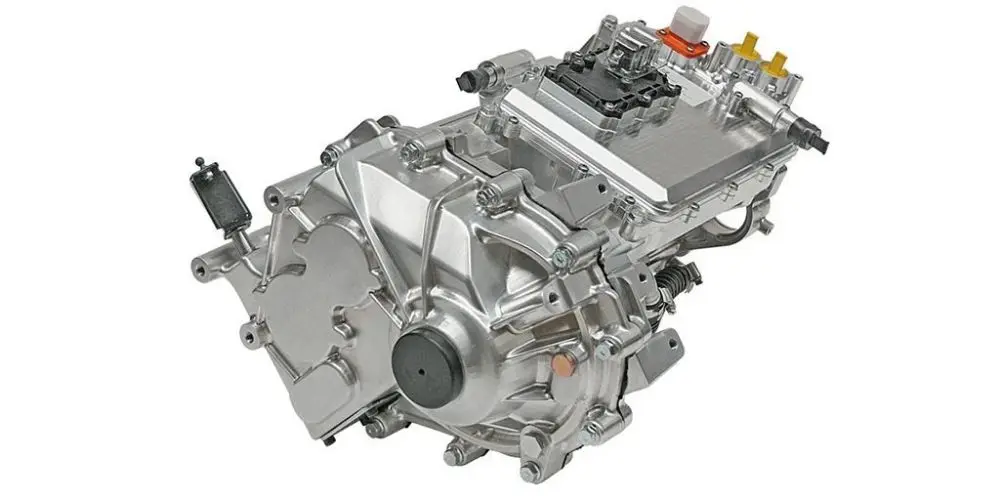
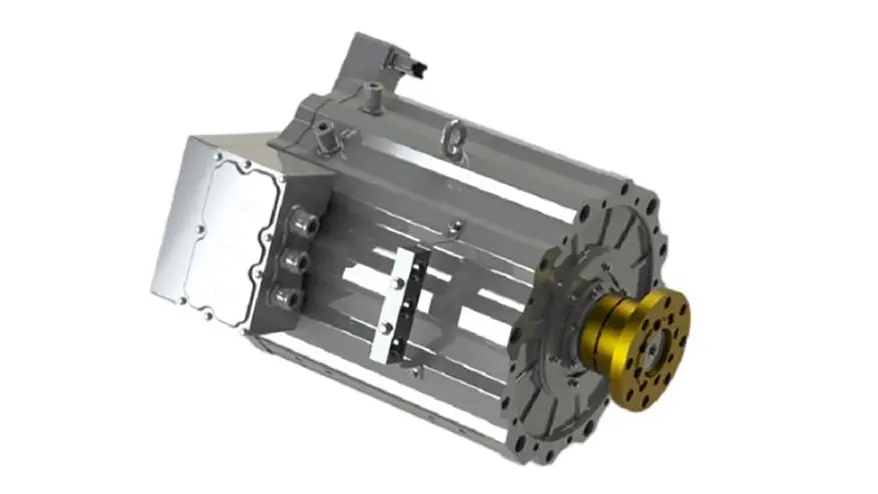
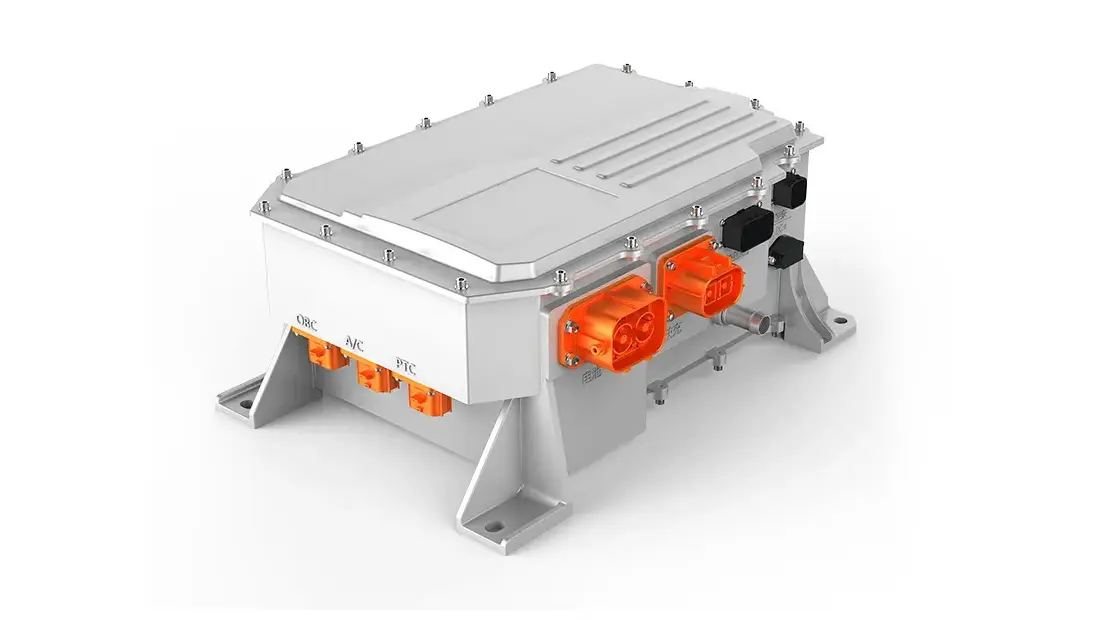
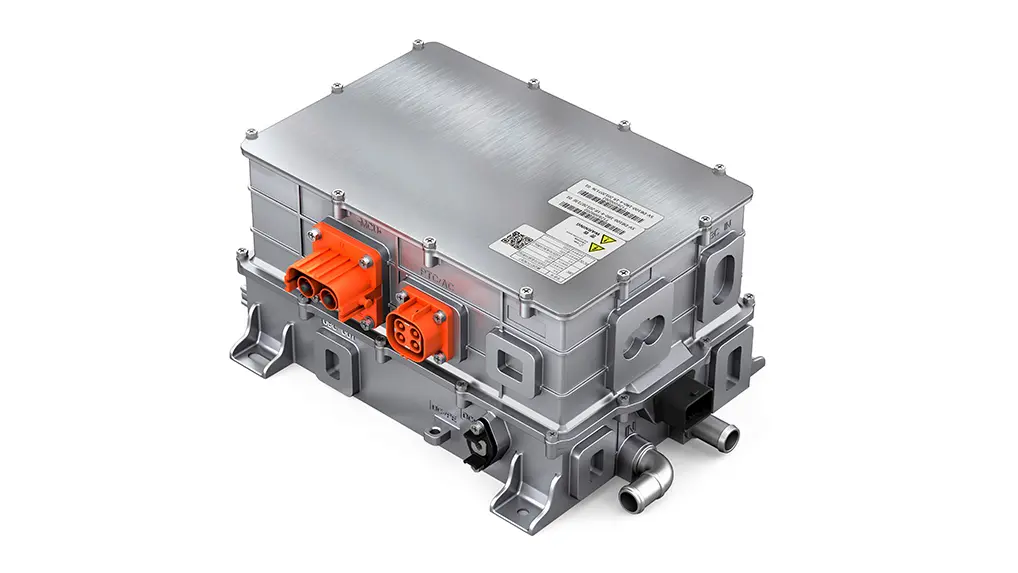
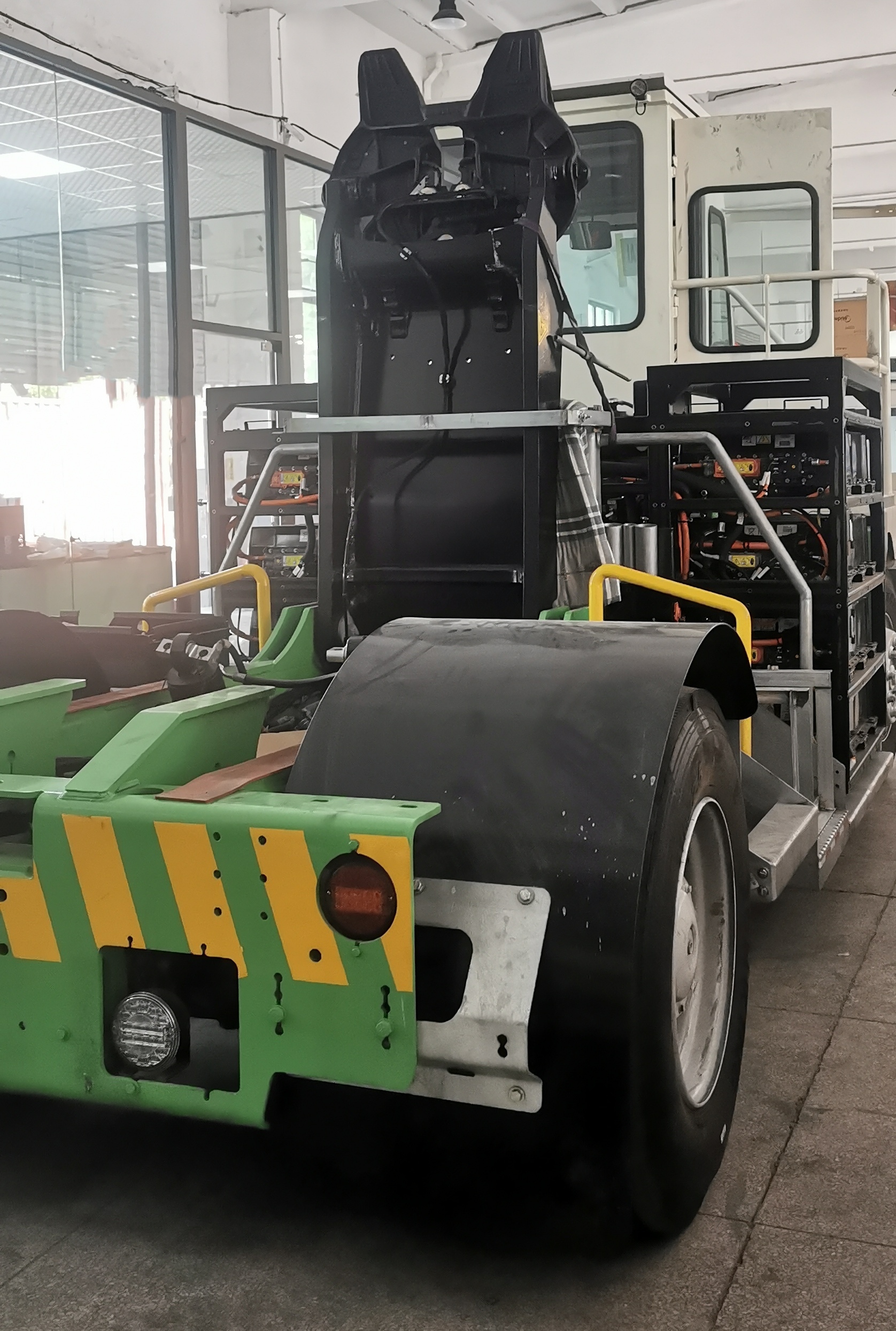
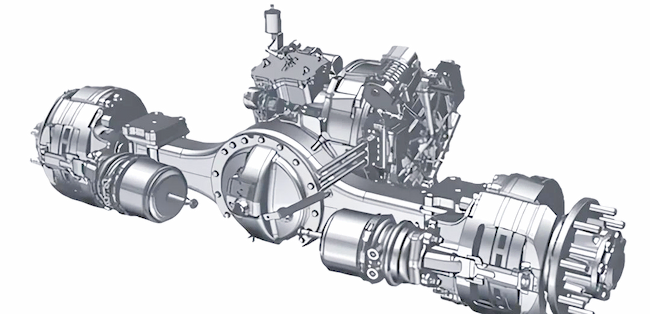
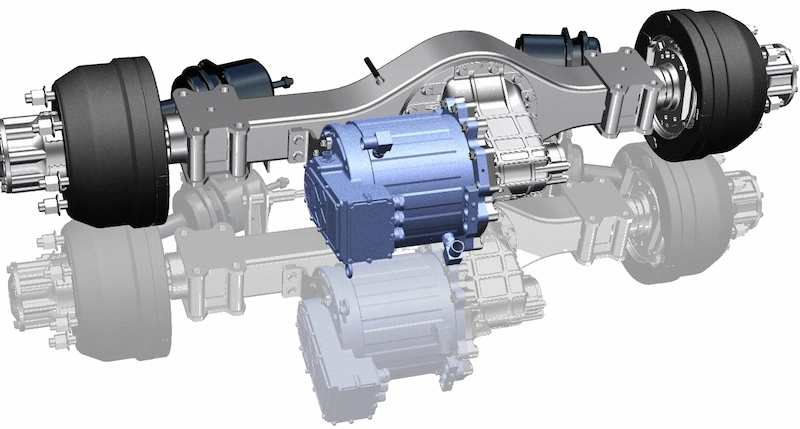
The E-Axle, or electric axle, integrates the motor, power electronics, and transmission directly into the axle structure, creating a compact and highly efficient propulsion system. For trucks, which require both power and durability to move heavy loads over long distances, the E-Axle represents a paradigm shift. It enables higher energy efficiency, reduces mechanical complexity, and optimizes space utilization, making electric trucks not just viable but competitive with their diesel counterparts.
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of E-Axles, their key components, benefits, challenges, and their growing role in shaping the future of electric commercial vehicles.
2.What is an E-Axle?
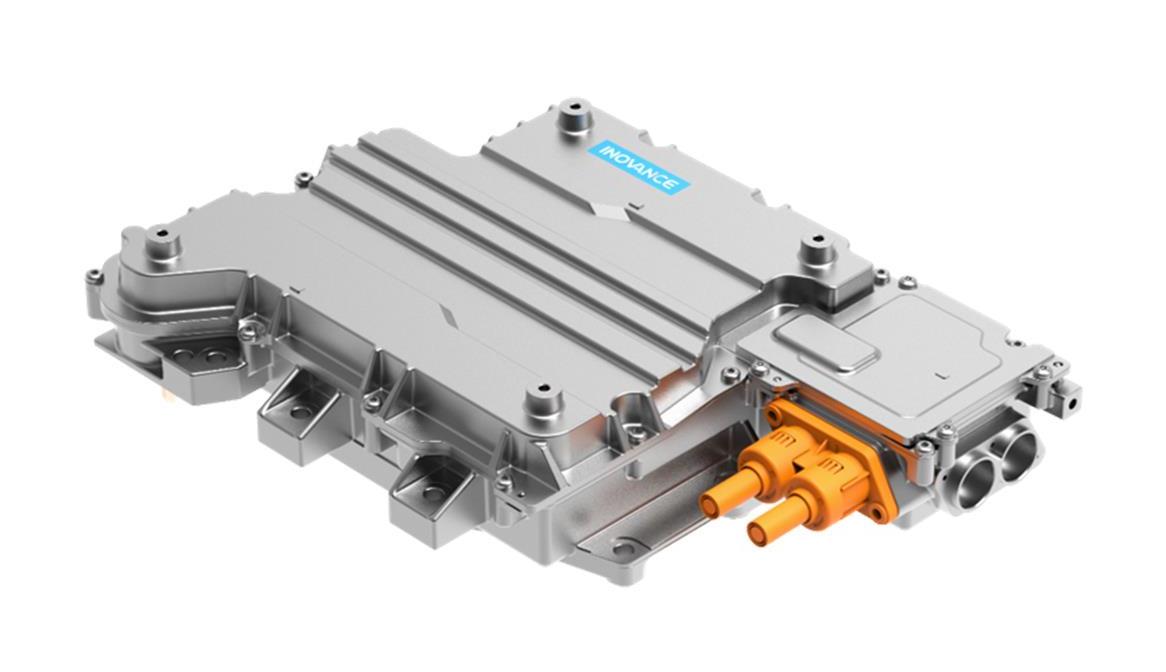
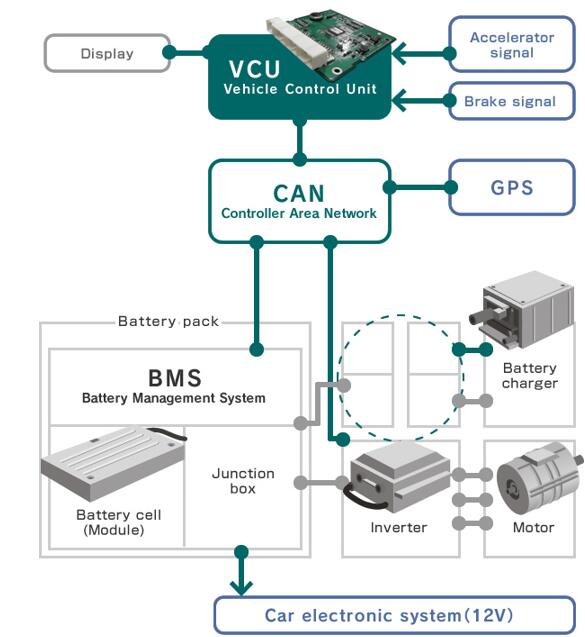
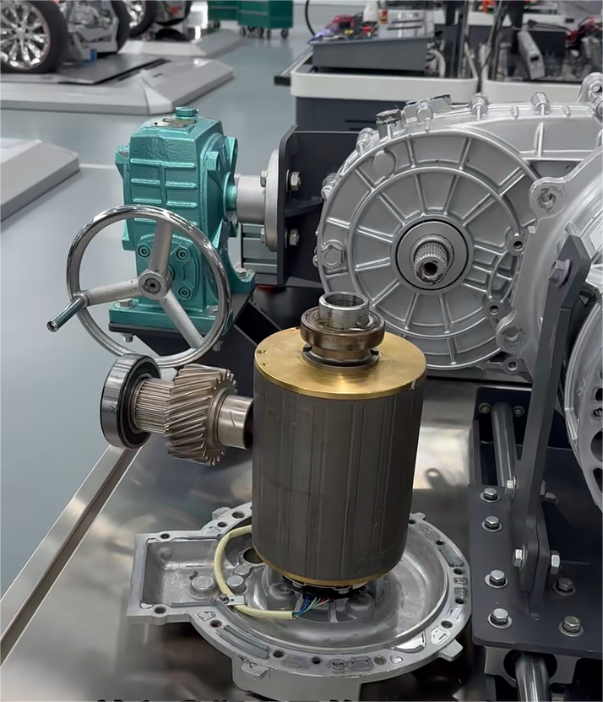
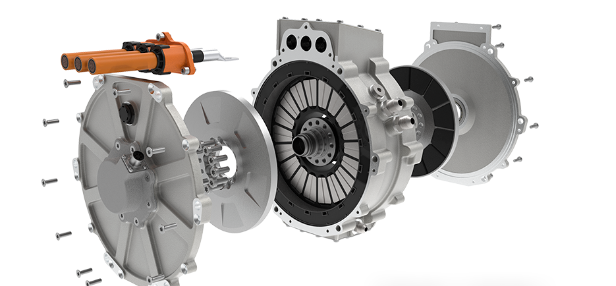
An E-Axle is an integrated electric drive solution that combines several critical components—electric motor, inverter, gearbox, and control systems—into a single compact unit housed within the axle of a vehicle. Instead of relying on a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) with a complex powertrain (engine, transmission, driveshaft, differential, etc.), the E-Axle simplifies the drivetrain and delivers power directly to the wheels.
Key Characteristics of an E-Axle:
- Integration: Motor, inverter, and transmission built into one module.
- Compactness: Reduced space requirement compared to traditional layouts.
- Efficiency: Higher energy transfer efficiency with fewer mechanical losses.
- Scalability: Can be used in light-duty vans, medium trucks, and heavy commercial vehicles.
In electric trucks, the E-Axle enables manufacturers to optimize vehicle architecture. For instance, removing bulky transmissions or large drivetrains allows for bigger battery packs, increasing driving range—an essential factor for long-haul transport.
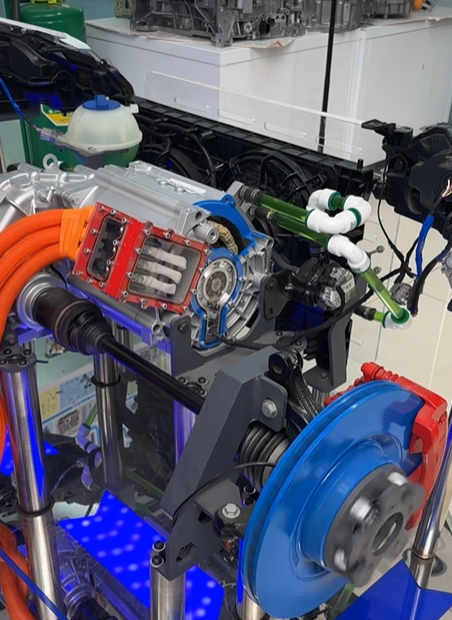
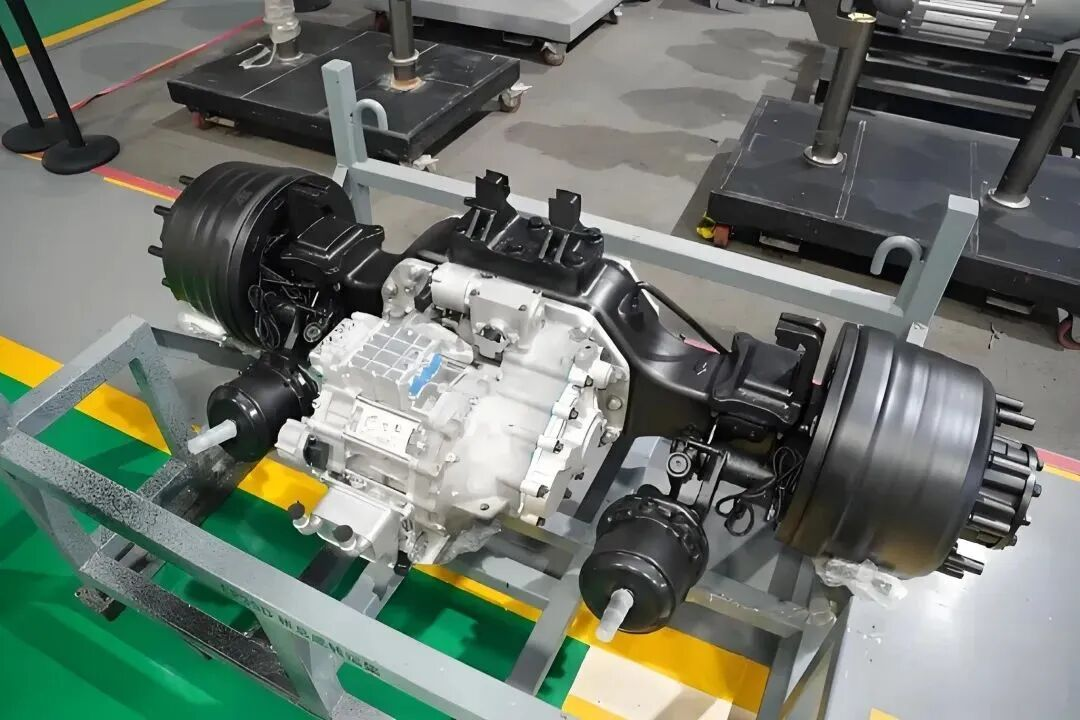
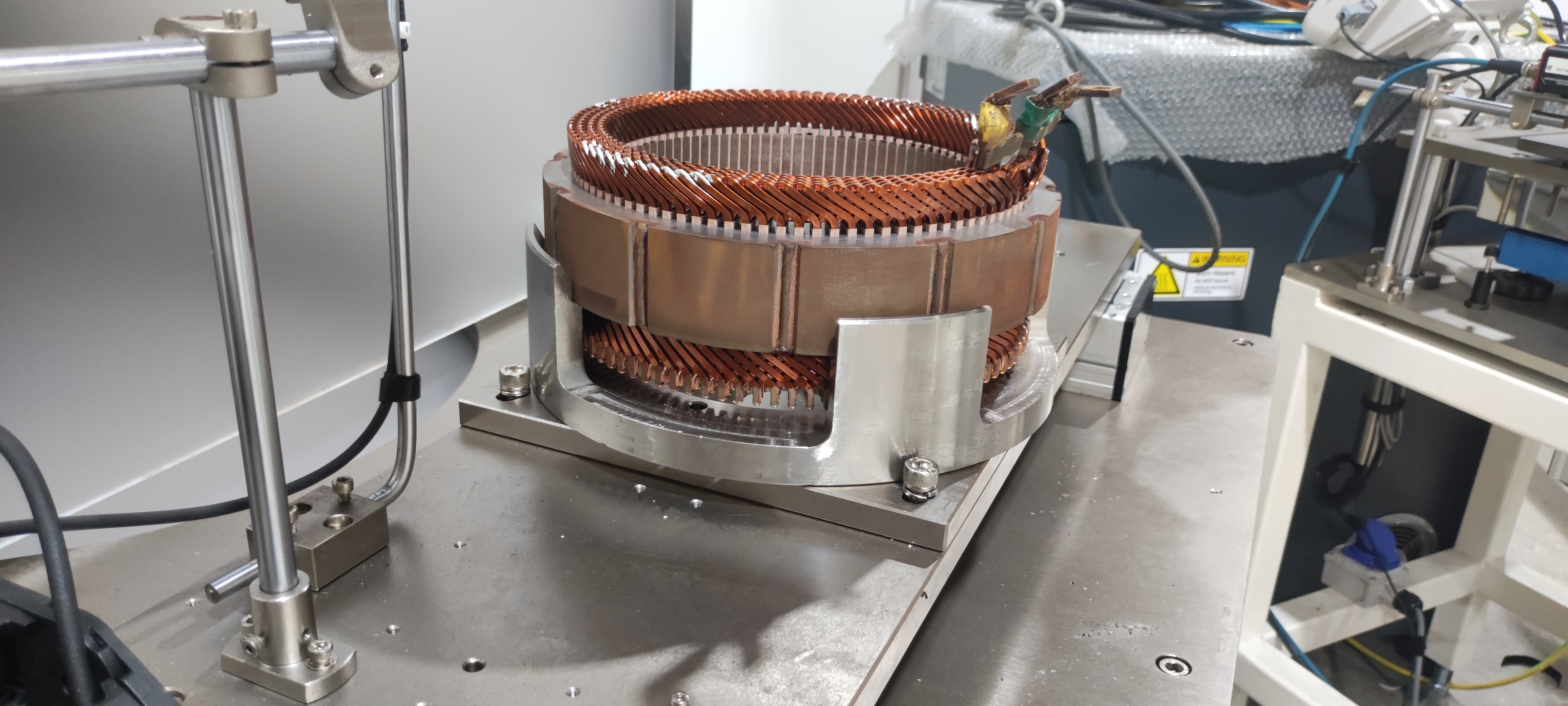
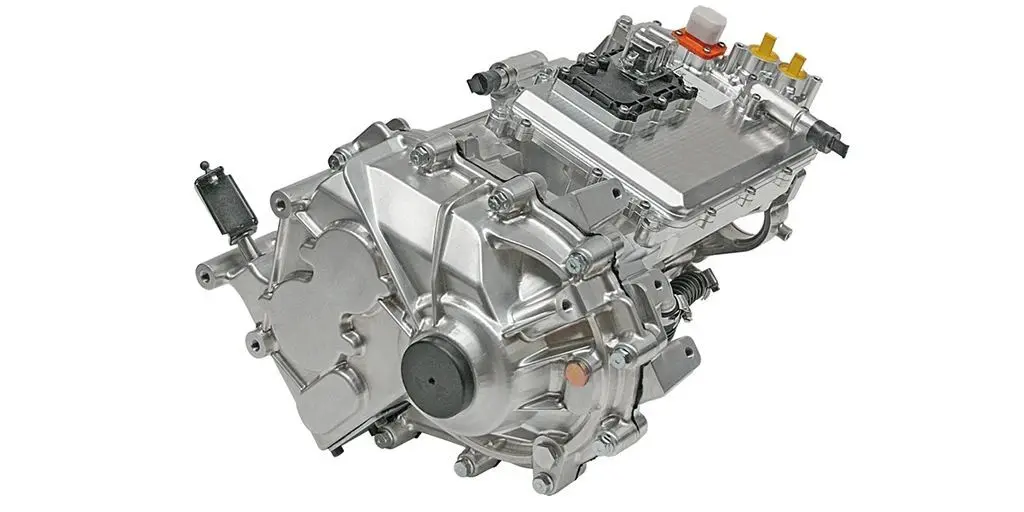
3.Key Components and Technology
An E-Axle is more than just a motor and axle; it is a sophisticated system that integrates several technologies:
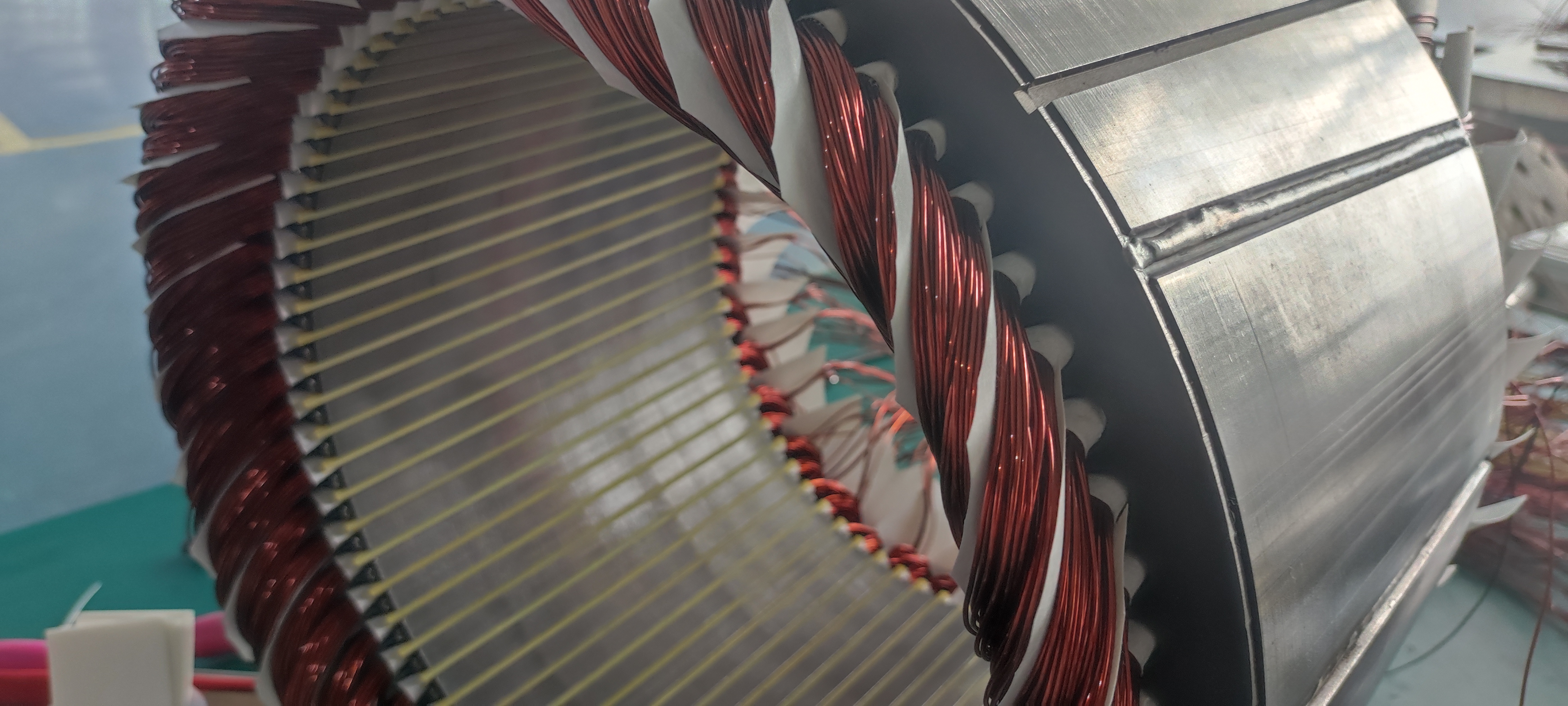
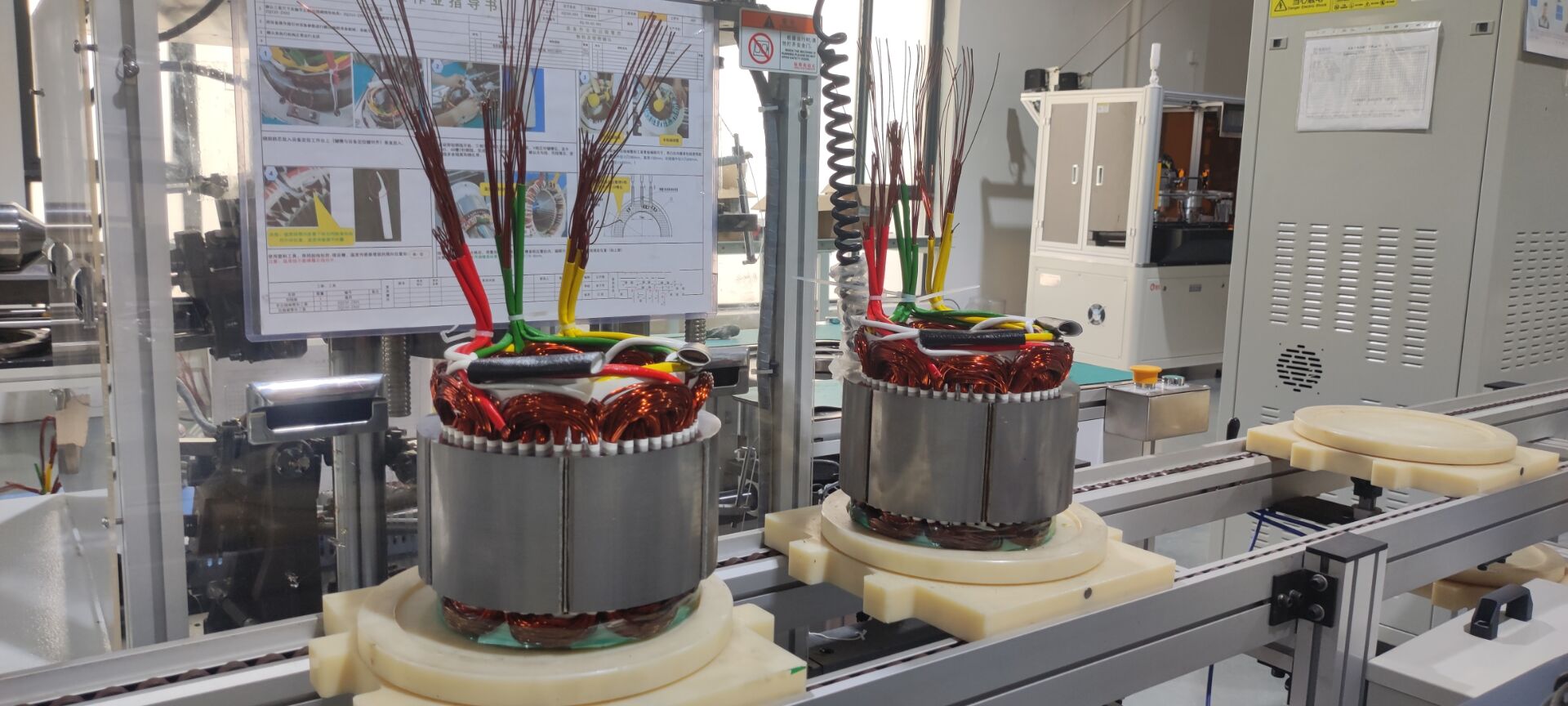
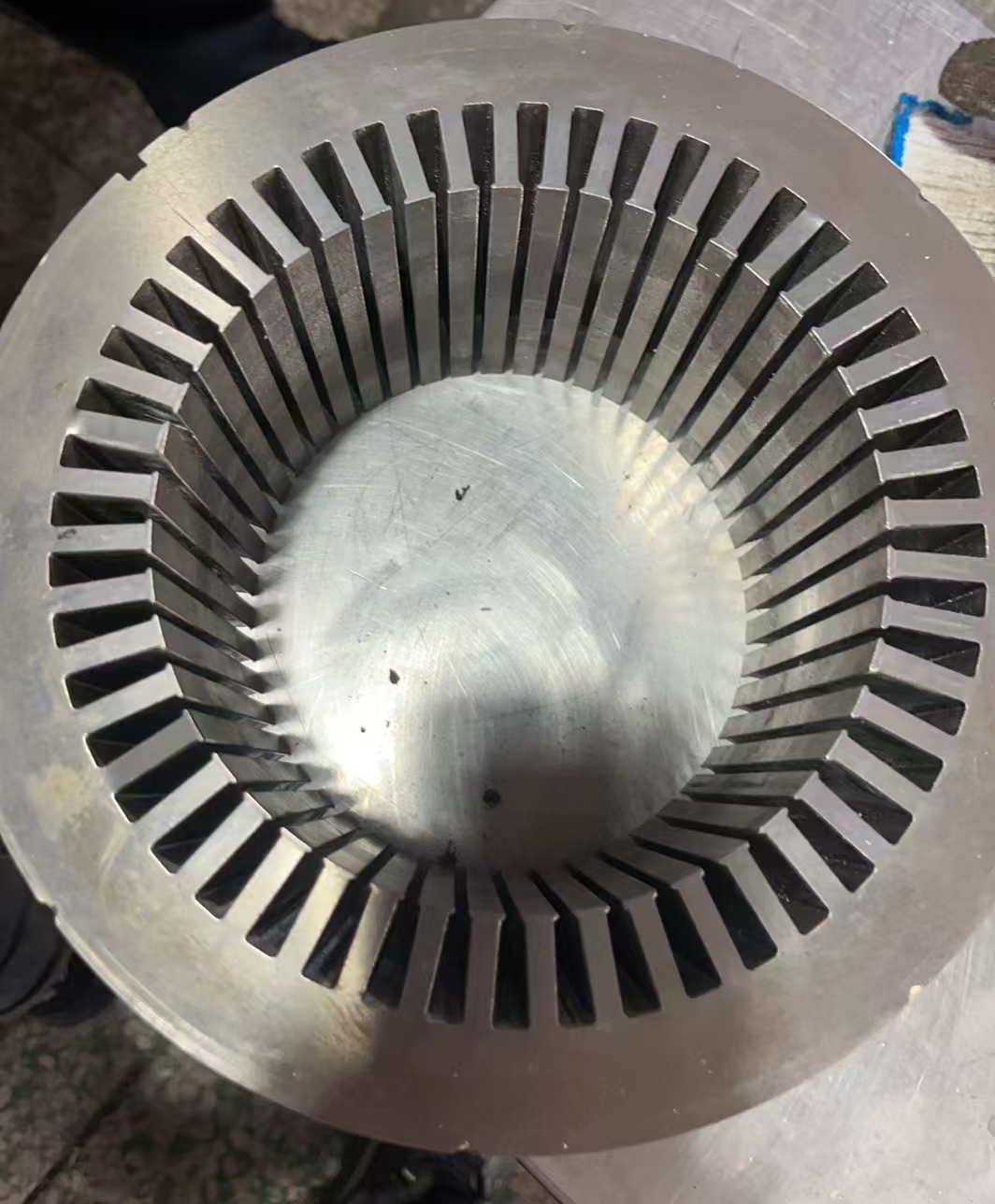
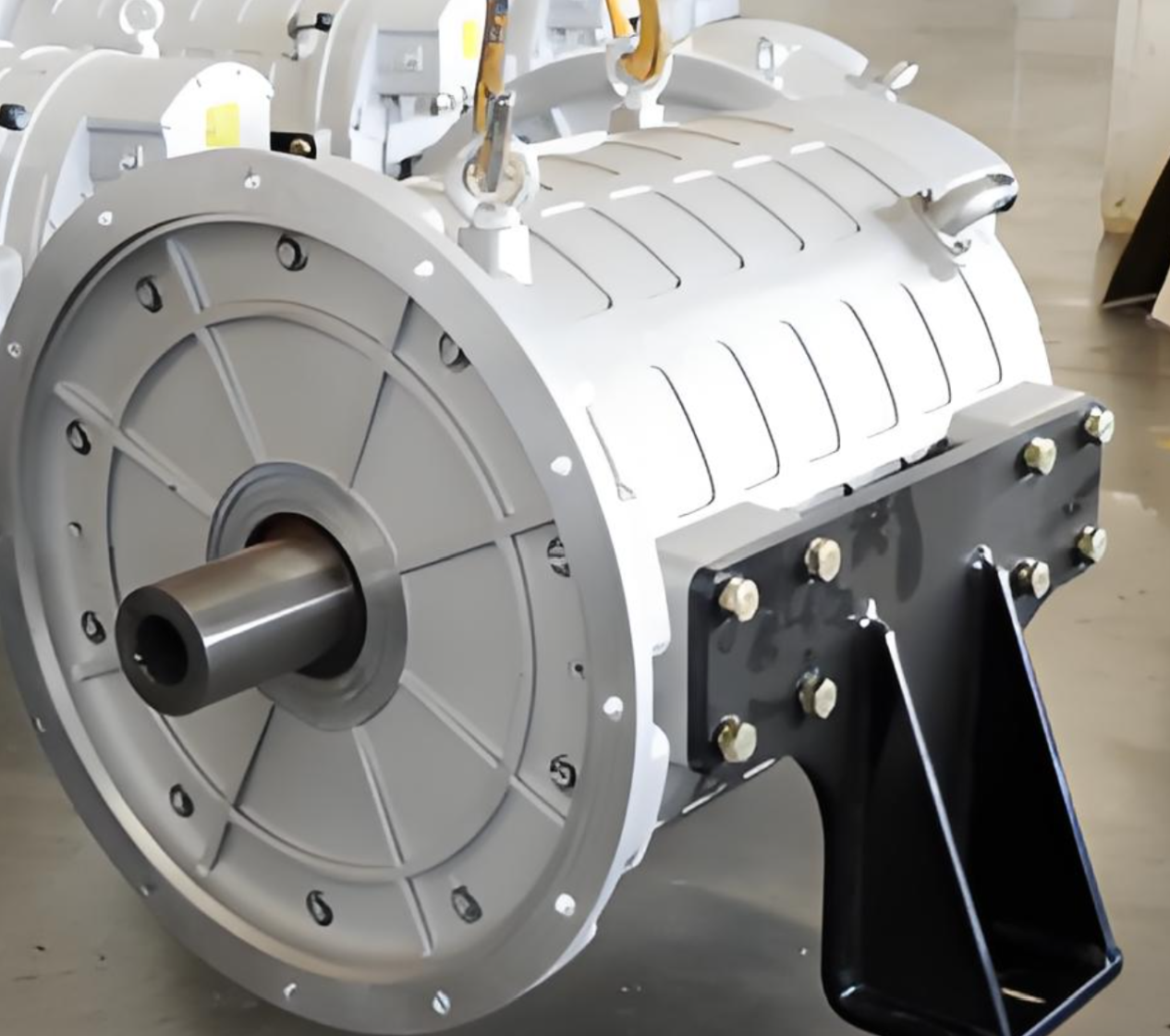
1. Electric Motor
The motor is the heart of the E-Axle. Common motor types used include:
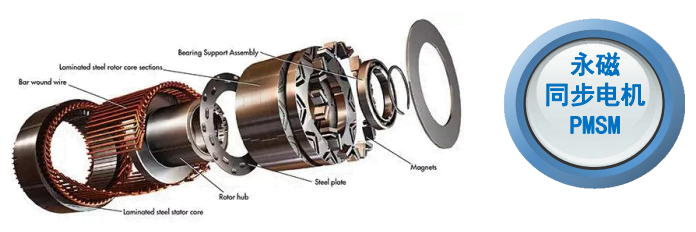
·Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM): Highly efficient and compact.
·Induction Motors (IM): More affordable but slightly less efficient.
·Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM): Gaining attention for cost and durability.
For heavy-duty trucks, PMSM motors are most popular due to their superior torque density and energy efficiency.

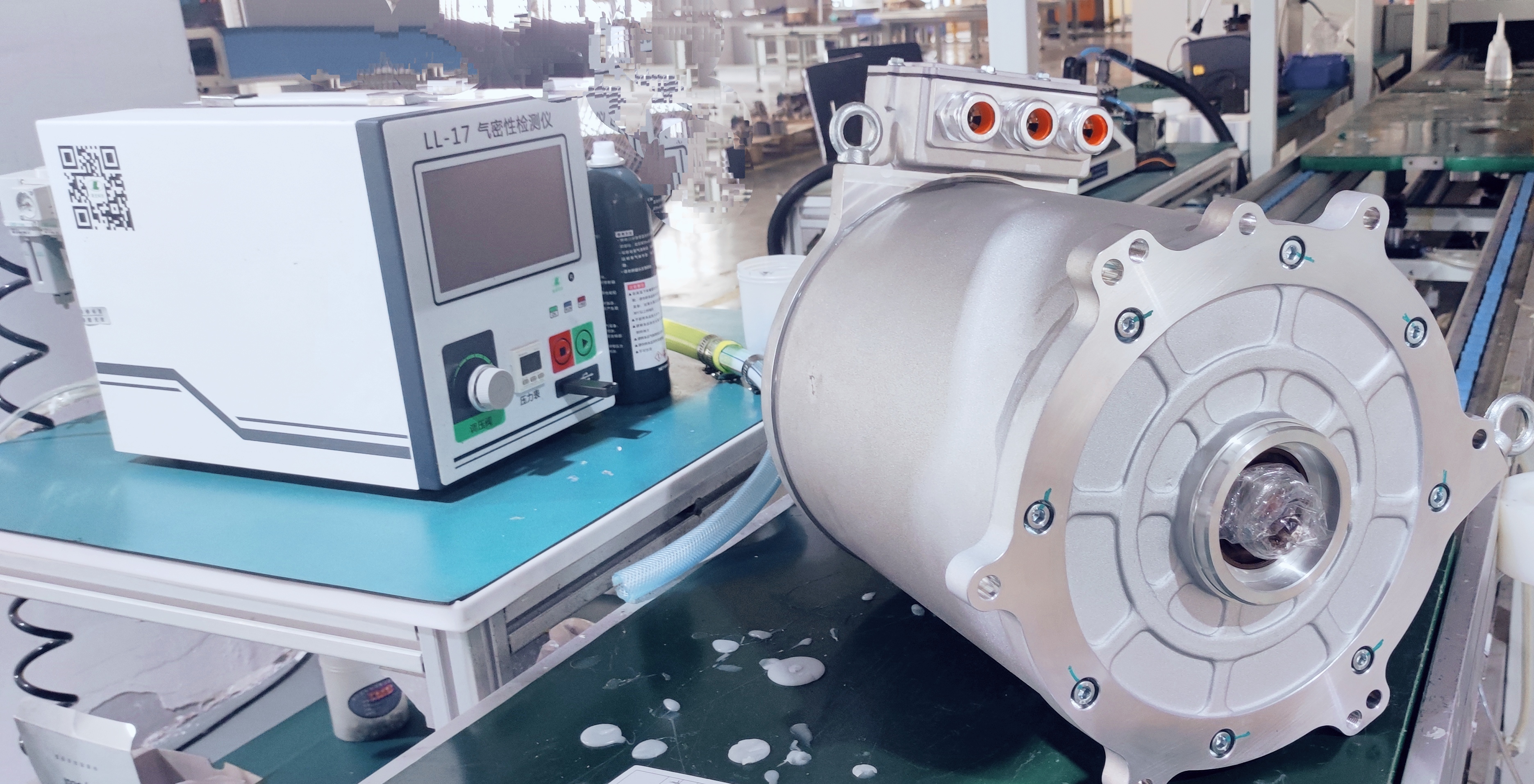
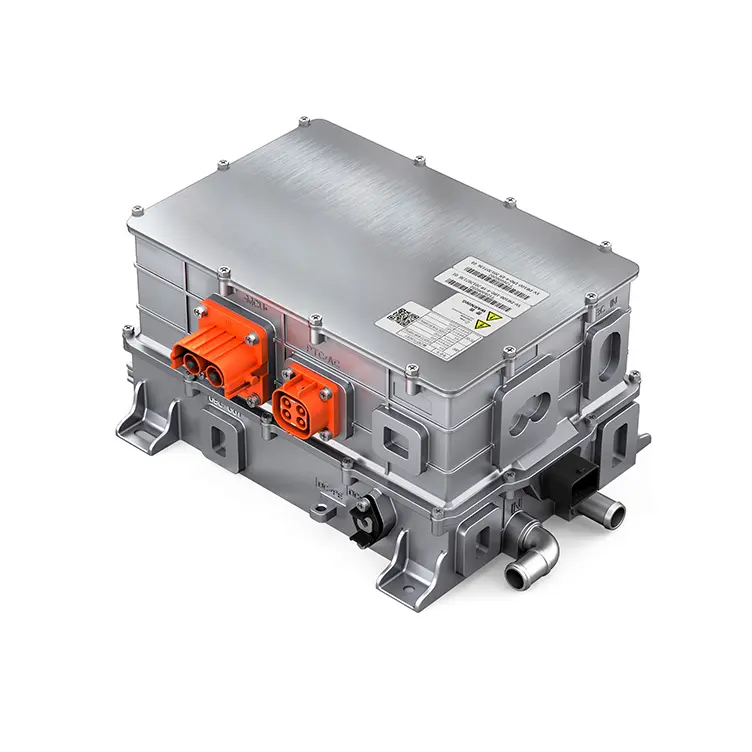
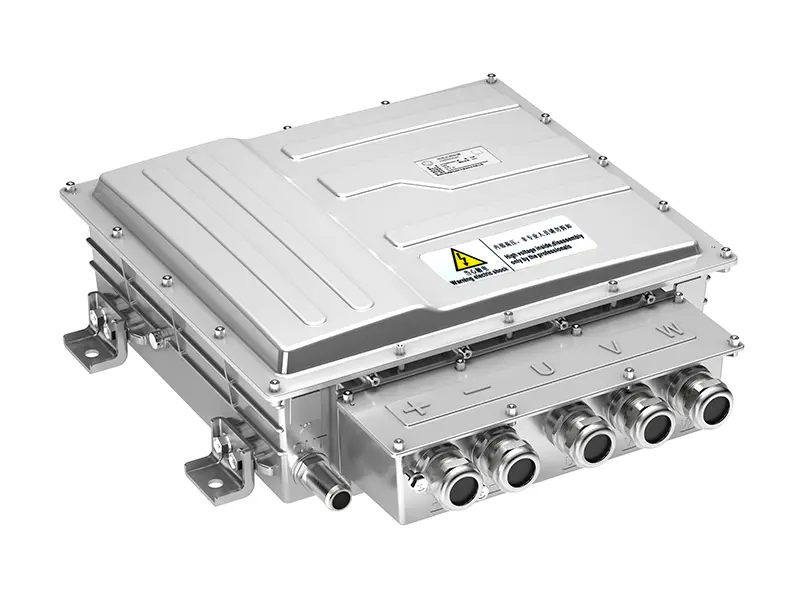
2. Inverter and Power Electronics
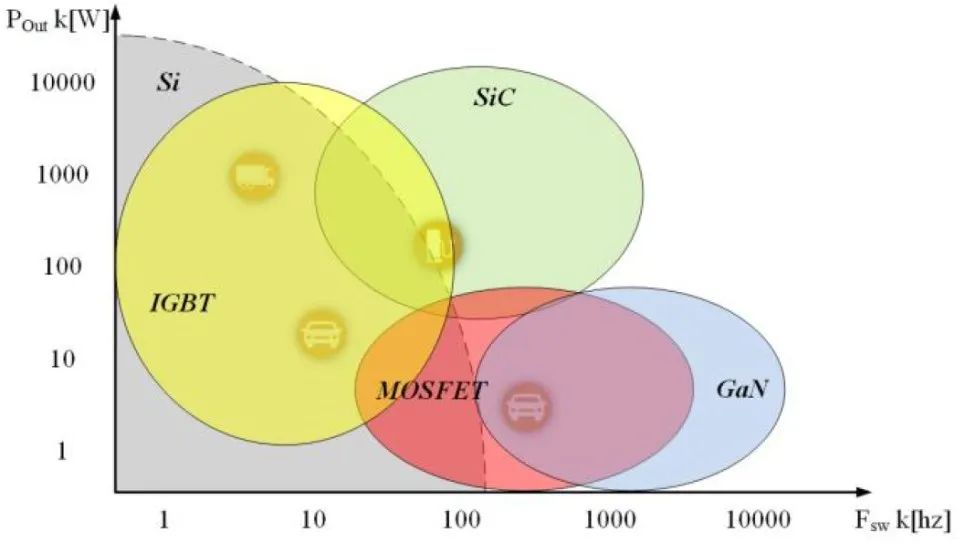
The inverter converts DC electricity from the battery into AC power for the motor. Power electronics also manage energy flow, regenerative braking, and efficiency optimization. Advanced silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors are increasingly used to improve efficiency and reduce heat losses.
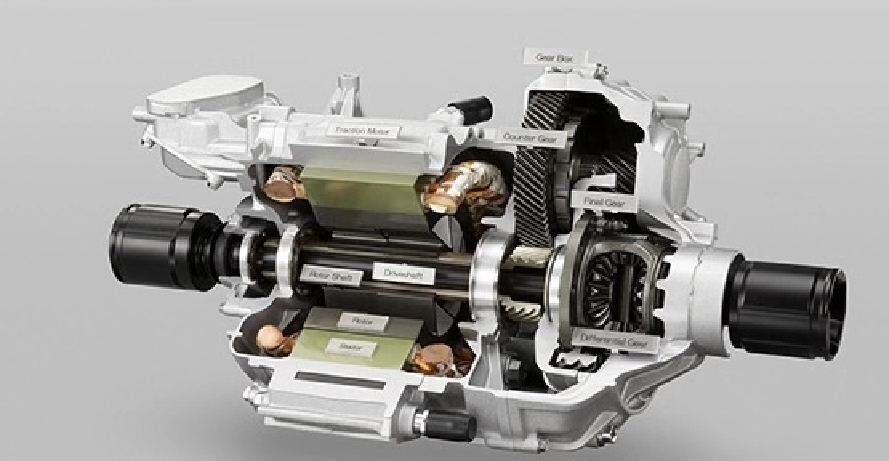
3. Gearbox (Transmission System)
Although electric motors can deliver high torque instantly, a gearbox is still necessary to optimize torque and speed balance. E-Axles often feature a single-speed or two-speed reduction gearbox. For heavy-duty trucks carrying massive loads, multi-ratio solutions may be implemented to ensure both acceleration and highway efficiency.
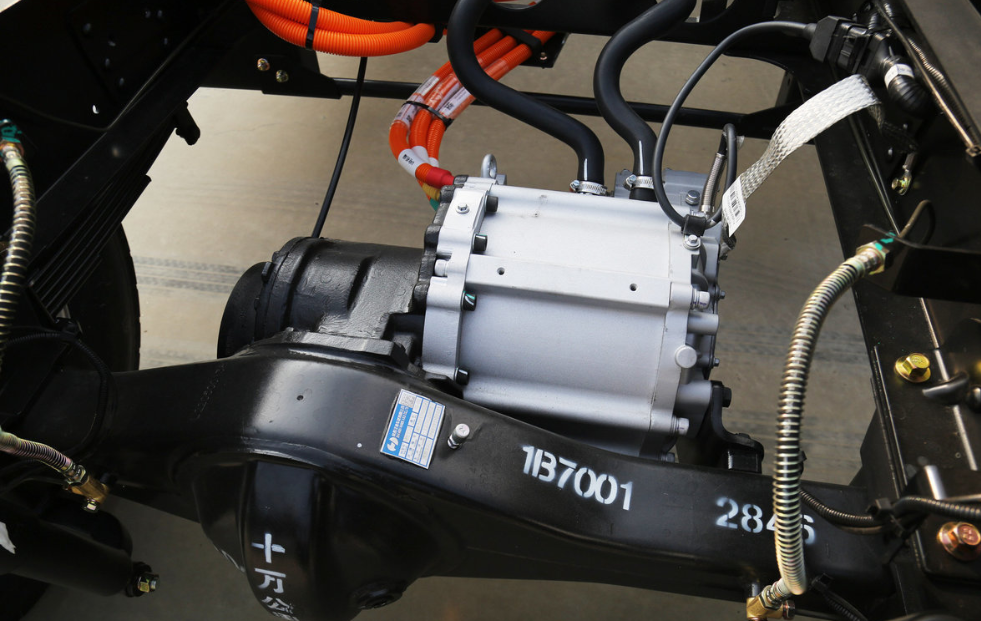
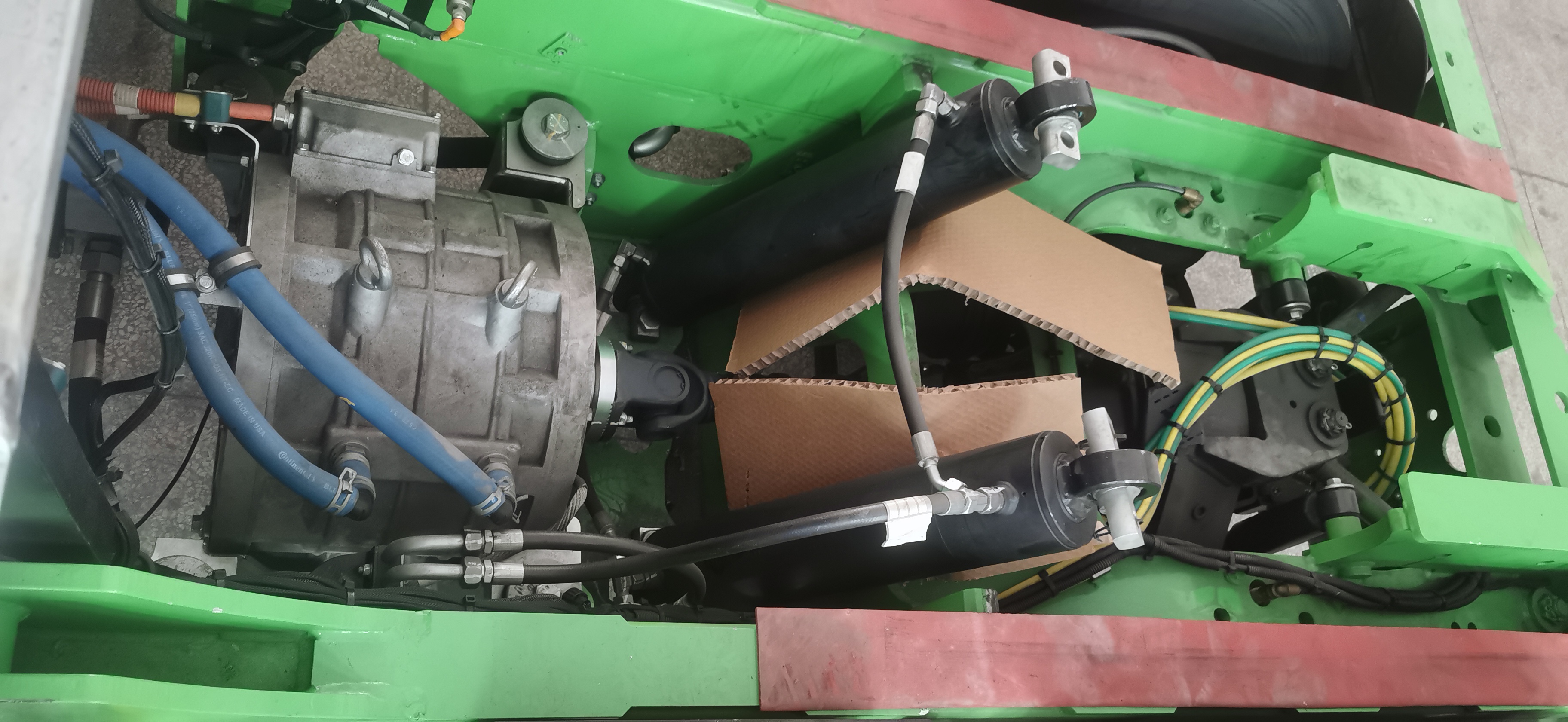
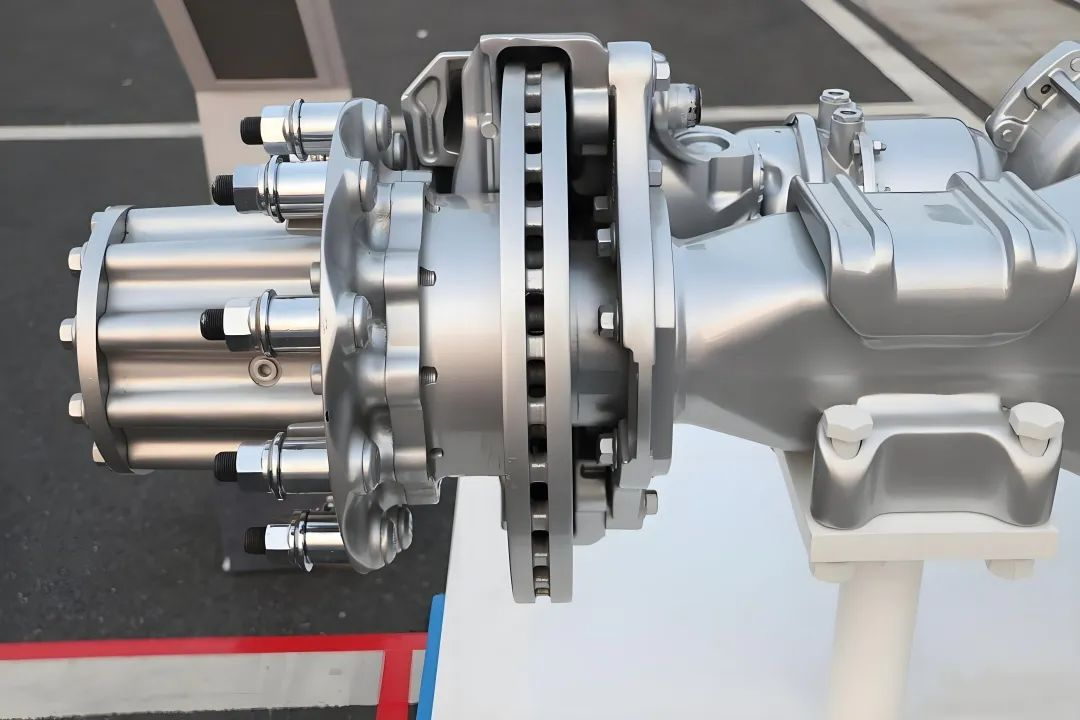
4. Differential and Axle Housing
The mechanical structure of the axle distributes power to the wheels. In trucks, robustness and durability are crucial, as the E-Axle must withstand demanding loads, rough terrain, and continuous operation.
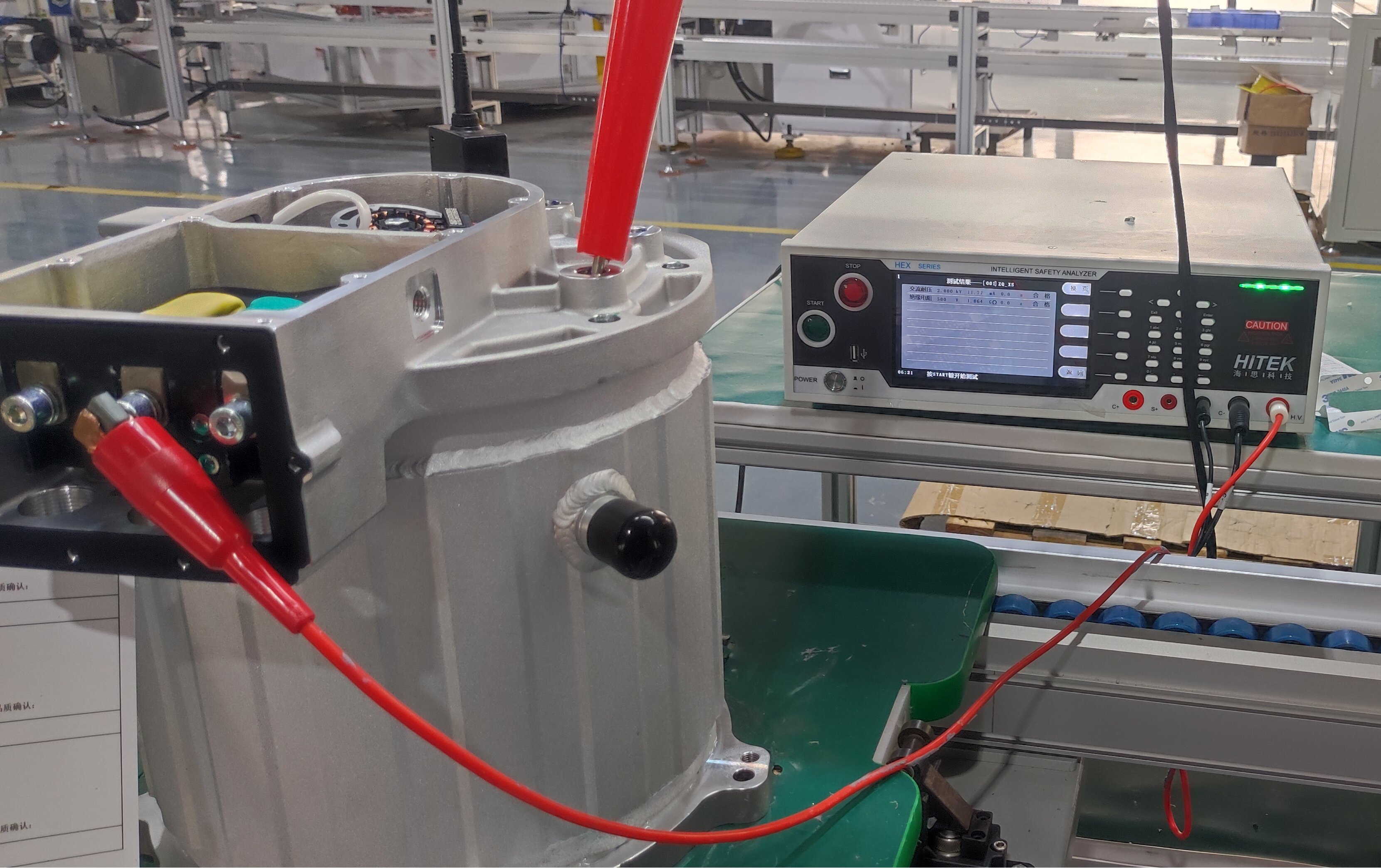
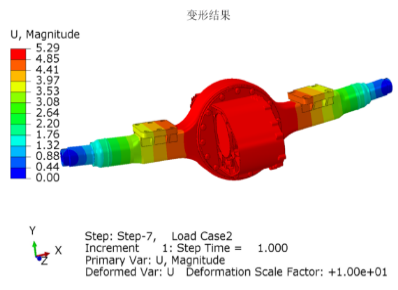
5. Cooling and Thermal Management Systems
High power density generates heat, which must be managed effectively. Advanced liquid cooling systems ensure consistent performance under demanding truck operations.
6. Control Software and Sensors
Intelligent software optimizes torque distribution, regenerative braking, energy consumption, and safety features. Integrated sensors monitor system health and efficiency in real-time, ensuring reliability for fleet operators.
4.Benefits of E-Axle in Trucks
The adoption of E-Axle technology in trucks provides a wide range of benefits:
Enhanced Efficiency
By eliminating unnecessary drivetrain components, mechanical losses are reduced, and more energy from the battery is used for propulsion. This directly translates into greater driving range per charge.
Compact and Lightweight Design
E-Axle’s integration saves space and reduces vehicle weight. The freed-up space can be used to accommodate larger battery packs or increase payload capacity.
High Torque Performance
Electric motors deliver instant torque, a crucial advantage for trucks that often carry heavy loads. This ensures better acceleration, hill-climbing ability, and smoother operation.
Reduced Maintenance
With fewer moving parts compared to ICE powertrains, E-Axle systems significantly reduce maintenance costs and downtime. For fleet operators, this is a major cost-saving advantage.
Lower Emissions and Sustainability
E-Axle powered trucks produce zero tailpipe emissions. Combined with renewable electricity, they can drastically reduce the carbon footprint of logistics and freight operations.
Noise Reduction
Electric drivetrains are much quieter, improving urban environments by reducing noise pollution—a growing concern in city logistics.
Scalability Across Vehicle Classes
E-Axle systems can be adapted for light-duty delivery vans, medium-duty distribution trucks, and heavy long-haul vehicles, making them versatile across logistics sectors.
5.Industry Trends and Market Drivers
Several key industry trends and market drivers are accelerating the adoption of E-Axle technology in trucks:
Global Emission Regulations
Governments worldwide are implementing strict emission targets. For instance, the European Union’s CO₂ standards and California’s Advanced Clean Truck (ACT) regulation mandate zero-emission truck adoption, driving E-Axle demand.
Battery Technology Advancements
Improved battery energy density, fast charging, and falling costs are enabling electric trucks to achieve ranges comparable to diesel trucks, making E-Axle systems more commercially viable.
Fleet Electrification
Major logistics companies like DHL, Amazon, and UPS are investing in electric truck fleets. Their demand for efficiency, range, and reliability boosts E-Axle integration.
OEM Commitments
Automakers like Daimler Trucks, Volvo, BYD, and Tesla are investing heavily in E-Axle solutions for their electric truck programs, signaling mainstream adoption.
Technological Integration
Advancements in AI-driven predictive maintenance, telematics, and smart fleet management enhance E-Axle system performance and appeal to commercial operators.
6.Applications in Commercial Vehicles
E-Axles are being deployed across various categories of trucks and commercial vehicles:
Light-Duty Trucks and Delivery Vans
Urban delivery vehicles benefit from compact E-Axles that provide efficiency, quiet operation, and low emissions in congested city centers.
Medium-Duty Distribution Trucks
For regional logistics, E-Axles provide reliability and sufficient range to cover predictable routes between warehouses and retail outlets.
Heavy-Duty Long-Haul Trucks
Though still in early development, E-Axles with advanced cooling, multi-speed gearboxes, and larger battery packs are being designed for long-distance freight transport.
Specialized Commercial Vehicles
Municipal vehicles such as garbage trucks, buses, and construction trucks are adopting E-Axles due to their stop-and-go duty cycles, which maximize regenerative braking benefits.
7.Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promise, several challenges must be addressed before E-Axles achieve widespread adoption in trucks:
Cost
E-Axle systems, particularly those for heavy trucks, are still expensive due to advanced materials, power electronics, and manufacturing processes.
Battery Limitations
Range anxiety and long charging times remain critical hurdles for long-haul trucks. While E-Axles improve efficiency, overall vehicle performance is still tied to battery capabilities.
Thermal Management
High-power E-Axle systems generate heat, and failure to manage it can compromise reliability in demanding operations.
Infrastructure Development
Widespread adoption requires robust charging networks, particularly along freight corridors. Without supporting infrastructure, E-Axle trucks face deployment barriers.
Durability and Lifecycle Testing
Trucks often operate in extreme conditions, and E-Axles must prove durability in cold climates, high temperatures, and rough terrains.
Supply Chain Dependencies
Rare earth materials for permanent magnets and semiconductor shortages could pose risks for scaling E-Axle production.
8.Future Outlook
The future of E-Axles in trucks is bright, supported by both regulatory pressure and technological advancements. Several trends shape the outlook:
- Next-Generation Materials: Increased use of silicon carbide inverters, lightweight composites, and improved thermal systems.
- Battery Innovation: Solid-state batteries and ultra-fast charging technologies will extend range and reduce downtime.
- Integration with Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Hybrid solutions combining E-Axle propulsion with hydrogen fuel cells could power long-haul trucks, overcoming range limitations.
- Global Market Growth: Analysts project the global E-Axle market for commercial vehicles to grow at double-digit CAGR through 2030.
- Fleet Optimization Software: AI-based energy management and predictive analytics will enhance fleet performance.
9.Conclusion
The E-Axle is redefining the future of electric trucks, offering a powerful blend of efficiency, compact design, and sustainability. By integrating motor, inverter, and gearbox into one intelligent unit, E-Axle technology simplifies the drivetrain while enhancing performance—a critical advantage for commercial vehicles tasked with moving goods reliably and economically.
As governments, industries, and fleets push toward zero-emission transport, E-Axle-powered trucks are set to become a cornerstone of commercial mobility. Challenges remain, particularly around cost, batteries, and infrastructure, but the momentum is undeniable. With continuous innovation and growing adoption, the E-Axle is not just driving the future of electric trucks—it is driving the transformation of the entire commercial vehicle industry.