What is the purpose for having a controller in an electric car?
When you think about the key components that make an electric car run smoothly and safely, the battery and motor often come to mind first. But a hidden hero is working behind the scenes: the electric car controller. Often referred to as the “brain” of an electric vehicle (EV), this component is responsible for orchestrating the flow of energy, regulating performance, and ensuring every system works in harmony. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into what an electric car controller does, explore its core purposes, and explain why it’s indispensable for modern EVs—plus, we’ll clarify common misconceptions, like how it differs from an inverter.
1. Introduction: Why the Controller Is the “Brain” of an Electric Car
Just as your brain processes sensory input, makes decisions, and sends signals to your body, the electric car controller acts as the central command center for an EV. Without it, the high-voltage energy from the battery would be uncontrollable, the motor wouldn’t know when to speed up or slow down, and safety systems would fail to activate when needed. Whether you’re accelerating onto the highway, braking to a stop, or simply cruising, the ev motor controller is working tirelessly to translate your driving inputs into precise actions. Its role is so critical that a well-designed electric car controller can make the difference between a smooth, efficient ride and a frustrating, unsafe one.
2. What Is an Electric Car Controller?
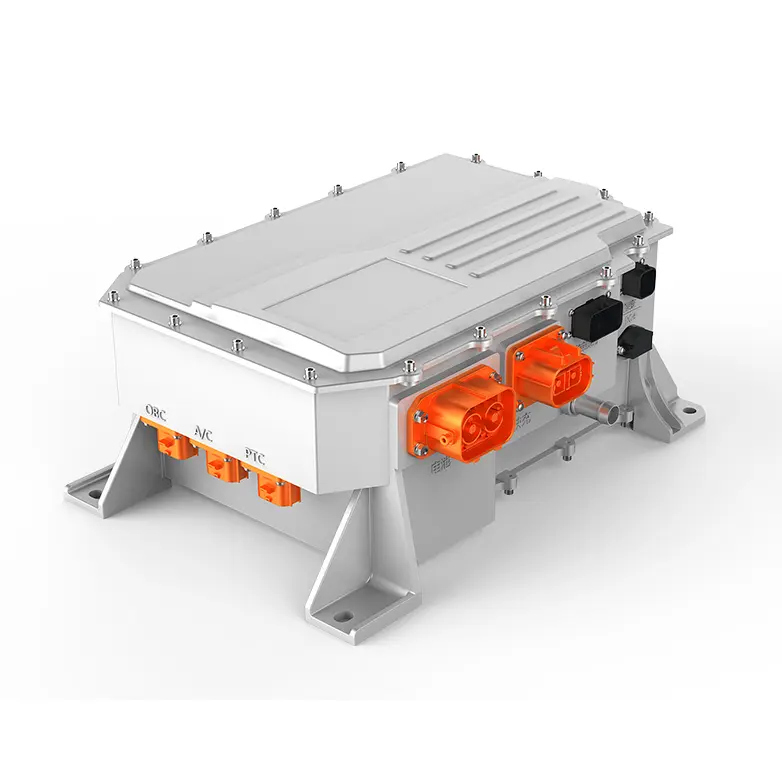
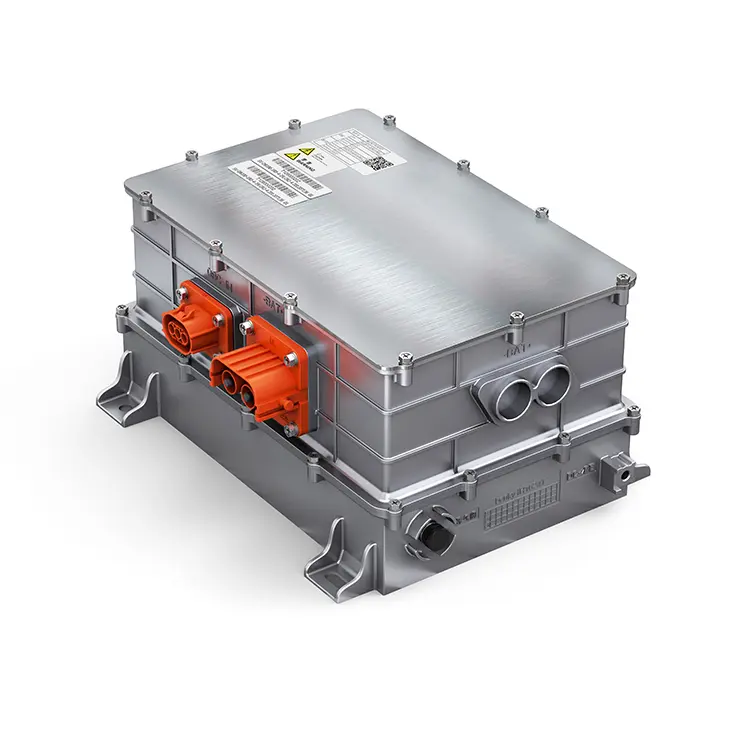
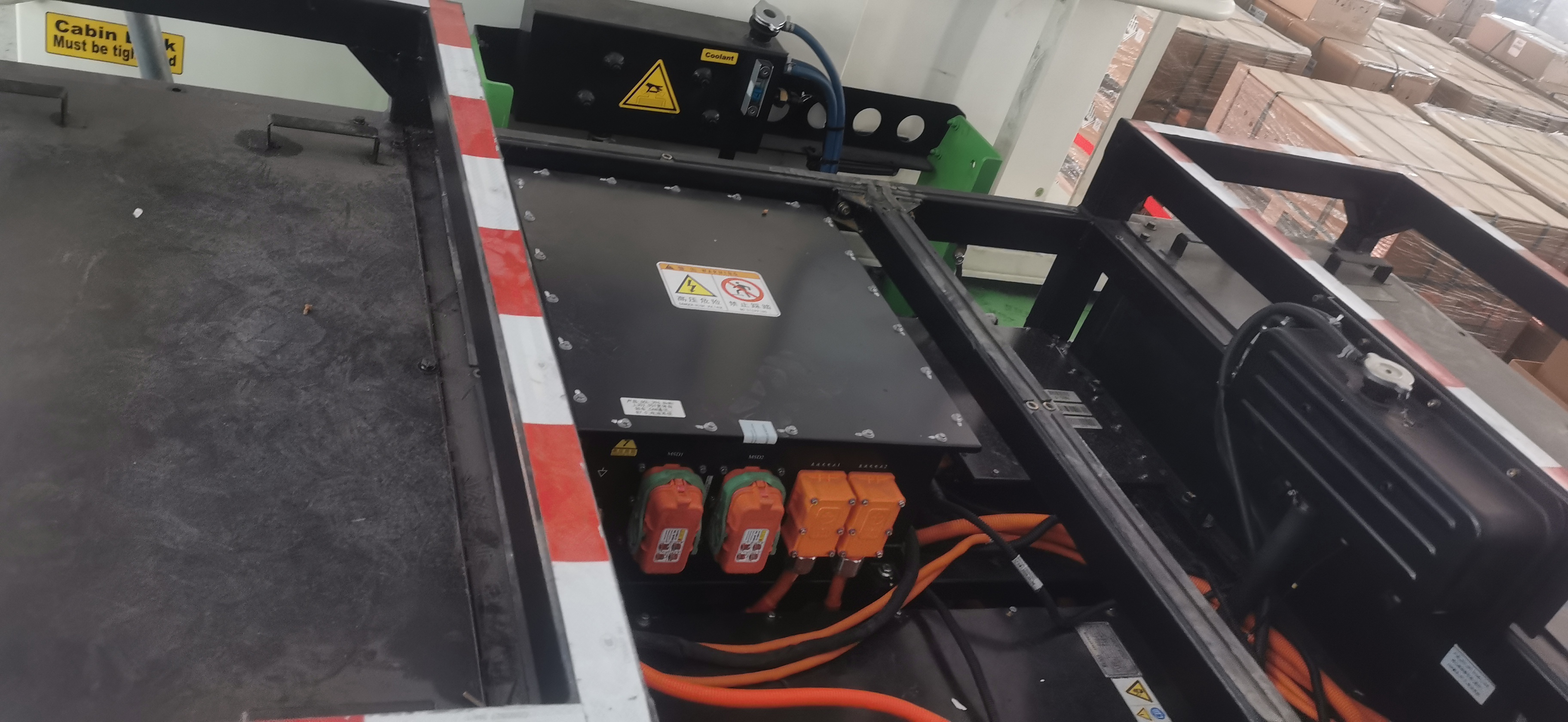
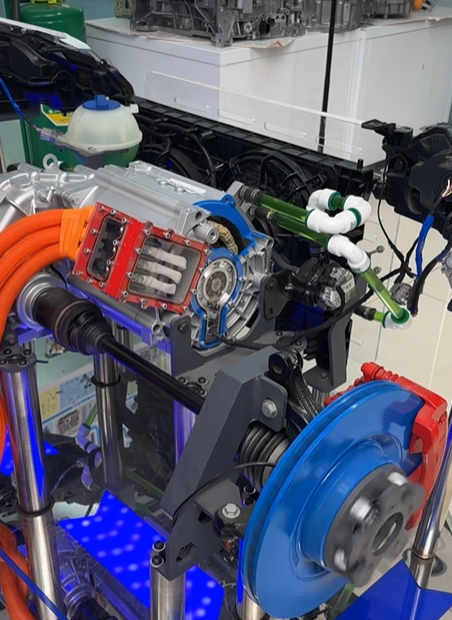
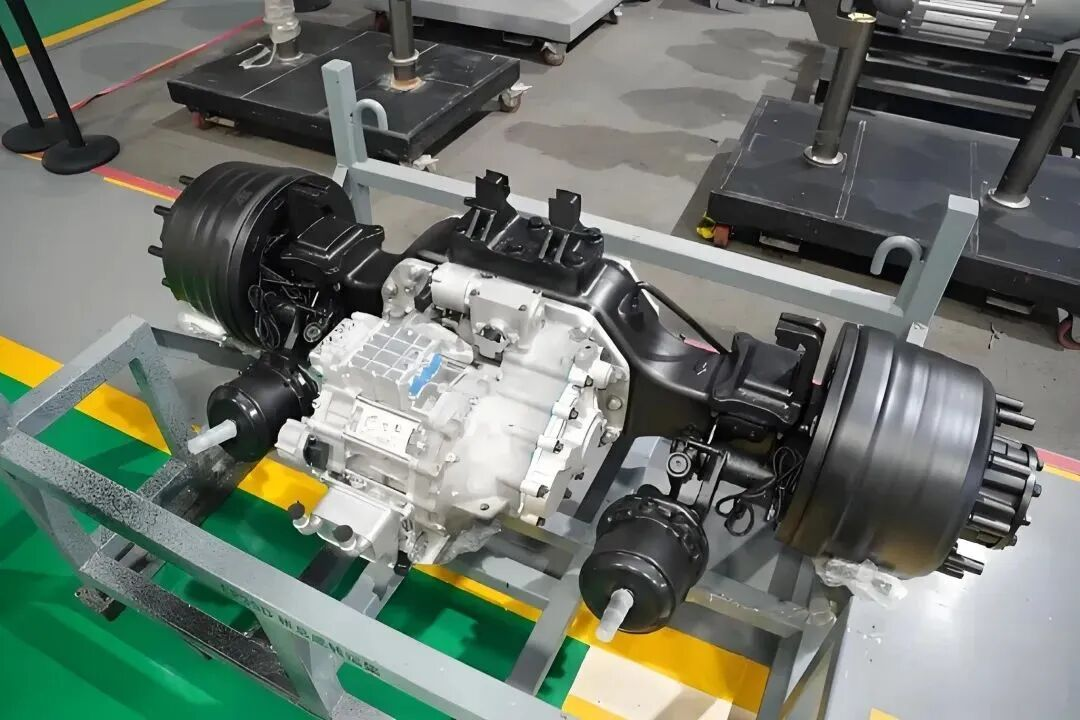
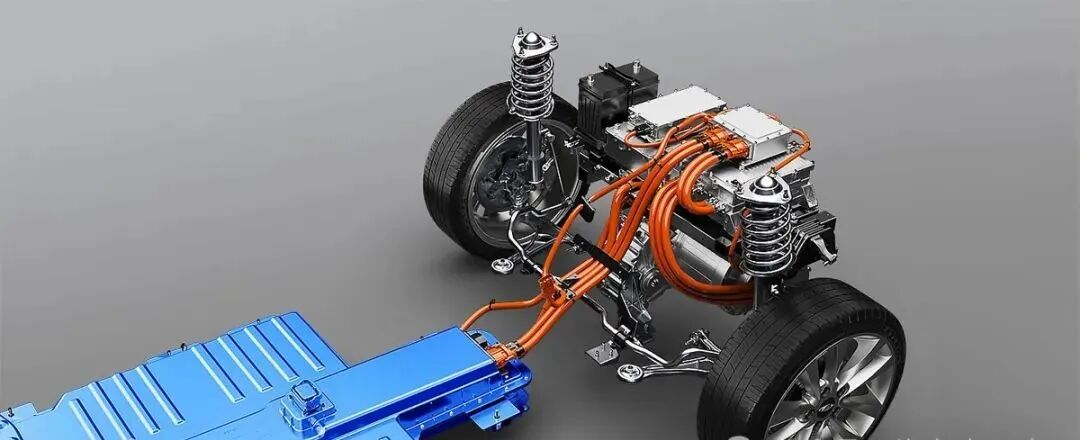
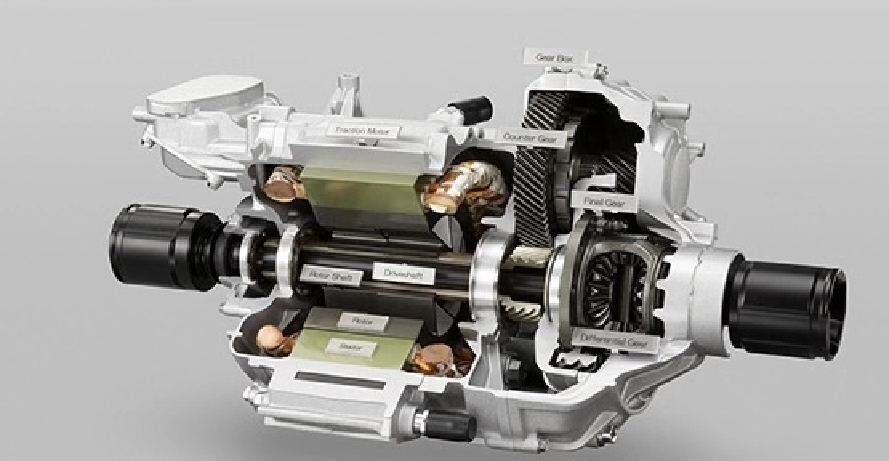
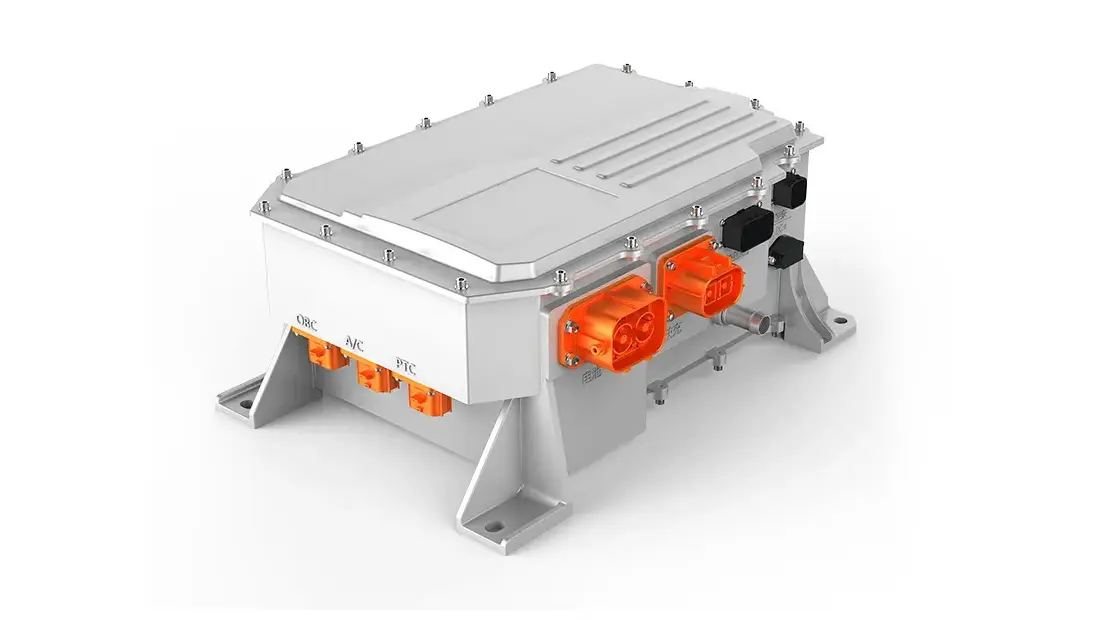
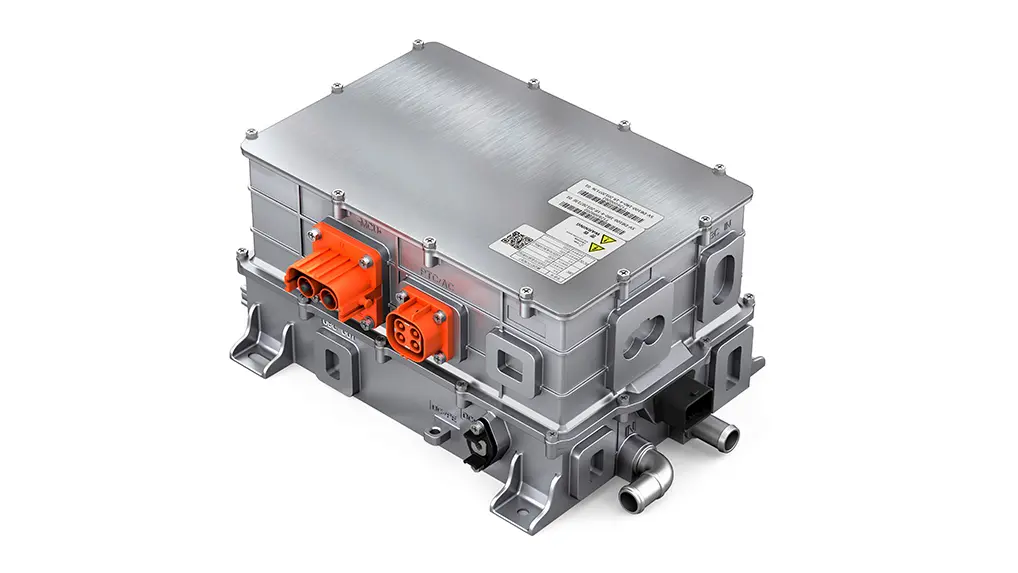
An electric car controller is an electronic device that manages the flow of electrical energy between the EV’s battery and motor. It takes the direct current (DC) power stored in the battery and converts it to alternating current (AC) power—required by most modern EV motors—while regulating the voltage and current to meet the motor’s needs. Unlike basic electrical components, the EV motor controller is a smart device that uses sensors and software to make real-time adjustments based on driving conditions, driver inputs (like pressing the accelerator or brake), and feedback from other EV systems. In short, it’s the bridge between the battery’s stored energy and the motor’s mechanical power.
3. Core Purpose 1: Power Regulation Between Battery and Motor
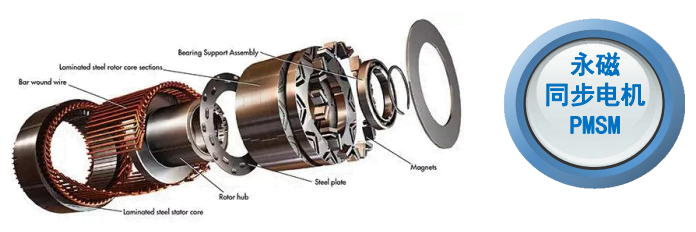
One of the primary jobs of the electric car controller is to regulate the transfer of power between the battery and the motor. EV batteries supply high-voltage DC power, but most EV motors (such as AC induction motors or permanent magnet synchronous motors) require AC power to operate. The EV motor controller handles this conversion efficiently, ensuring that the motor receives the right amount of power at the right voltage. For example, when you press the accelerator, the controller increases the current flow to the motor, delivering more power for acceleration. When you ease off the accelerator, it reduces the current, conserving battery energy. This precise power regulation not only optimizes performance but also prevents damage to the battery and motor from voltage spikes or overloads.
4. Core Purpose 2: Precise Motor Speed and Torque Control
Smooth and responsive driving depends on the electric car controller’s ability to control motor speed and torque with precision. Torque is the rotational force that gets the car moving, and the controller adjusts torque output based on how hard you press the accelerator. By varying the frequency of the AC power sent to the motor (a process called pulse-width modulation, or PWM), the ev motor controller can fine-tune the motor’s speed—whether you’re crawling in traffic or speeding down the highway. This level of precision is far beyond what a mechanical system could achieve, and it’s one of the reasons EVs offer such a smooth driving experience. Without this control, the motor would either run at a fixed speed or respond unpredictably, making the car nearly undrivable.
5. Core Purpose 3: Direction Control and Regenerative Braking
The electric car controller also manages two key functions related to movement: direction control and regenerative braking. When you shift an EV into reverse, the controller reverses the phase sequence of the AC power sent to the motor, causing it to spin in the opposite direction. This simple yet critical adjustment is handled seamlessly by the EV motor controller, ensuring smooth and safe direction changes. Additionally, during braking, the controller activates regenerative braking—a feature that converts the motor into a generator. As the car slows down, the motor captures kinetic energy, converts it back to DC power, and sends it to the battery for storage. The controller regulates this process, balancing the amount of braking force (so it feels natural to the driver) with the amount of energy recovered, maximizing efficiency.
6. Core Purpose 4: Motor Protection and System Safety
Safety is paramount in EVs, and the electric car controller plays a central role in protecting the motor and the entire electrical system. The EV motor controller is equipped with sensors that monitor key parameters like motor temperature, current flow, voltage levels, and battery state of charge. If any of these parameters go outside safe limits—for example, if the motor overheats or the current becomes too high—the controller immediately takes action. It might reduce power to the motor, shut off the power supply entirely, or trigger warning lights on the dashboard. This proactive protection prevents costly damage to the motor, battery, and other electrical components, and it also keeps the driver and passengers safe by avoiding system failures that could lead to accidents.
7. Core Purpose 5: Communication With Other EV Systems
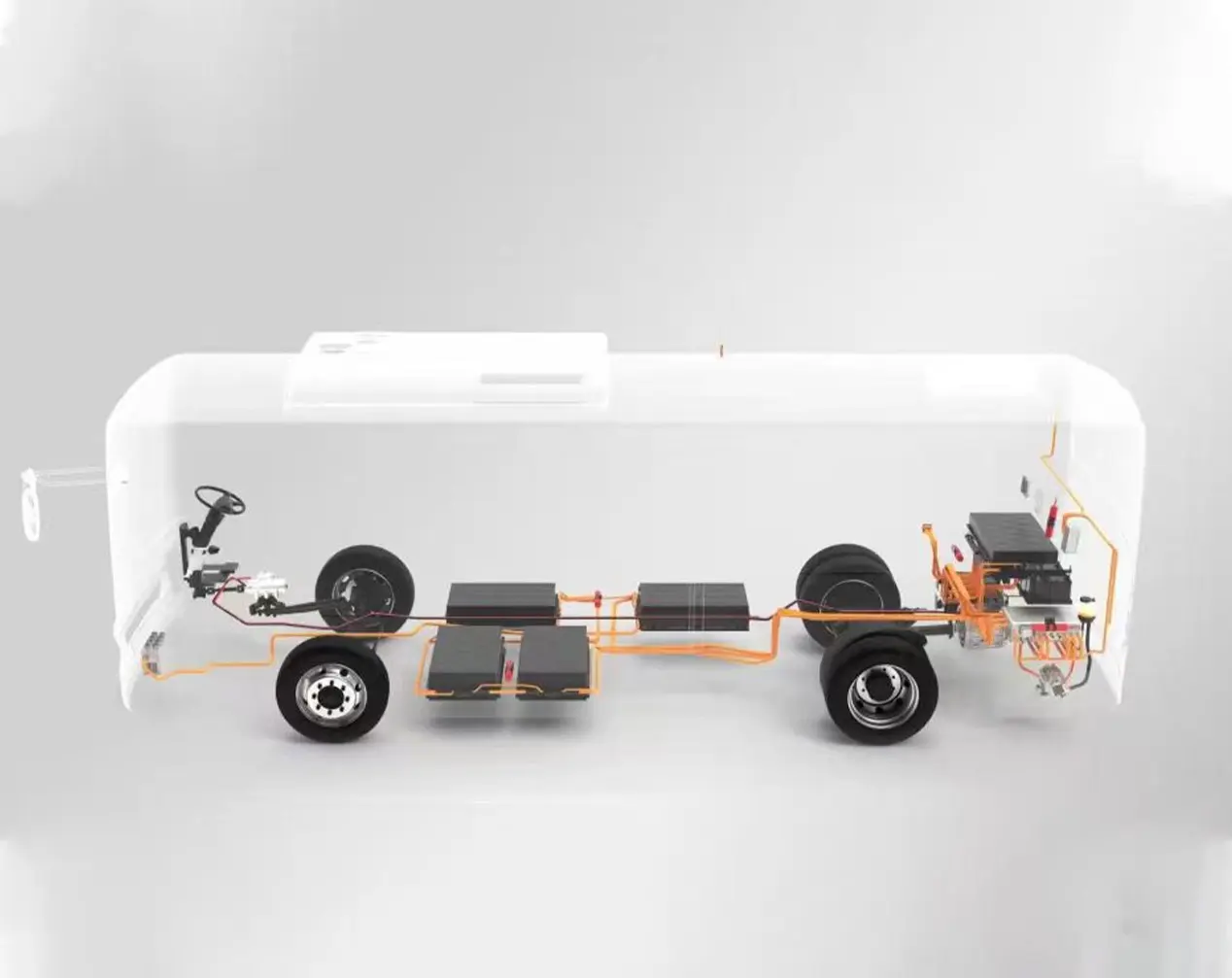
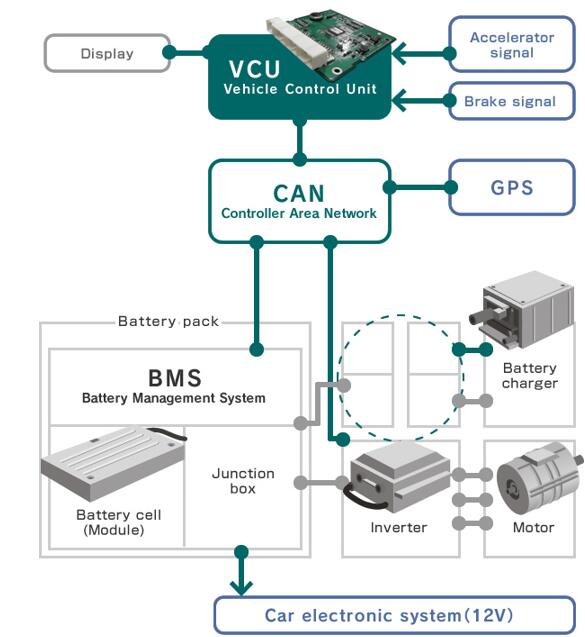
Modern EVs are complex machines with multiple interconnected systems, and the electric car controller acts as the communication hub for many of them. It exchanges data with the battery management system (BMS) to get real-time information about battery charge level and health, ensuring the motor doesn’t draw more power than the battery can safely supply. It also communicates with the vehicle’s onboard computer, infotainment system, and safety systems (like anti-lock brakes and traction control). For example, if the traction control system detects a wheel slipping, it sends a signal to the EV motor controller, which reduces power to the affected wheel to restore grip. This seamless communication ensures that all systems work together in harmony, optimizing performance and safety.
8. Types of EV Motor Controllers Used in Electric Cars
EV motor controllers come in several types, each designed for specific motor technologies and vehicle applications. The most common types include:
- DC Motor Controllers: Used in older or low-power EVs with DC motors. These controllers regulate the voltage sent to the motor to control speed and torque.
- AC Motor Controllers: The most widely used type in modern EVs (e.g., Tesla, Nissan Leaf). These controllers convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the motor and use PWM to control speed and torque precisely.
- Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor Controllers: Designed for BLDC motors, which are common in hybrid and small EVs. These controllers offer high efficiency and reliability.
- Sinusoidal Controllers: A type of AC controller that delivers smoother power to the motor, reducing noise and improving efficiency, making them ideal for high-performance EVs.
The choice of electric car controller depends on the motor type, vehicle power requirements, and desired efficiency levels.
9. How the Electric Car Controller Affects EV Performance and Efficiency
The electric car controller has a direct and significant impact on an EV’s performance and efficiency. A high-quality EV motor controller can deliver power to the motor more efficiently, reducing energy waste and extending the vehicle’s range. For example, a controller with advanced PWM technology can minimize power losses during DC-to-AC conversion, maximizing the amount of energy used for propulsion. In terms of performance, a responsive controller ensures that the motor delivers torque instantly when the driver presses the accelerator, giving EVs their characteristic quick acceleration. Conversely, a poorly designed controller can lead to laggy acceleration, reduced range, and higher energy consumption. For EV manufacturers, optimizing the electric car controller is a key way to improve vehicle performance and appeal to consumers.
10. Common Problems Caused by a Poor-Quality Controller
Investing in a high-quality electric car controller is essential because a subpar one can lead to a host of problems. Some common issues include:
- Reduced Performance: Laggy acceleration, slow response to driver inputs, and limited top speed.
- Poor Efficiency: Higher energy consumption, leading to shorter battery range.
- Motor Damage: Inconsistent power delivery can cause the motor to overheat or wear out prematurely.
- Safety Risks: Failure to protect the system from voltage spikes or overloads can lead to electrical fires or system failures.
- Regenerative Braking Issues: Unpredictable braking force or reduced energy recovery.
These problems not only diminish the driving experience but also increase maintenance costs and safety risks, highlighting the importance of a reliable ev motor controller.
11. Electric Car Controller vs Inverter: Are They the Same?
A common misconception is that an electric car controller and an inverter are the same thing—but they’re not, though they work closely together. An inverter’s primary job is to convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the motor. An electric car controller, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive system that includes an inverter as one of its components. In addition to conversion, the ev motor controller handles speed and torque control, direction control, regenerative braking, safety monitoring, and communication with other systems. Think of it this way: the inverter is a “tool” that the controller uses to manage power, while the controller is the “brain” that decides how and when to use that tool. Some manufacturers may use the terms interchangeably in marketing, but technically, they’re distinct components with different roles.
12. Conclusion: Why the Electric Car Controller Is Critical to Every EV
From regulating power flow to ensuring safety, from optimizing performance to enabling regenerative braking, the electric car controller is the unsung hero of modern EVs. It’s the component that turns raw battery power into a smooth, responsive, and safe driving experience. Without a high-quality EV motor controller, even the best battery and motor would fail to deliver the performance and efficiency that make EVs so popular today. As EV technology continues to evolve, controllers will only become more advanced, with better efficiency, faster response times, and more seamless integration with other vehicle systems. Whether you’re an EV owner, a prospective buyer, or just curious about how electric cars work, understanding the role of the controller is key to appreciating the engineering marvel that is the modern electric vehicle.