News
E-Axle: The Revolutionary Evolution of the Electric Vehicle Drive Axle – From Traditional Axle to Intelligent Power Hub - A Complete Analysis
Introduction: Redefining the Drive Axle in the Electric Era
As we shift our focus from the mechanical roar of internal combustion engine vehicles to the quiet efficiency of electric vehicles, not only has the primary energy source fundamentally changed, but the entire architecture of the power transmission system is undergoing a silent revolution. In this wave of transformation, the E-Axle (Electric Drive Axle), as the core driving unit of electric vehicles, is redefining the century-old concept of the "drive axle" through integration and intelligence. So, what role exactly does the drive axle play in the electric motor system? This is not merely a question of mechanical engineering; it is crucial to the efficiency, performance, and future development trends of electric vehicles.
The Paradigm Shift from Traditional Axle to E-Axle: More Than Simple Power Transfer
The Limitations of the Traditional Drive Axle
Throughout over a century of internal combustion engine vehicle development, the drive axle had evolved into a complex yet effective mechanical transmission system. The traditional powertrain followed a lengthy power chain: "ICE - Clutch/Torque Converter - Transmission - Driveshaft - Differential - Half-shafts - Wheels". Each link in this chain incurred energy losses, weight penalties, and occupied space.
The distribution of typical mechanical losses is telling:
-
Engine Internal Friction Loss: 4-7%
-
Transmission Loss: 2-4%
-
Driveshaft & Universal Joint Loss: 1-2%
-
Differential Loss: 2-3%
-
Total Mechanical Loss: As high as 9-16%
This distributed design not only limited efficiency but also posed challenges for NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness) control, with every connection point being a potential source of vibration and noise.
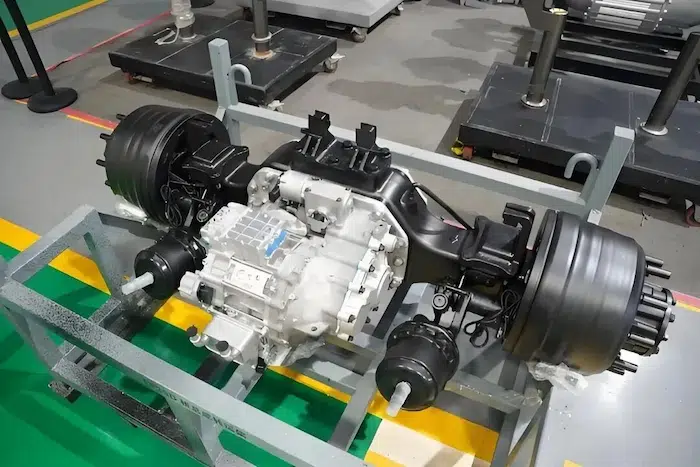
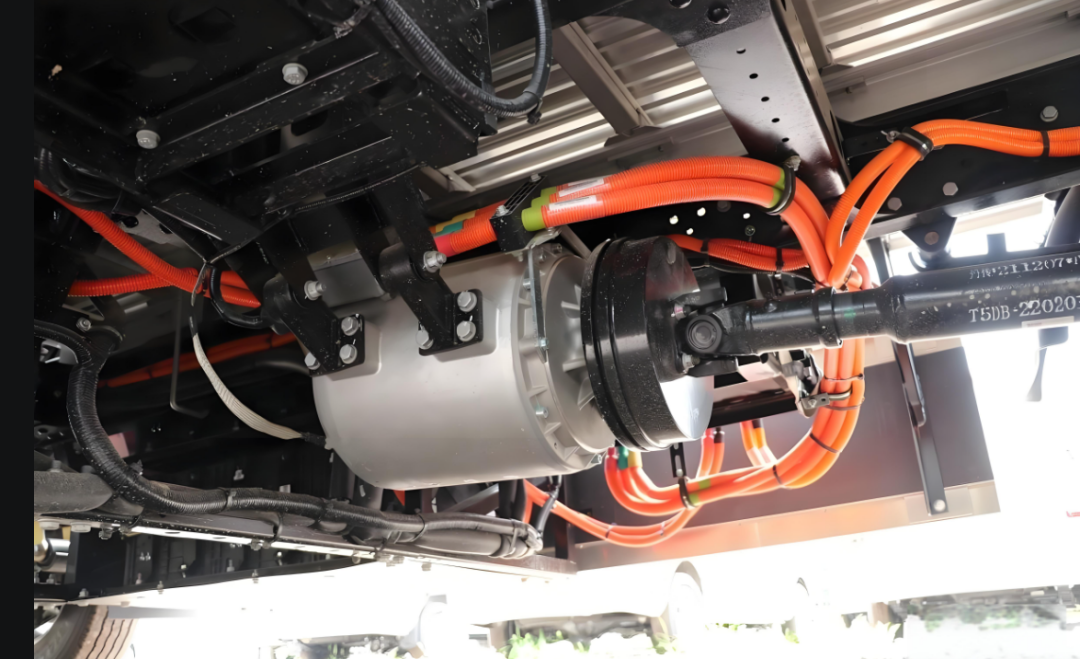
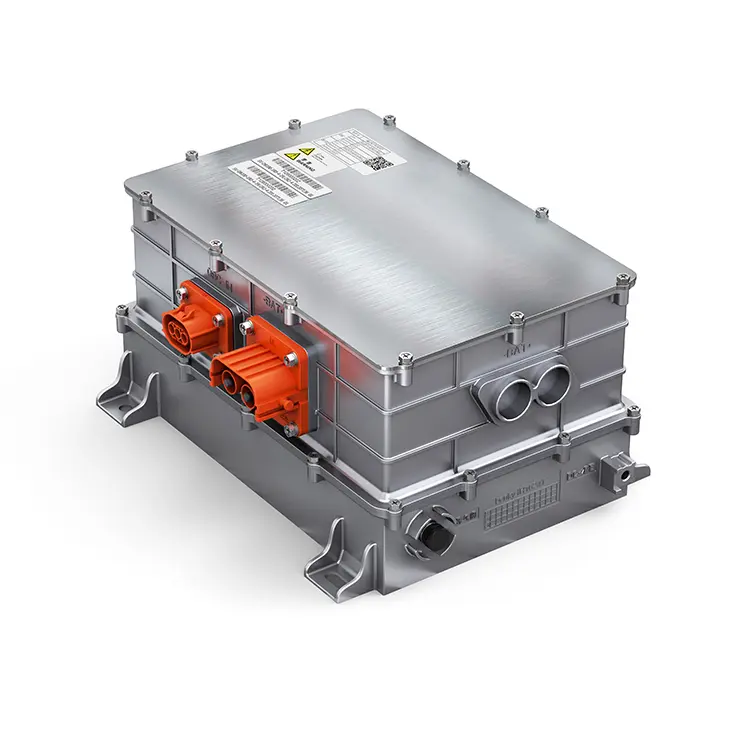
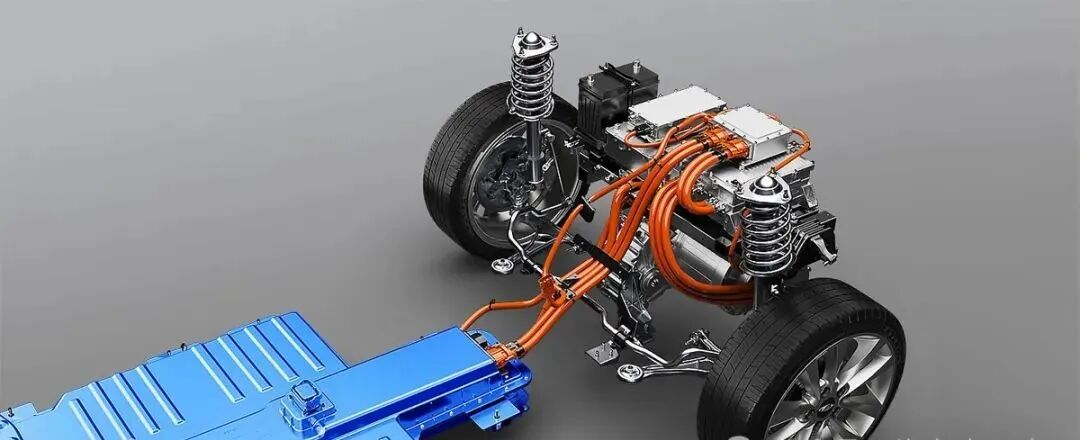
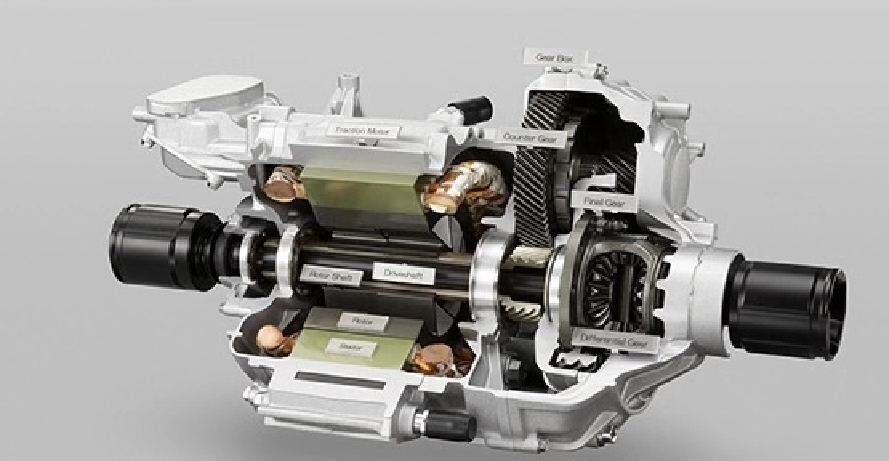
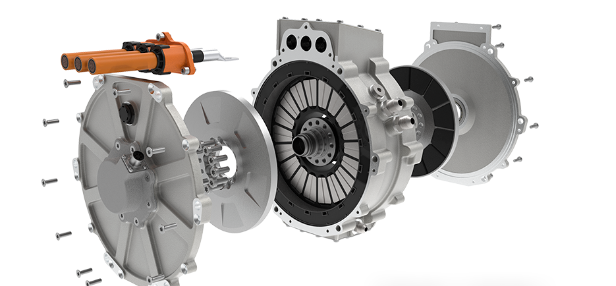
The Integration Revolution of the E-Axle
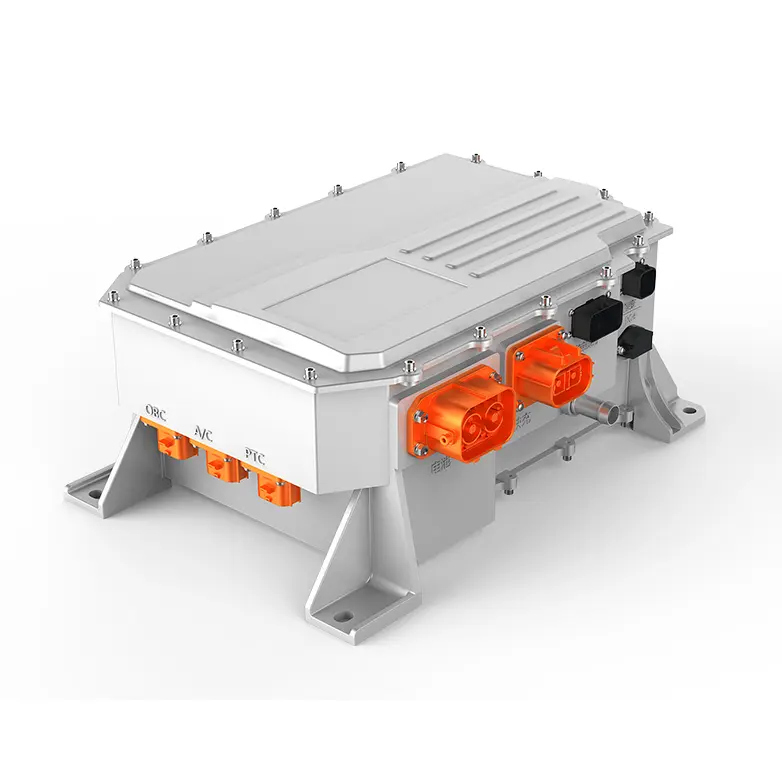
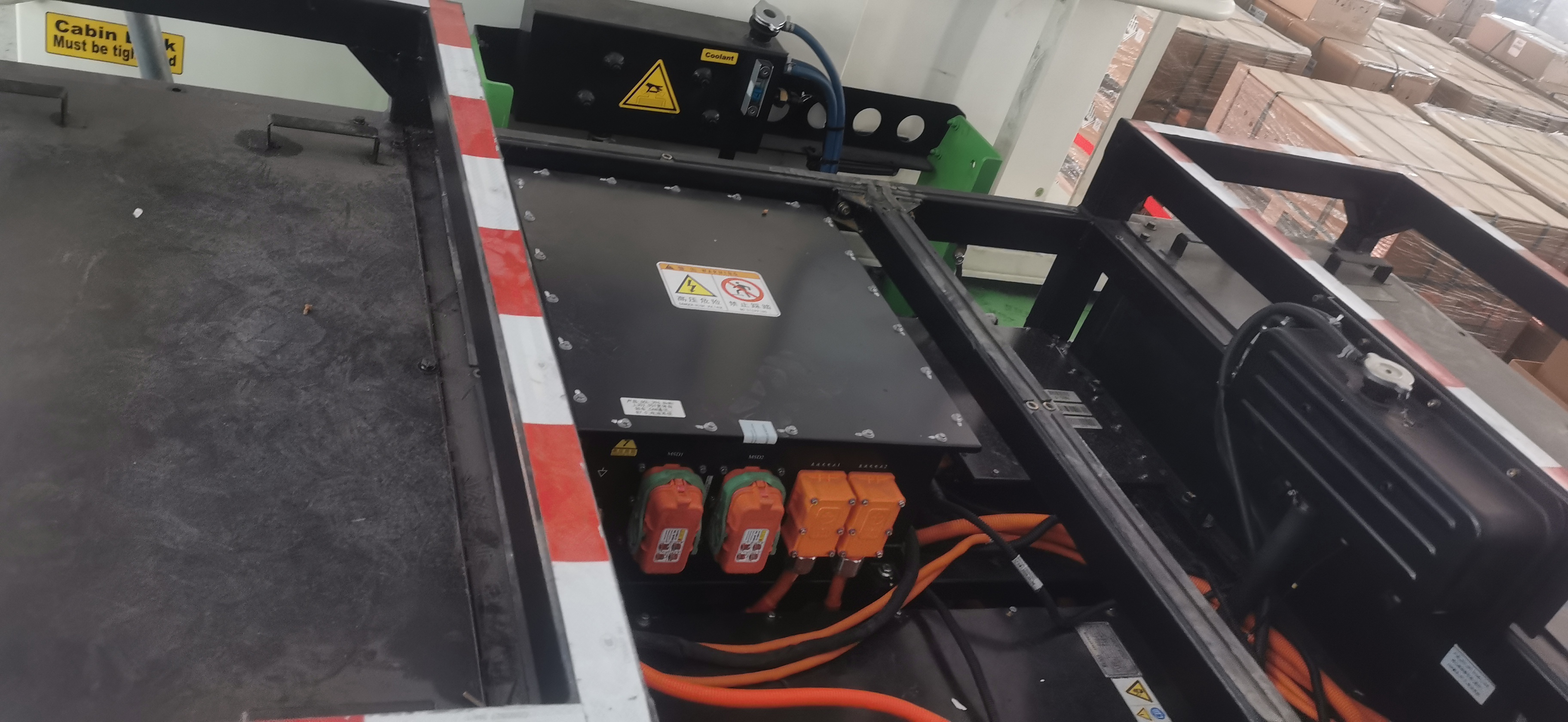
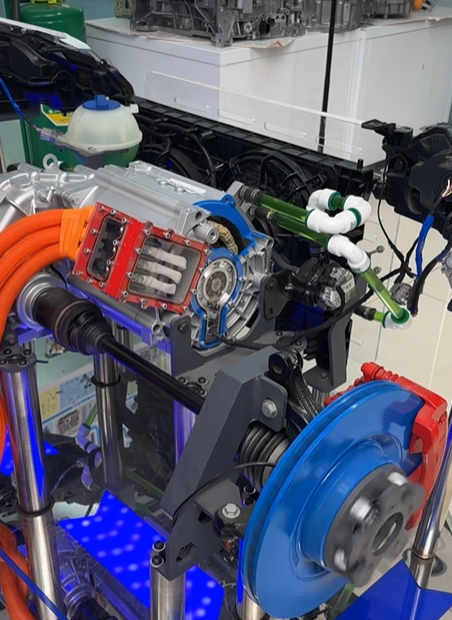
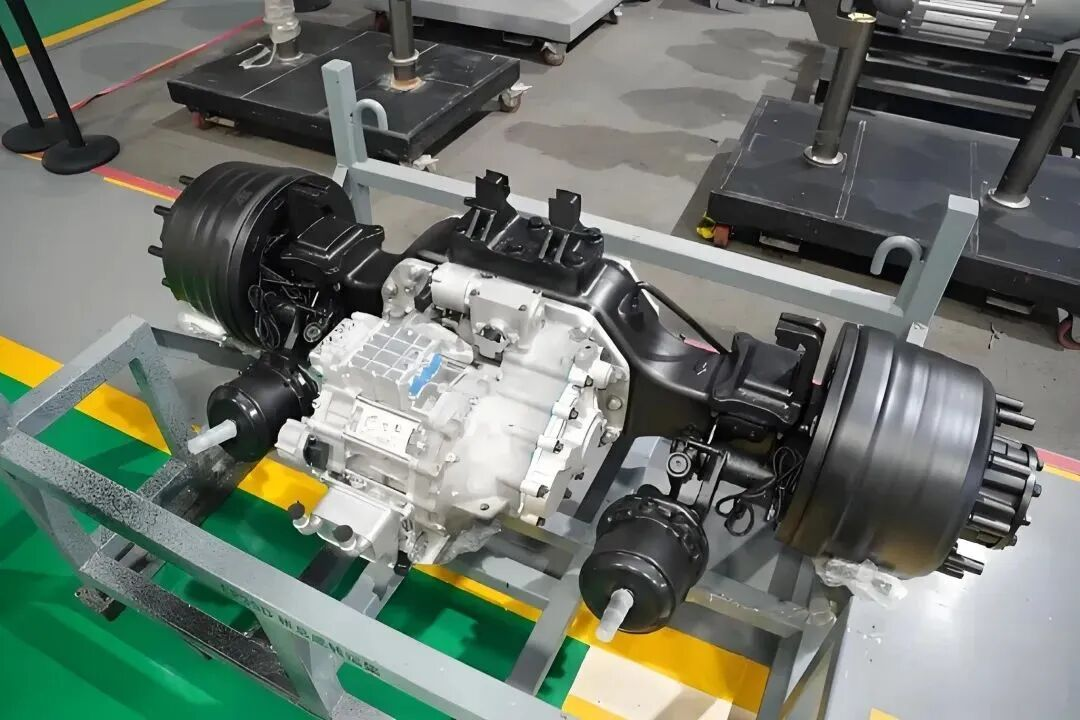
The emergence of the E-Axle has completelyed this paradigm. It is not just a driving unit; it is a highly integrated electric powertrain system solution. By integrating the electric motor, inverter, reduction gear, and differential (sometimes including the electronic controller) within a compact housing, the E-Axle achieves:
-
Space Revolution: Volume reduced by 30-50%, freeing up valuable chassis space.
-
Weight Optimization: Overall weight reduced by 20-35%, directly increasing driving range.
-
Efficiency Leap: System efficiency reaching 94-97%, far surpassing the 30-40% of ICE systems.
-
Cost Advantage: Significant reduction in manufacturing, assembly, and logistics costs.
This high level of integration is not mere physical stacking but a deep fusion design based on electromagnetics, thermodynamics, structural mechanics, and power electronics technologies.
In-Depth Technical Dissection of the E-Axle: Transcending the Functional Boundaries of Traditional Axles
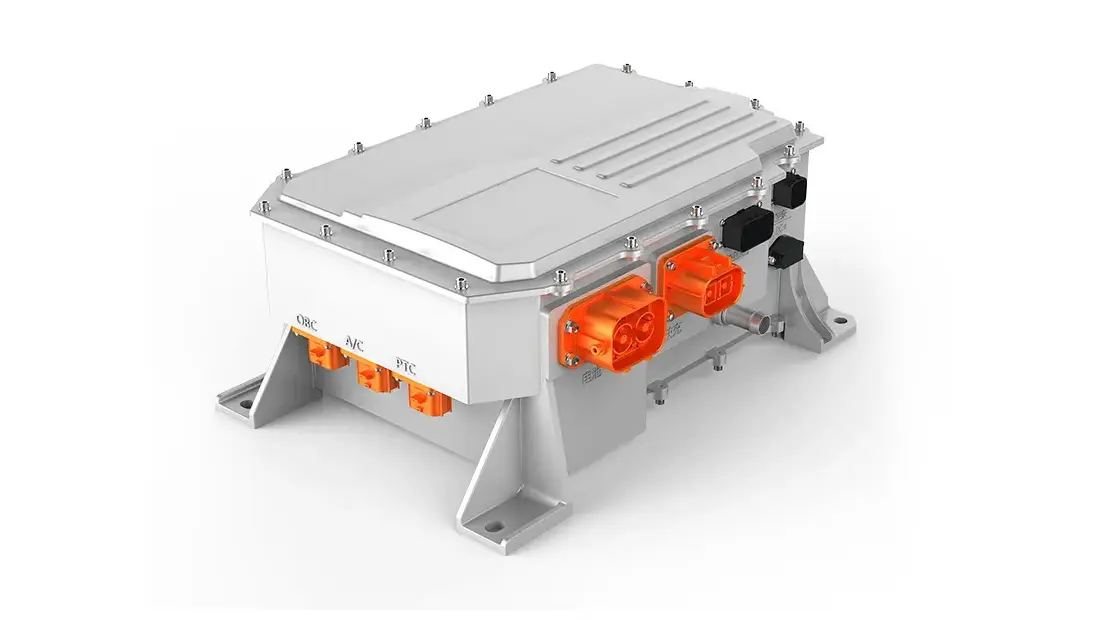
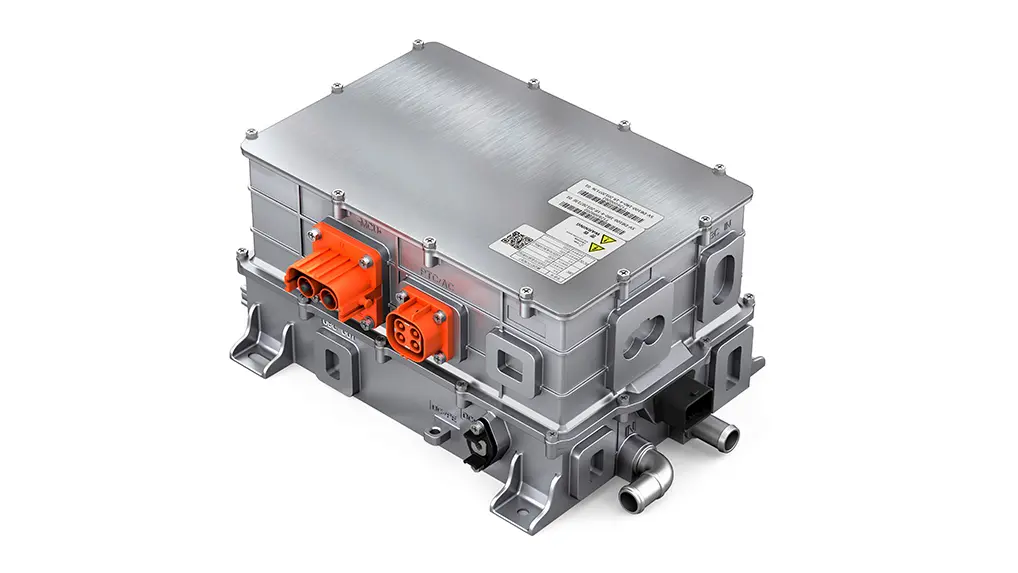
The "Intelligent Heart" of Power Electronics
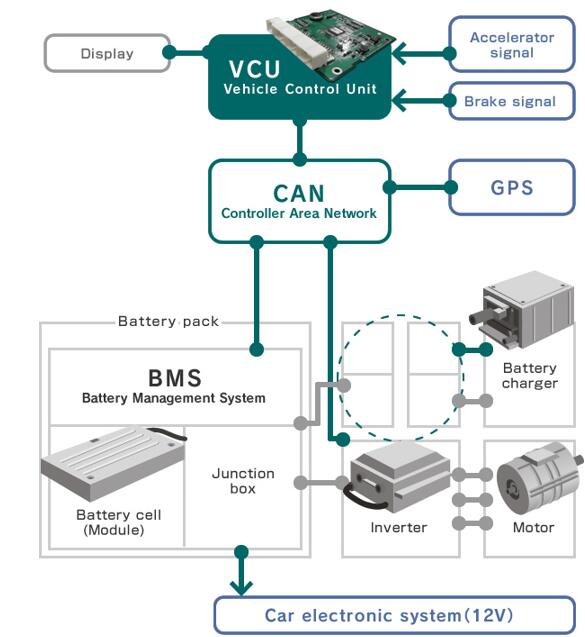
In a traditional axle, power transmission is a purely mechanical process. In the E-Axle, the power electronics module (inverter) becomes the system's "intelligent heart." It is responsible not just for simple current conversion but for real-time control systems:
-
Precise Vector Control: Controls the motor's magnetic field accurately through complex algorithms for efficient torque output.
-
Multi-Objective Optimization: Finds dynamic balance points between efficiency, power, heat generation, and noise.
-
Fault Diagnosis & Tolerance: Monitors system status in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance for potential faults.
-
Integrated Thermal Management: Works in concert with the cooling system to ensure power devices operate within optimal temperature windows.
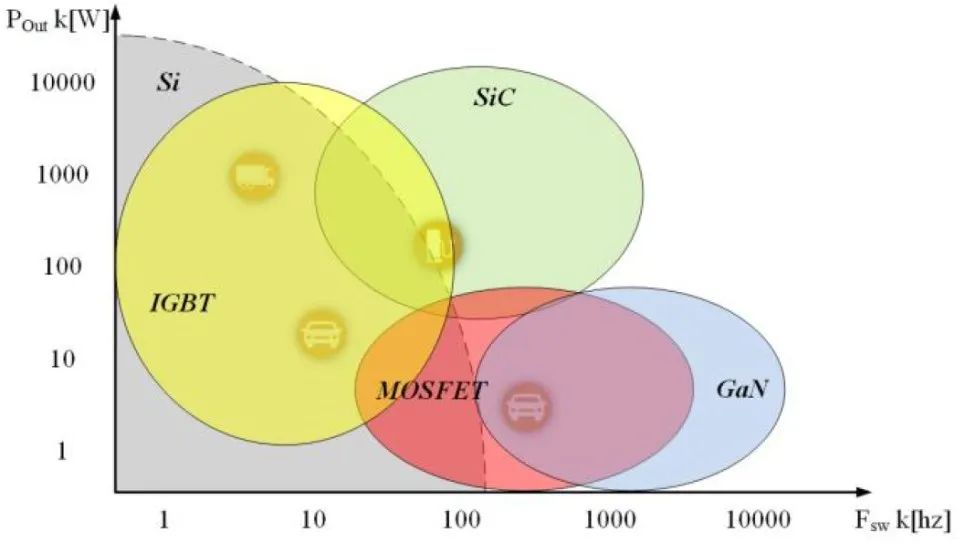
Advanced Silicon Carbide (SiC) power devices are becoming key to enhancing E-Axle performance. Compared to traditional silicon-based IGBTs, they offer switching frequencies 3-5 times higher and improve system efficiency by an additional 3-5%—a technological advancement utterly unattainable by traditional mechanical axles.
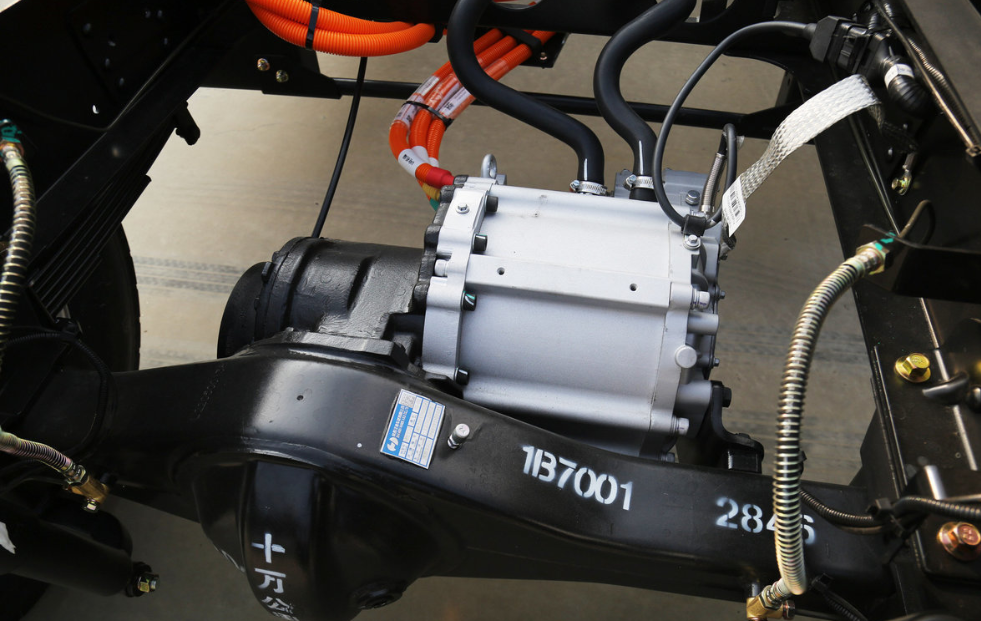
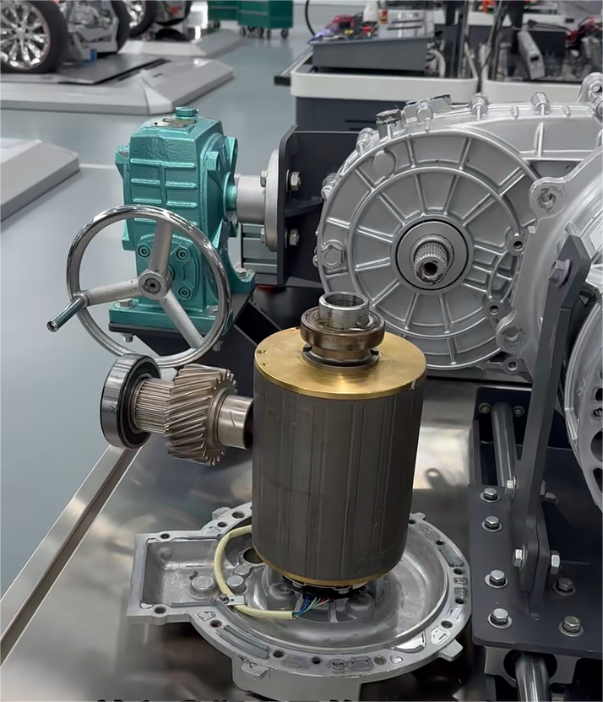
Deep Integration of Reduction Gear and Differential
The mechanical transmission part of the E-Axle has also undergone revolutionary design:
-
High-Efficiency Reduction Device:
-
Utilizes planetary or parallel-axis gear designs with transmission efficiency exceeding 98%.
-
Single-speed ratio design (typically 8:1 to 12:1) perfectly matches motor characteristics.
-
Integrates a parking lock mechanism for electronic shifting and secure parking.
-
-
Intelligent Differential Technology:
-
Mechanical differential works in synergy with electronic control systems.
-
In specific vehicle models, dual-motor direct drive is used to achieve torque vectoring分配.
-
Enhances cornering stability and driving safety through precise torque control.
-
Multi-Mode Integration of the Cooling System
Thermal management is a critical challenge and core technology in E-Axle design. Advanced E-Axle systems employ a multi-layer cooling strategy:
-
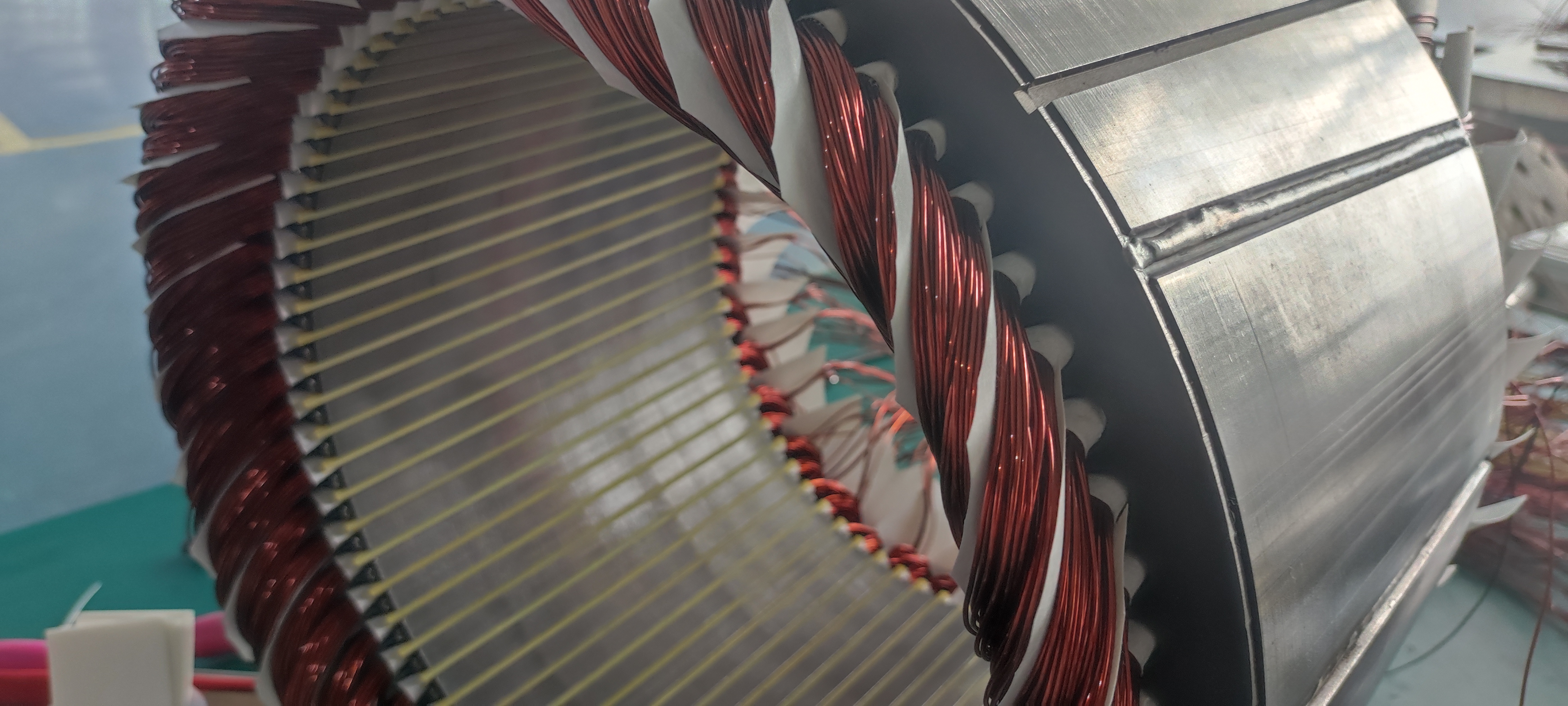
Stator Cooling: Typically uses a water jacket for direct cooling of the stator core and windings.
-
Rotor Cooling: Employs oil mist cooling or hollow shaft oil cooling technology, breaking through traditional rotor heat dissipation bottlenecks.
-
Power Electronics Cooling: Dedicated cold plate design ensures stable operation of IGBT/SiC modules under high temperatures.
-
Gearbox Oil Cooling: Integrated oil cooling system lubricates gears and bearings while dissipating heat.
This comprehensive thermal management strategy allows the E-Axle to sustain high power output without derating, solving the thermal衰退 issue during high-speed driving and continuous hill climbing in EVs.
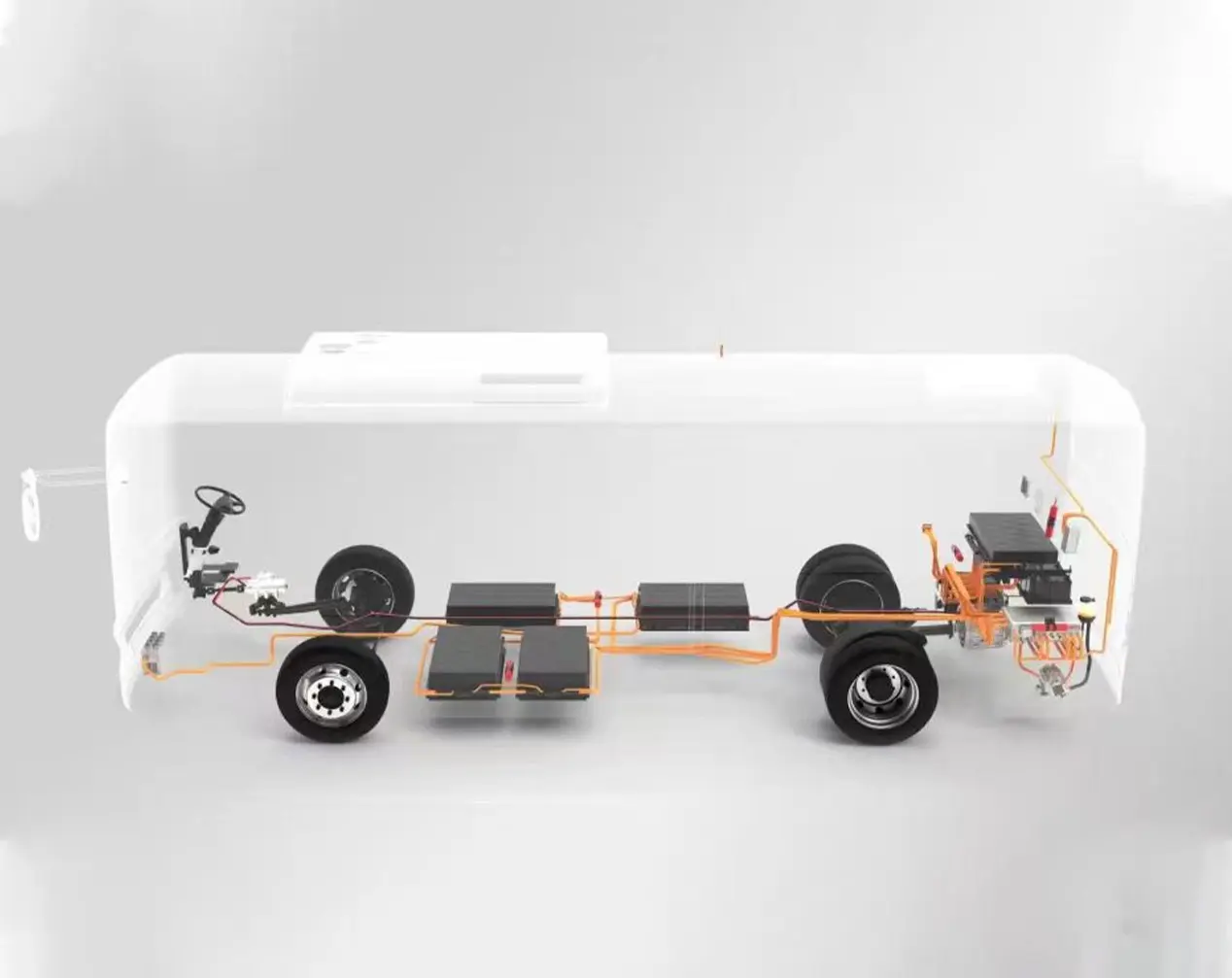
Multidimensional Functions of the E-Axle: From Power Transmission to Whole-Vehicle Energy Management
Core Powertrain Functions
-
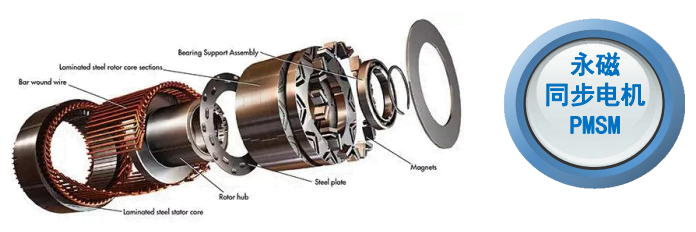
Efficient Energy Conversion & Transmission: The E-Axle receives high-voltage DC (400V or 800V) from the battery, converts it to three-phase AC via the inverter to drive a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) or Induction Motor. The motor's rotational motion is amplified in torque by an efficient reduction device (a typical single-stage reducer provides an 8-12:1 reduction ratio), and finally transmitted to the drive wheels via the differential and half-shafts. Energy loss in this entire process is minimal, with system efficiency reaching 94-97%.
-
Precise Torque & Speed Control: Through advanced algorithms like Field-Oriented Control (FOC), the E-Axle can provide millisecond-level torque response and speed accuracy within 0.1%. This precise control not only enhances driving smoothness but also provides ideal actuator characteristics for Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving.
Extended Energy Management Functions
-
Regenerative Braking Energy Recovery: During deceleration and downhill driving, the E-Axle automatically switches to generator mode, converting vehicle kinetic energy back into electricity to recharge the battery. Advanced E-Axle systems can increase driving range by up to 30%, a function completely impossible in traditional fuel vehicles.
-
Bidirectional Energy Flow Support: Next-generation E-Axle systems are integrating bidirectional charging capabilities, enabling EVs to act as mobile energy storage units, supplying power to the grid (V2G), homes (V2H), or other devices (V2L). This functional extension fundamentally changes the role definition of the vehicle.
-
Driving Dynamics Optimization: Through torque vectoring, the E-Axle can actively adjust torque output to the left and right wheels, improving cornering performance and stability. Some high-performance E-Axle systems can even achieve single-wheel independent drive, bringing revolutionary changes to driving dynamics.
The Modular Evolution of E-Axles: Meeting Diverse Electric Vehicle Needs
Different Tiers of E-Axle Configurations
-
Basic E-Axle:
-
Power Range: 80-150 kW
-
Application: Compact sedans, city commuter vehicles.
-
Characteristics: Cost priority, high efficiency, compact design.
-
-
Performance E-Axle:
-
Power Range: 150-300 kW
-
Application: Mid-size sedans, SUVs, sporty vehicles.
-
Characteristics: High power density, enhanced cooling system, integrated electronic differential.
-
-
Flagship E-Axle:
-
Power Range: 300-500+ kW
-
Application: Luxury sedans, high-performance vehicles, flagship SUVs.
-
Characteristics: Extreme power, advanced thermal management, torque vectoring capability.
-
Flexibility in Drive Layouts
The modular nature of E-Axles supports various drive layouts:
-
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD): Economical choice for small/medium vehicles.
-
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): Preferred solution for mid-to-high-end vehicles.
-
Dual-Motor All-Wheel Drive (AWD): High-performance choice for all-wheel drive.
-
Wheel-side/Wheel-hub Motors: Frontier exploration for future architectures.
The Pumbaa EV Perspective: How E-Axle Innovation Shapes the Future of Electric Vehicles
In the strategy of EV specialists like Pumbaa EV (www.pumbaaev.com), the E-Axle is not merely a powertrain component; it is a core source of product differentiation and competitive advantage.
Focus on Technological Innovation Frontiers
-
High Power Density Design: Compacts more power into a smaller space through advanced electromagnetic design, optimized thermal management, and lightweight materials. For example, Pumbaa EV's latest 3rd generation E-Axle platform achieves a power density of 4 kW/kg, a 40% improvement over the first generation.
-
System-Level Efficiency Optimization: Moves beyond the limitations of individual component efficiency to focus on the entire energy flow path—from battery terminals to the tire contact patch. Achieves maximized system efficiency across a wide operating range through协同 optimization of motor electromagnetic design, inverter switching strategies, and reducer gear ratios.
-
NVH Engineering Innovation: Develops proprietary technologies targeting EV-specific high-frequency electromagnetic noise and gear whine. Reduces excitation forces at the source through electromagnetic design,配合 with structural dynamics optimization, achieving serenity that surpasses traditional luxury ICE vehicles.
Core Challenges and Breakthroughs in Mass Production Engineering
-
Manufacturing Process Innovation: Scaling E-Axle production faces multiple challenges in precision, consistency, and cost. Automated assembly lines, online quality monitoring, and digital traceability systems ensure every E-Axle meets stringent performance standards.
-
Reliability & Durability Validation: Developed a comprehensive validation system covering extreme temperatures, harsh environments, and loads, including bench tests equivalent to millions of kilometers and real-world vehicle testing under diverse global climatic conditions.
-
Building Cost Competitiveness: Achieves continuous cost reduction while maintaining high performance through platform化 design, supply chain optimization, and production process innovation, promoting the of electric vehicles.
Future Trends of E-Axles: Intelligence, Integration, and Platform
Technology Evolution Directions
-
800V High-Voltage Platform: Next-gen E-Axles are rapidly migrating towards 800V systems, enabling:
-
Charging power exceeding 350 kW, significantly reducing charging time.
-
Halved current for the same power, reducing wiring harness weight and cost.
-
Further system efficiency improvement of 1-2%.
-
-
Widespread Adoption of Silicon Carbide (SiC): As SiC device costs gradually decline, their penetration in E-Axles will increase rapidly, bringing comprehensive improvements in efficiency, power density, and high-temperature operating capability.
-
Deep Thermal Management Integration: The E-Axle will be deeply integrated with battery and cabin thermal management systems, forming a vehicle-wide integrated thermal management system to optimize energy distribution under extreme conditions.
Functional Expansion Boundaries
-
Execution Optimization for Autonomous Driving: To meet the high demands of autonomous driving on the powertrain, next-gen E-Axles will feature:
-
More precise torque control (<1 Nm accuracy).
-
Faster response speed (<10 ms).
-
Richer status feedback information.
-
-
Software-Defined Functions: Through OTA updates, E-Axles will enable software-defined functional iterations:
-
Driving mode optimization.
-
Energy recovery strategy updates.
-
Fault diagnosis algorithm upgrades.
-
-
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration: The E-Axle will be deeply integrated with the On-Board Charger (OBC), supporting intelligent bidirectional charging/discharging, transforming EVs into flexible nodes in the smart grid.
Conclusion: The Ultimate Evolution of the Drive Axle – From Mechanical Component to Intelligent Power Hub
The role of the drive axle in the electric motor system has undergone a fundamental transformation. It is no longer merely a "bridge" for power transmission but has become the intelligent power hub of the electric vehicle. Through highly integrated design, the E-Axle achieves multiple optimizations in space, weight, efficiency, and cost. Through advanced control and energy management strategies, it expands the functional boundaries of traditional axles.
As demonstrated by the practices of innovative enterprises like Pumbaa EV, E-Axle technology is becoming a core battleground in EV competition. With the continuous maturation of 800V platforms, SiC power devices, and deep integration technologies, future E-Axles will become more efficient, intelligent, and multifunctional, continuously driving breakthroughs in EV performance, range, and user experience.
The evolutionary story of the drive axle, from a simple mechanical shaft to a complex electric drive system, is not only a microcosm of technological progress but also a witness to the transformation of human mobility. When we talk about the E-Axle, we are talking not just about a method to turn wheels, but about the very possibilities of the electric vehicle future itself.