What is Flat Wire Used For?"Key Applications and Advantages in Modern Motors
Introduction
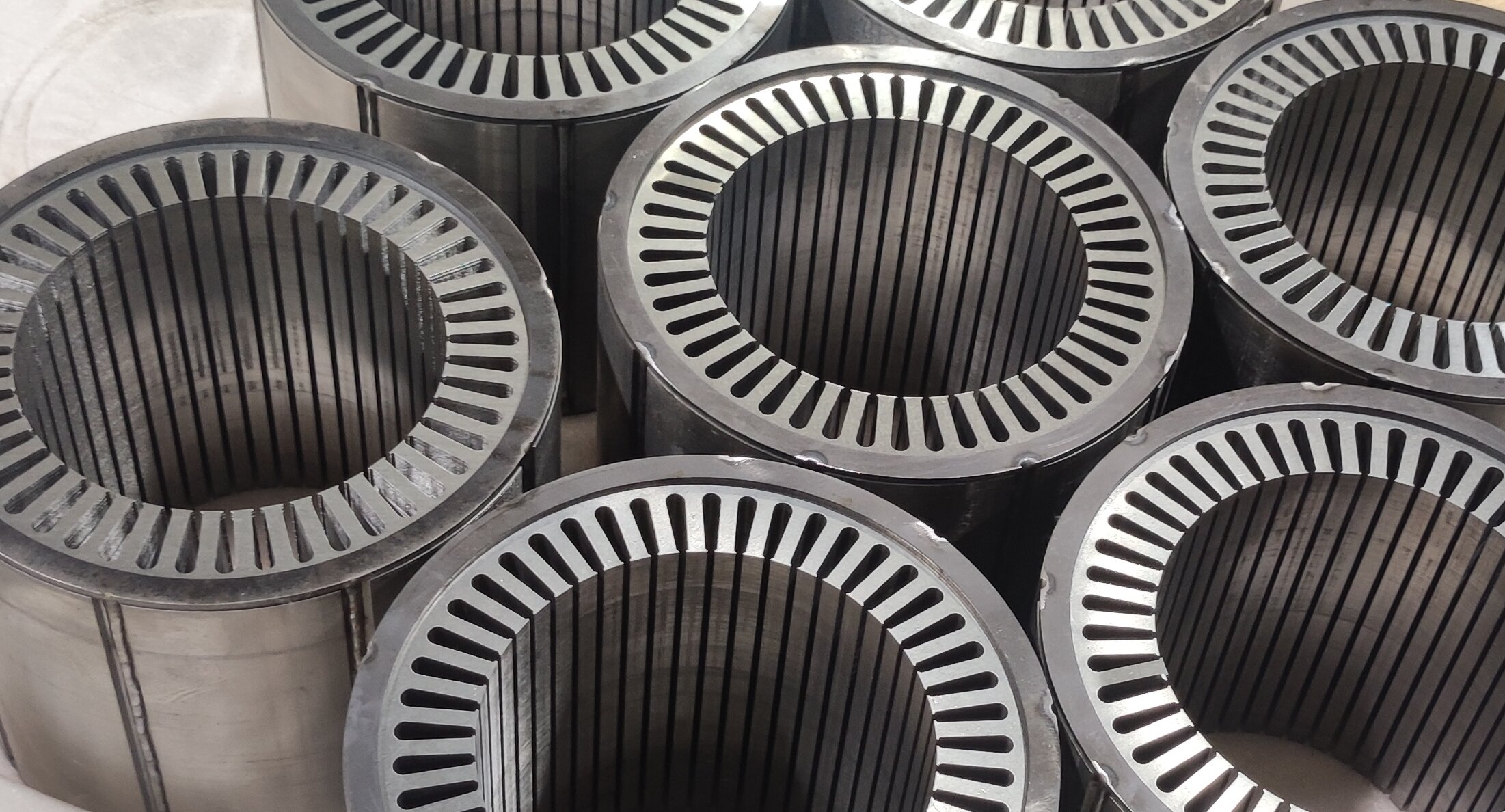
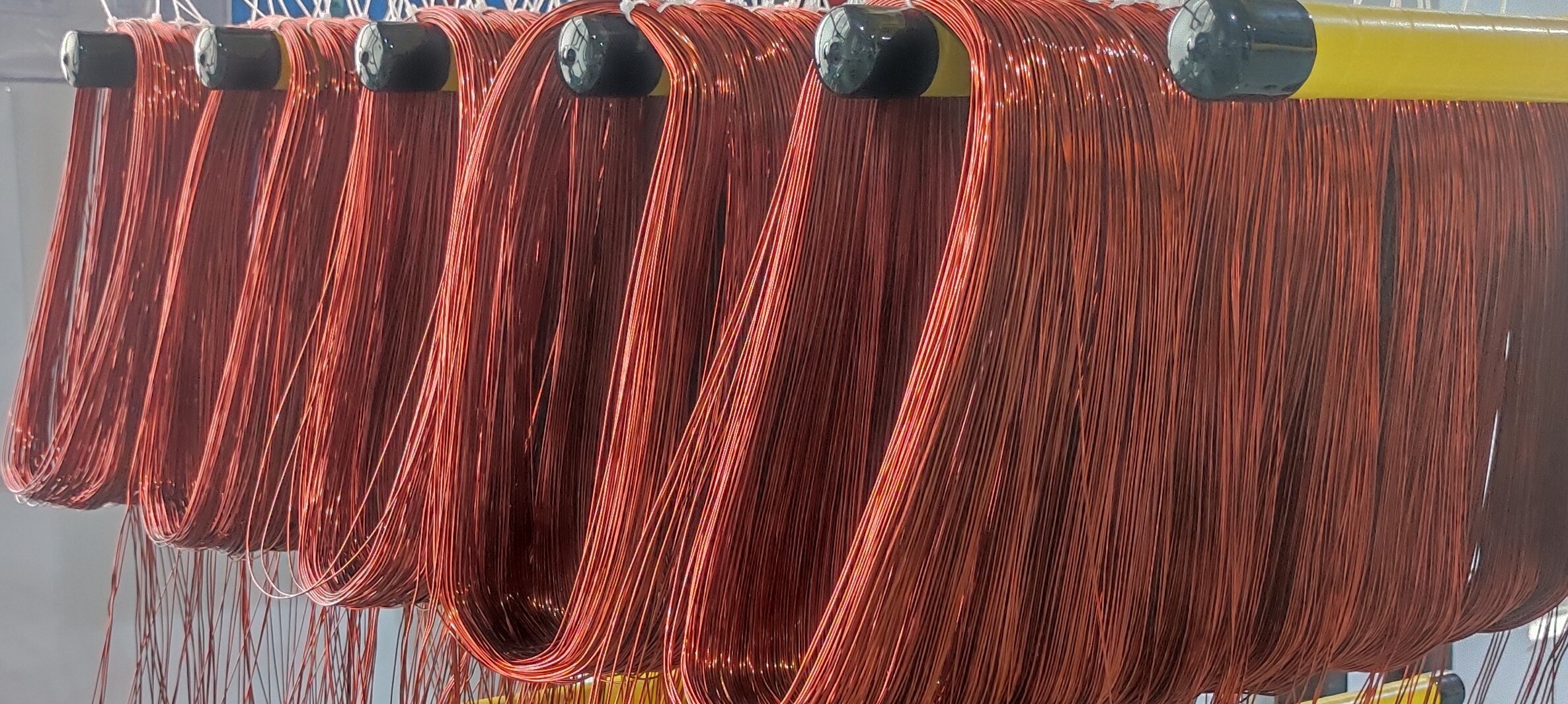
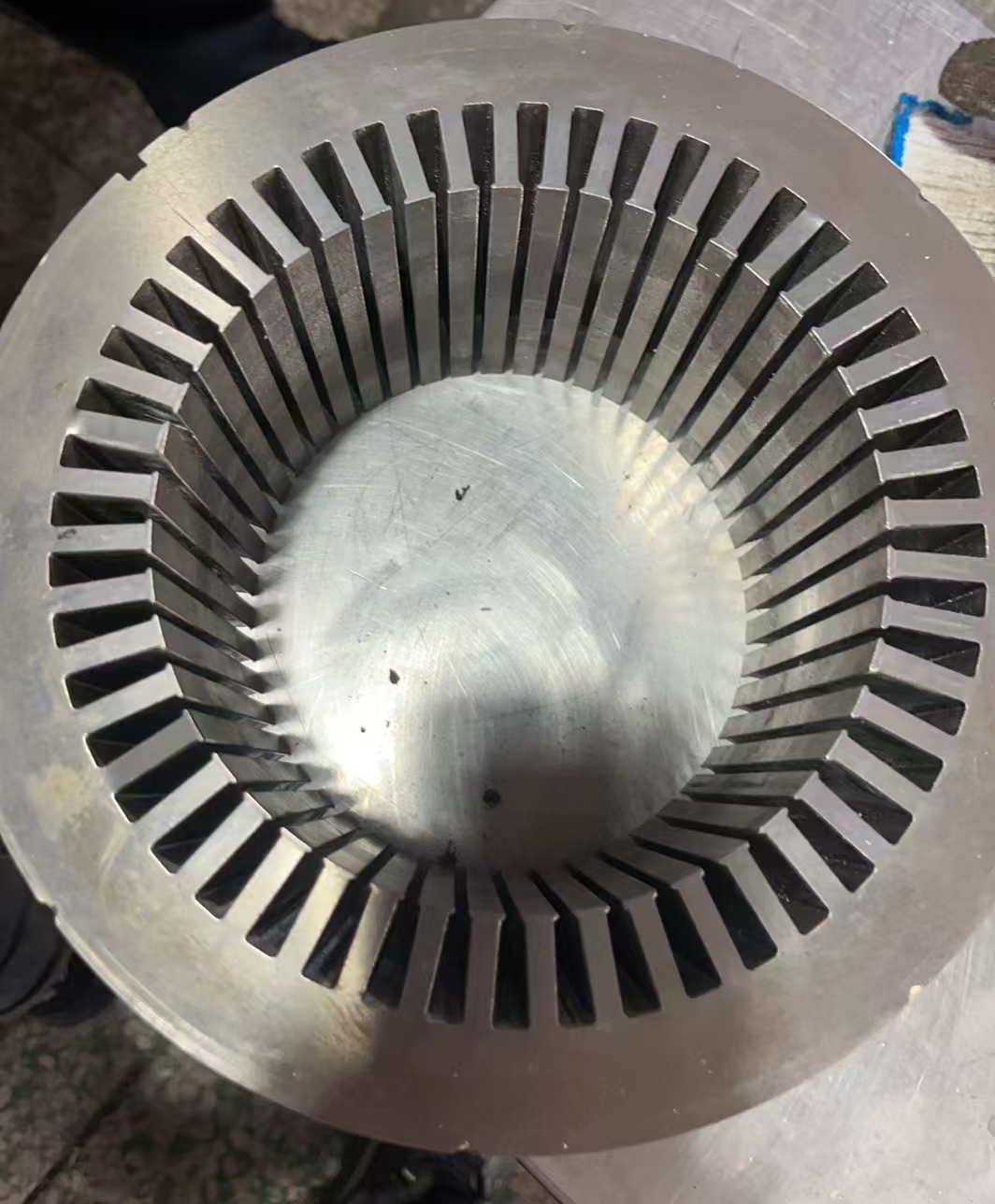
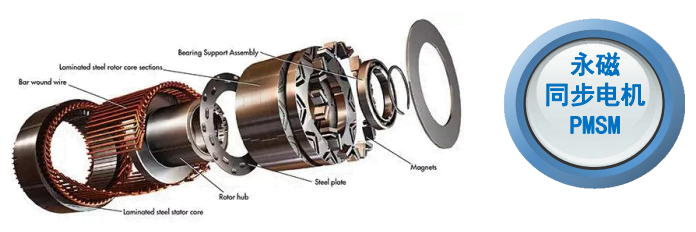
1. What is Flat Wire? A Basic Definition
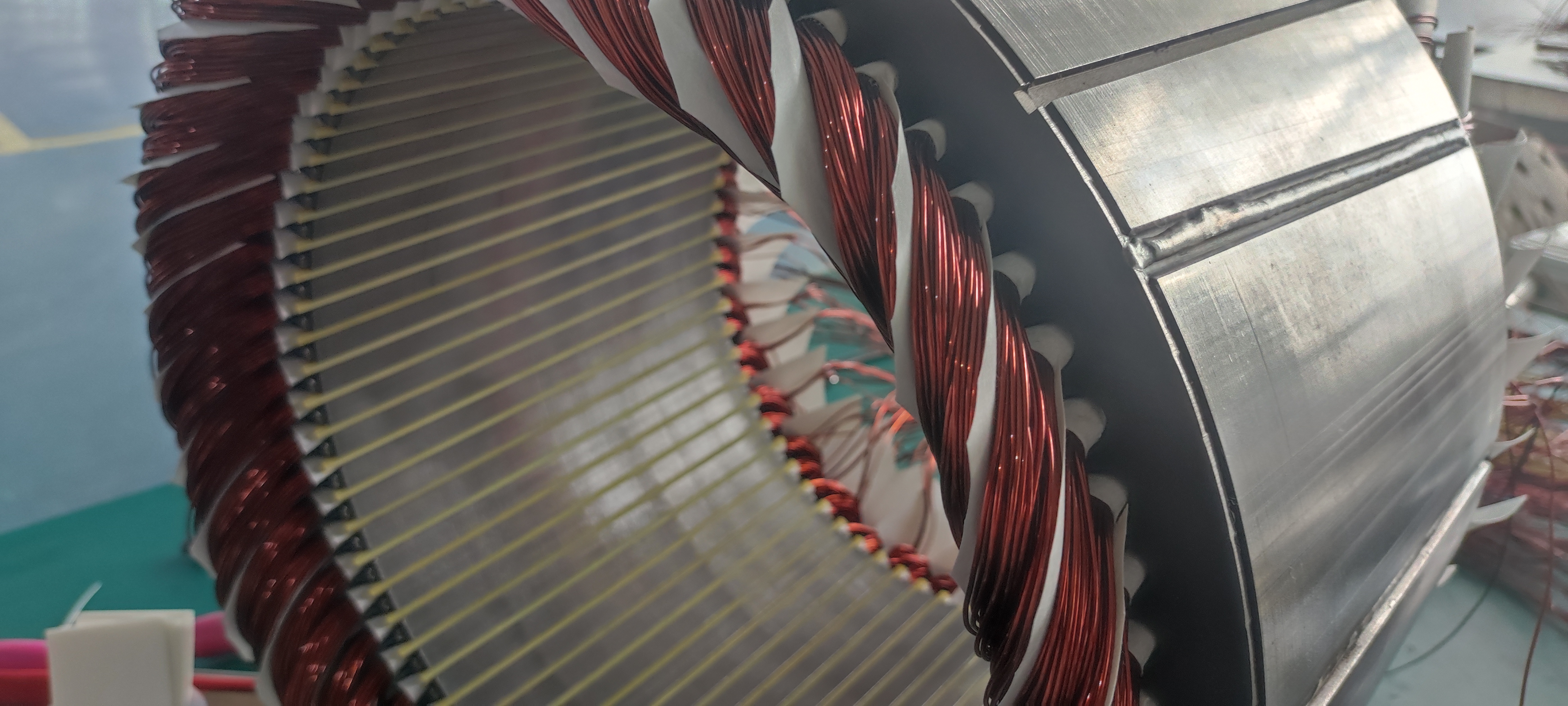
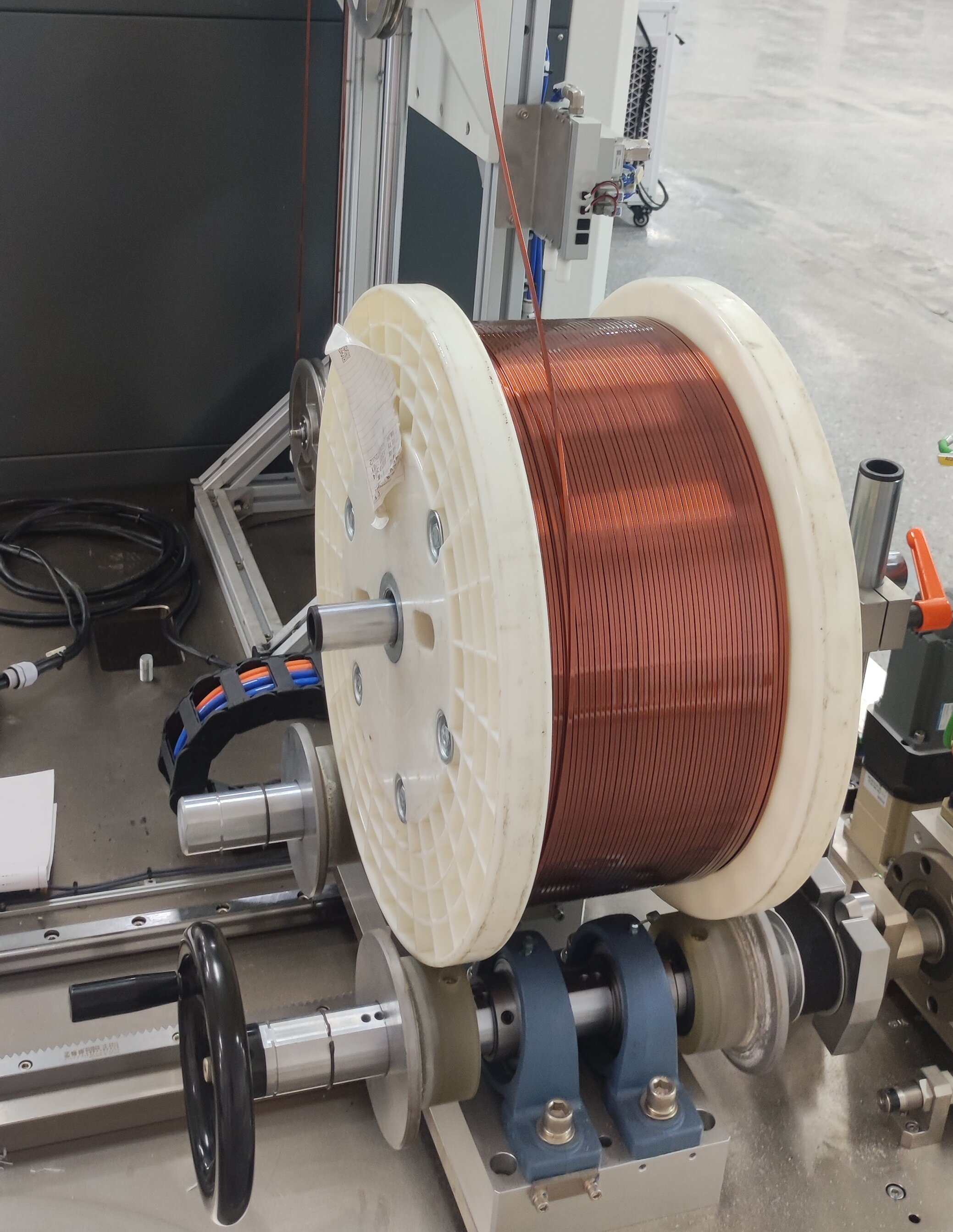
Technical definition: A conductive material with a rectangular/flat cross-section, saving space and offering larger surface area compared to round wire.
Comparison with round wire: Shape differences → winding complexity → heat dissipation/fill rate advantages (setting the stage for later benefits).
Types: Copper flat wire vs. aluminum flat wire, and their application distinctions.

2. Top Applications: Where is Flat Wire Used?
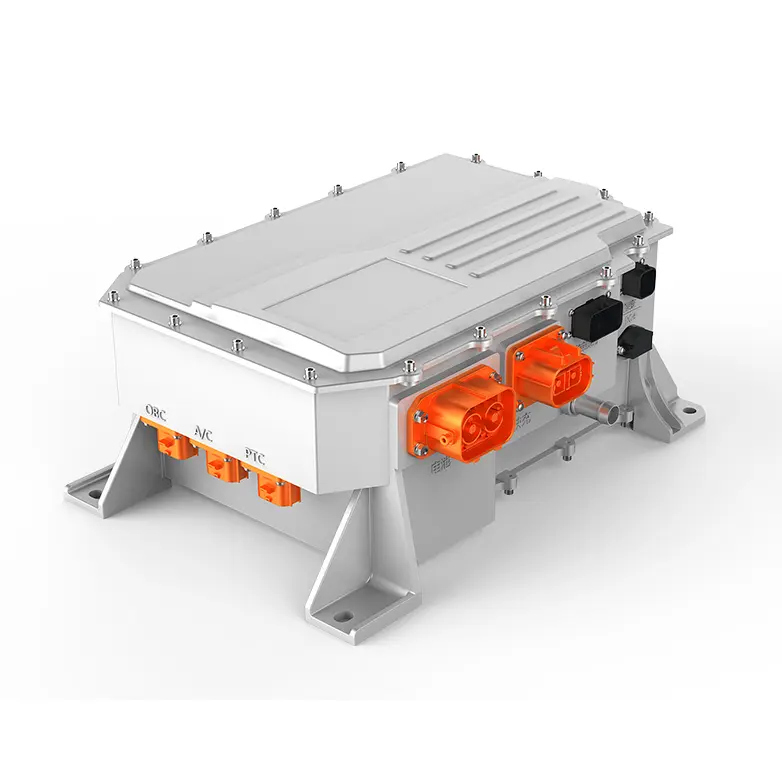
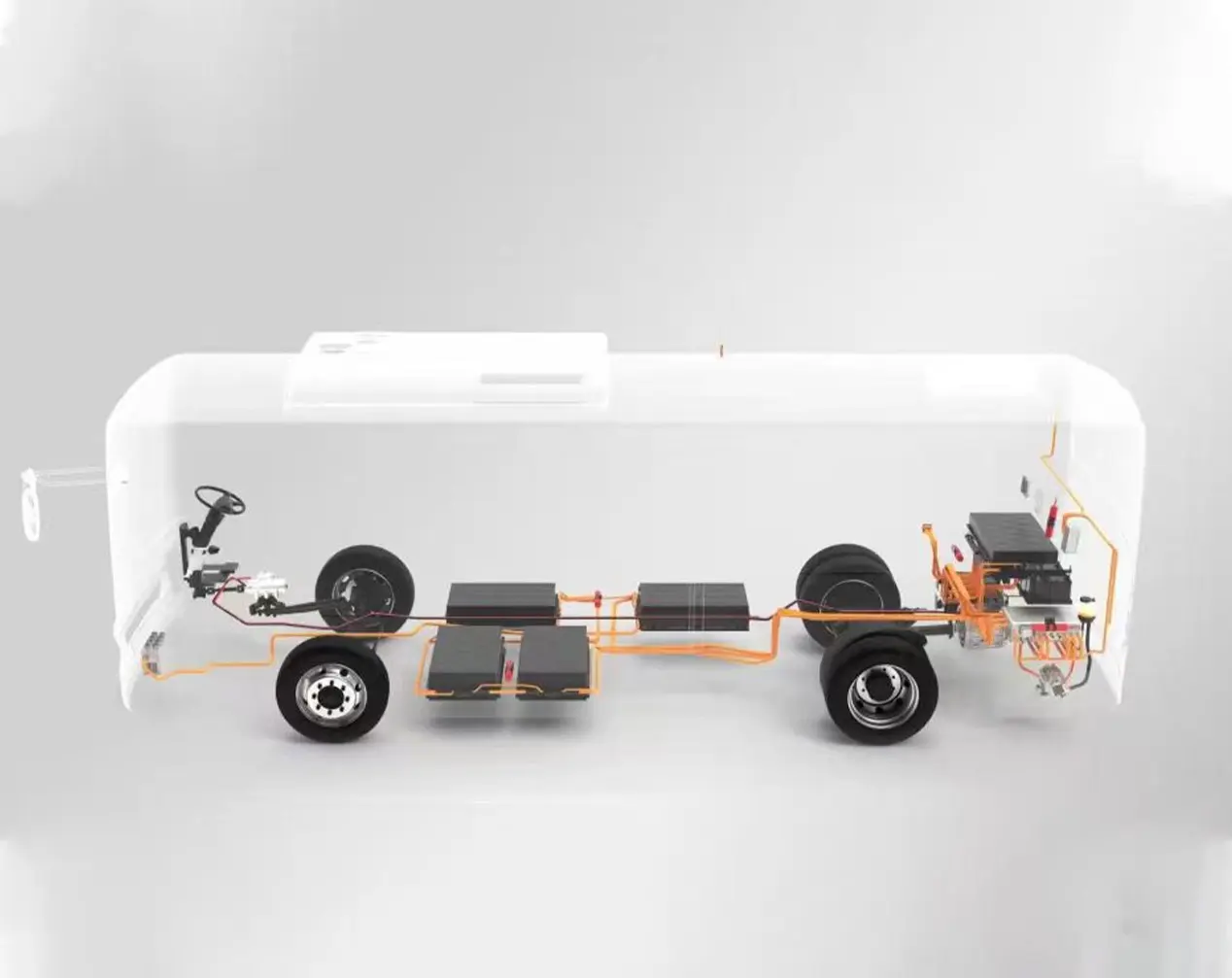
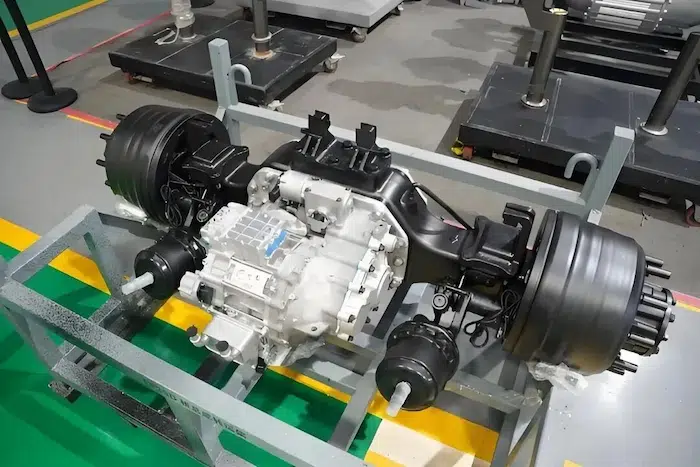
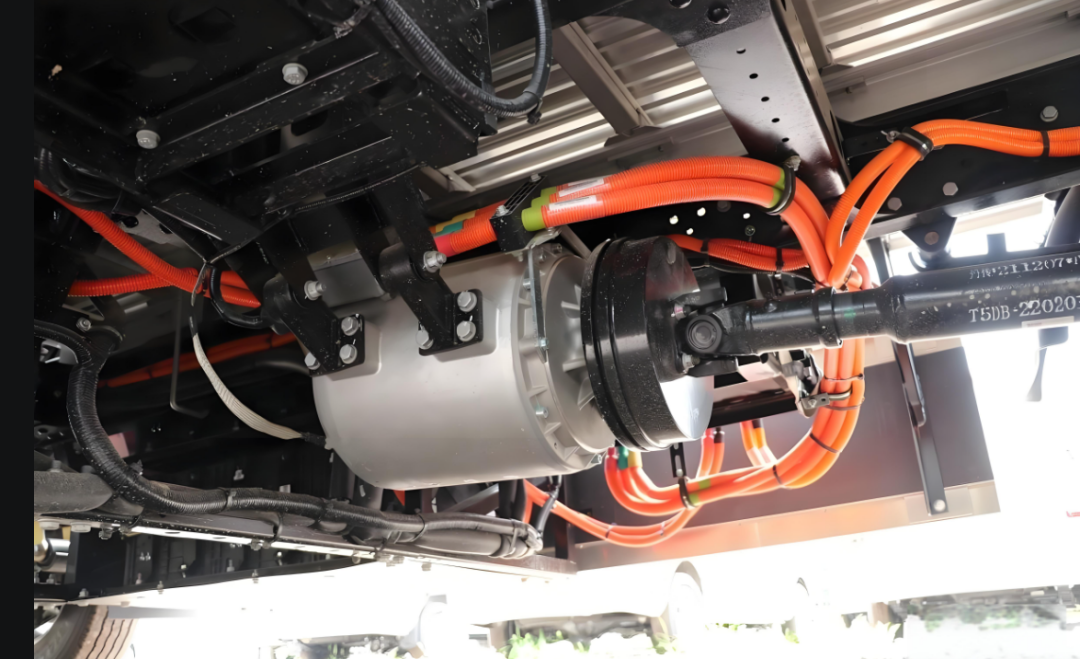
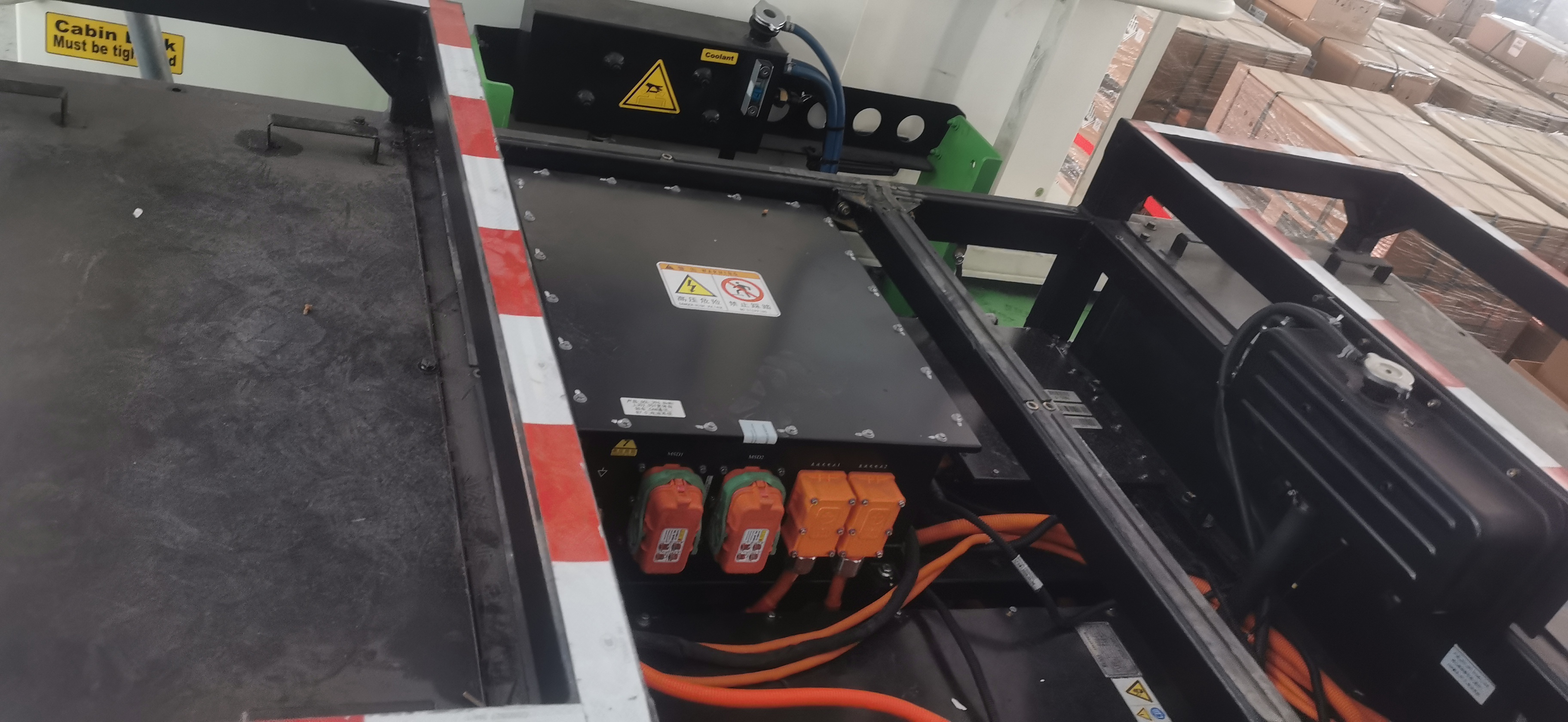
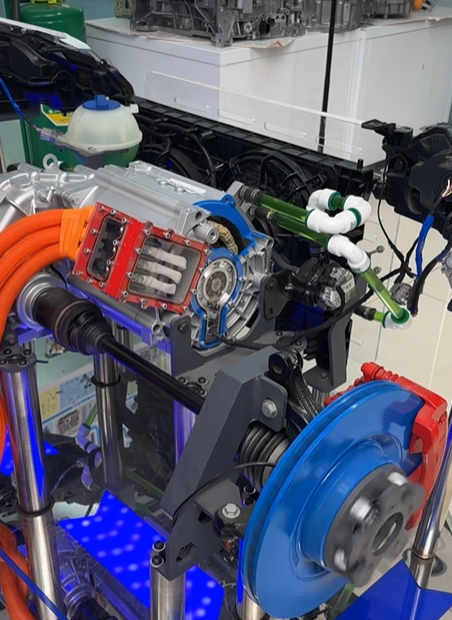
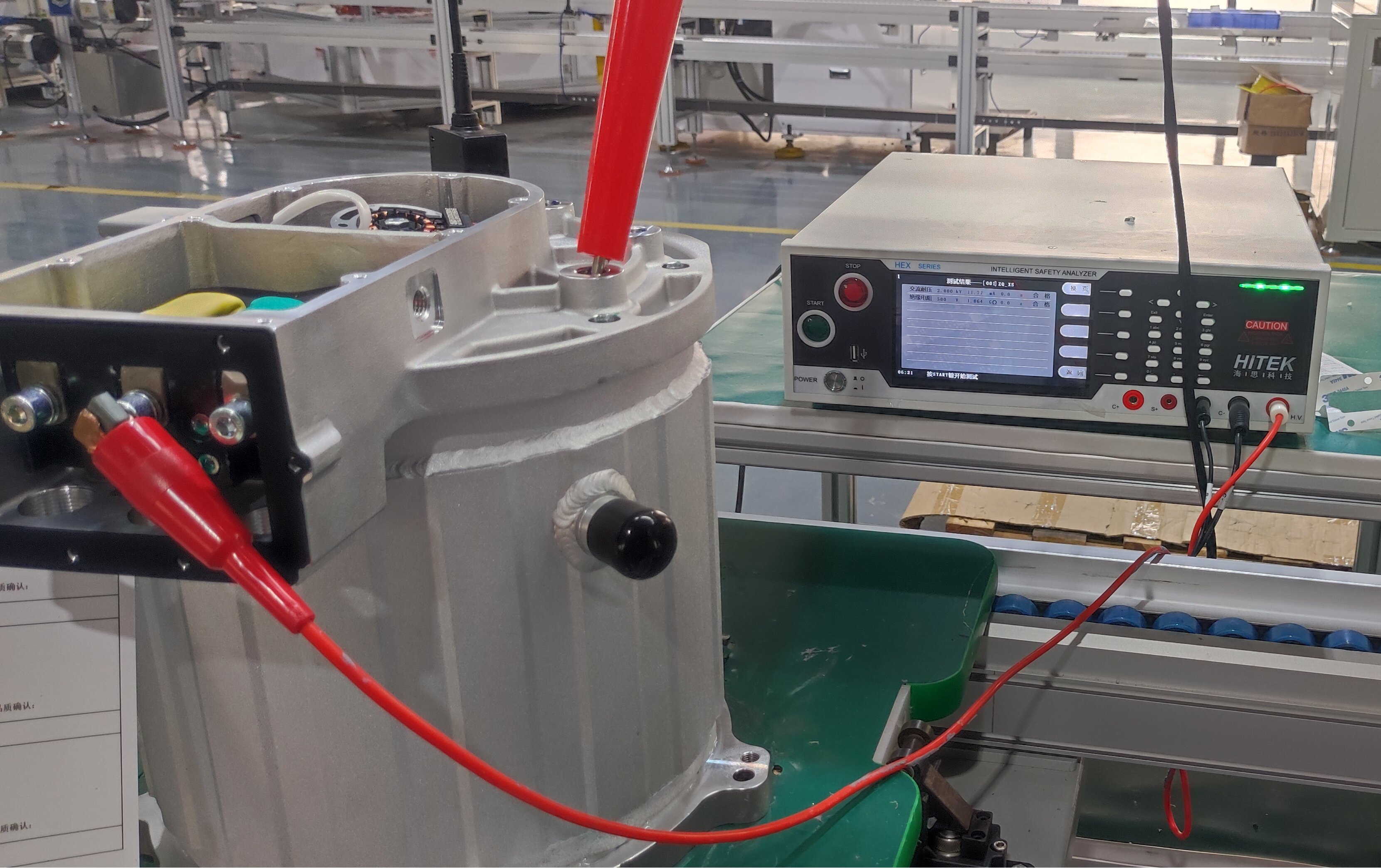
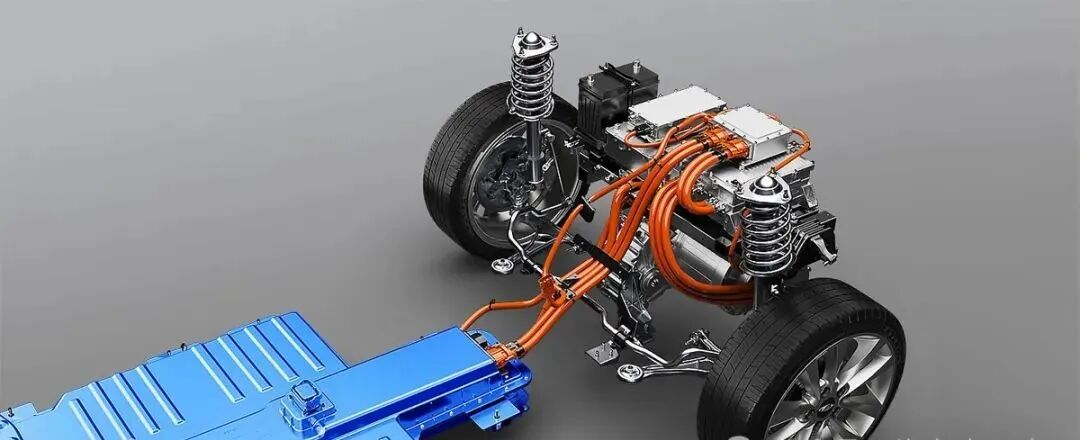
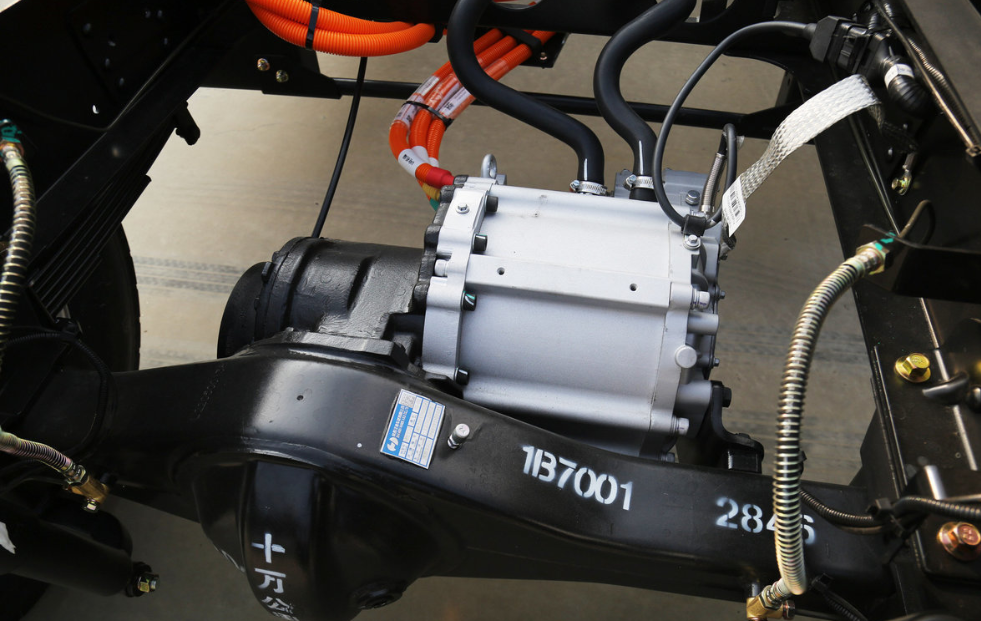
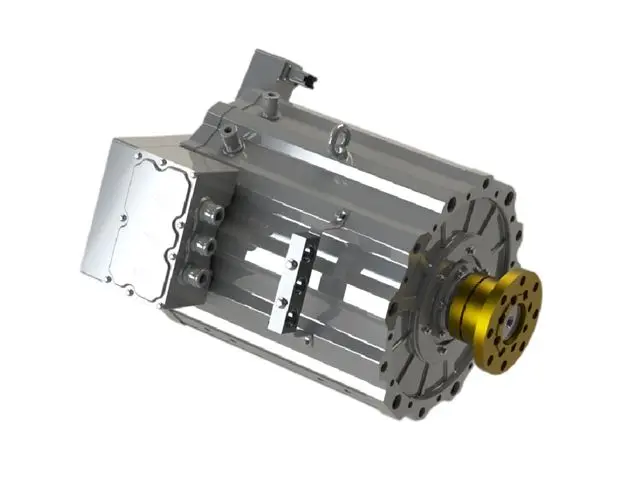
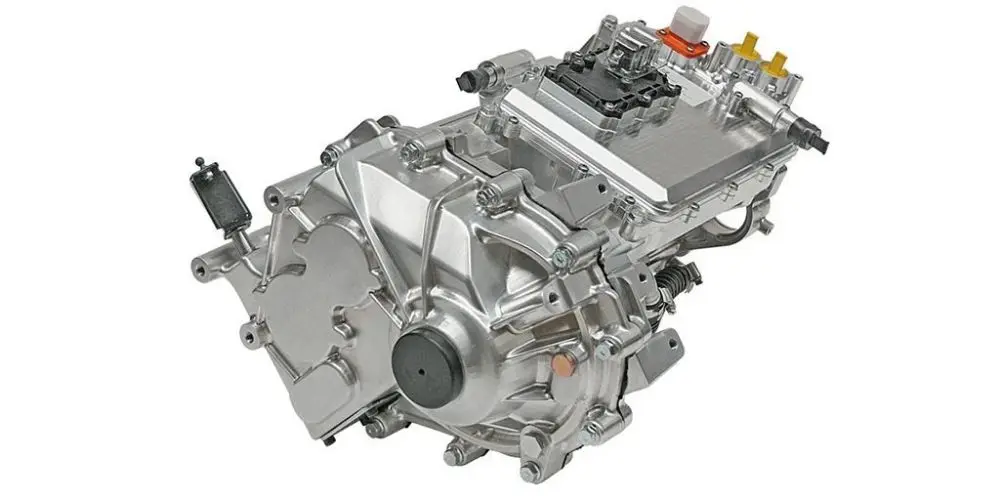
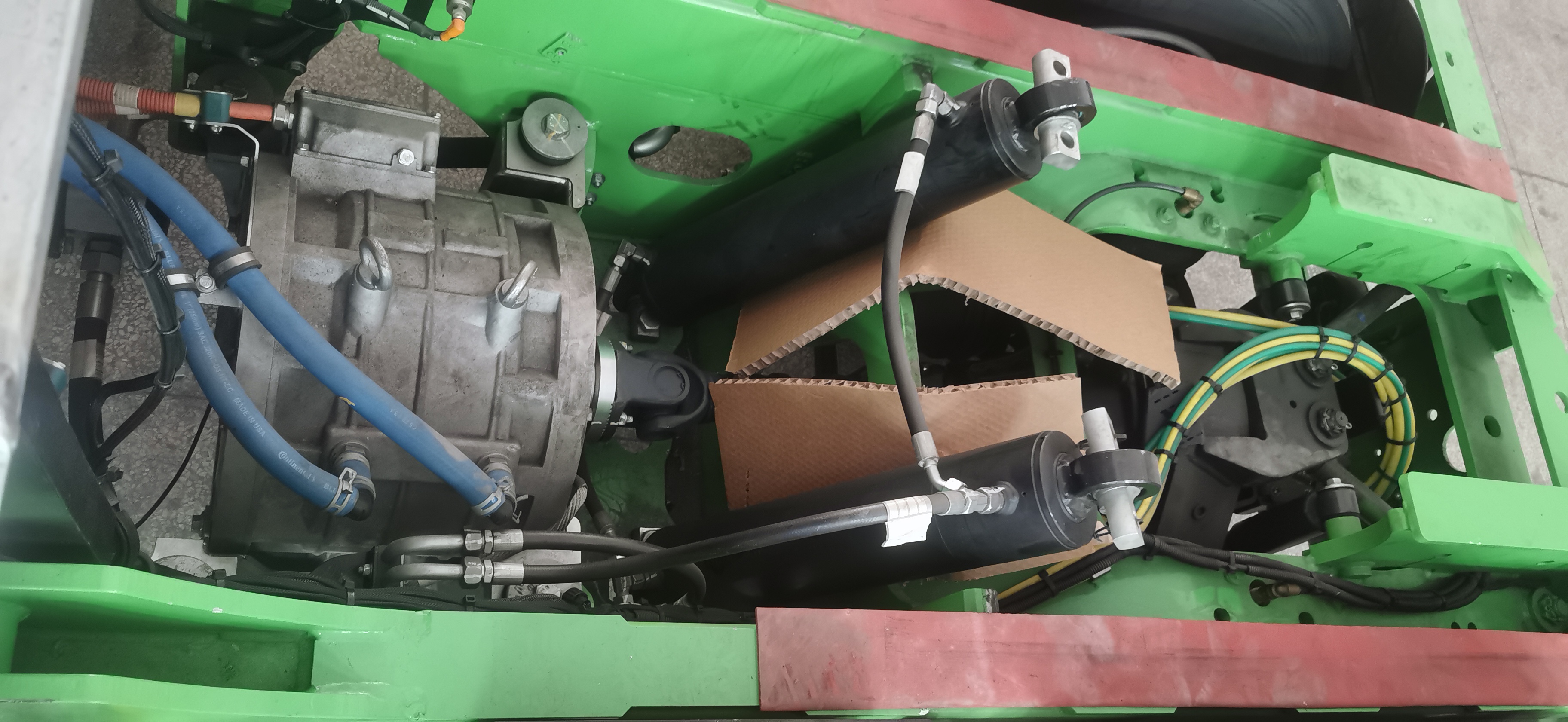
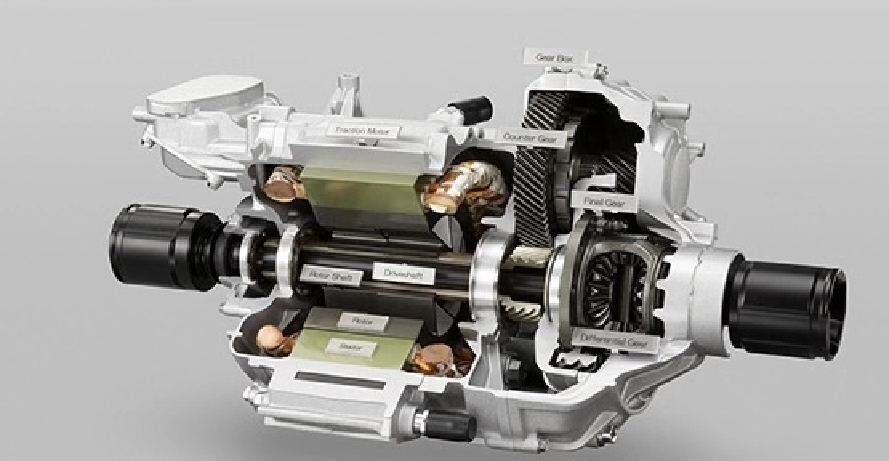
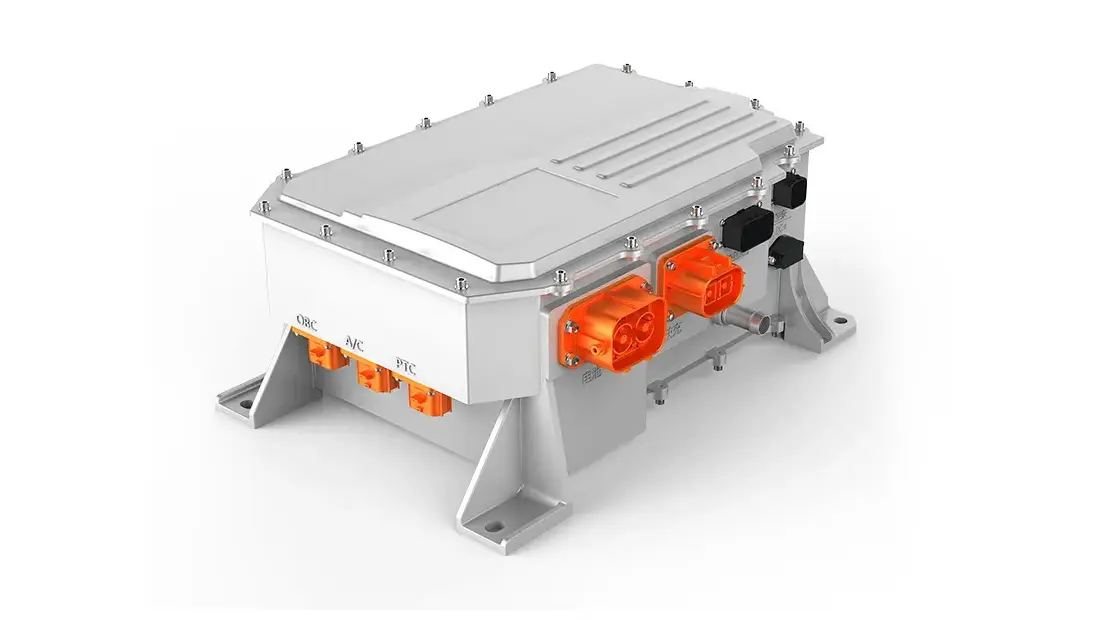
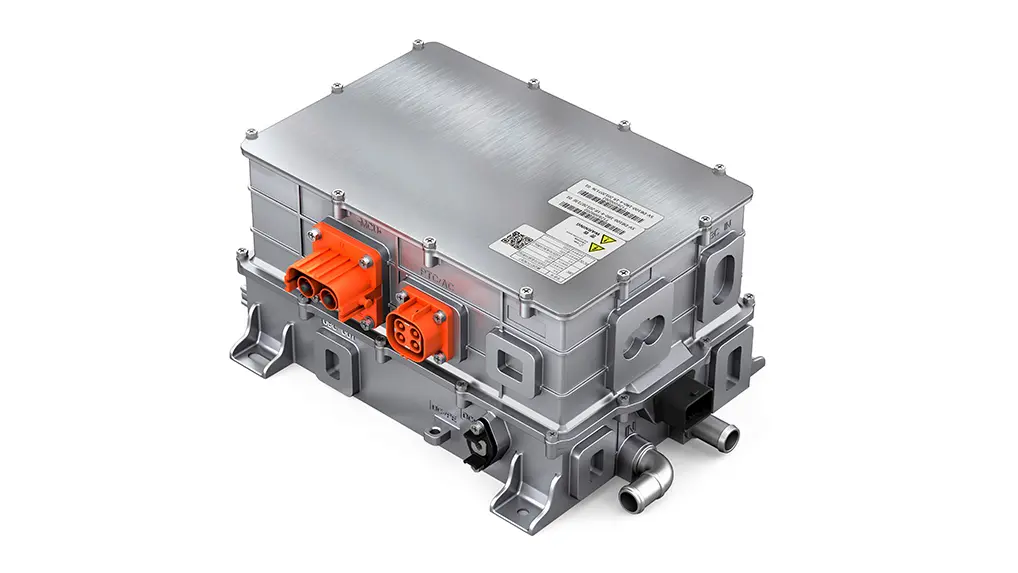
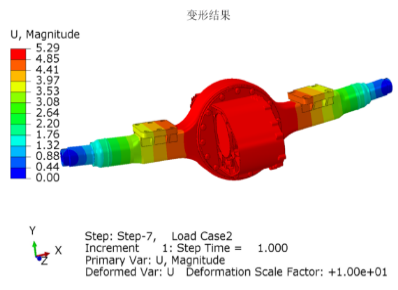
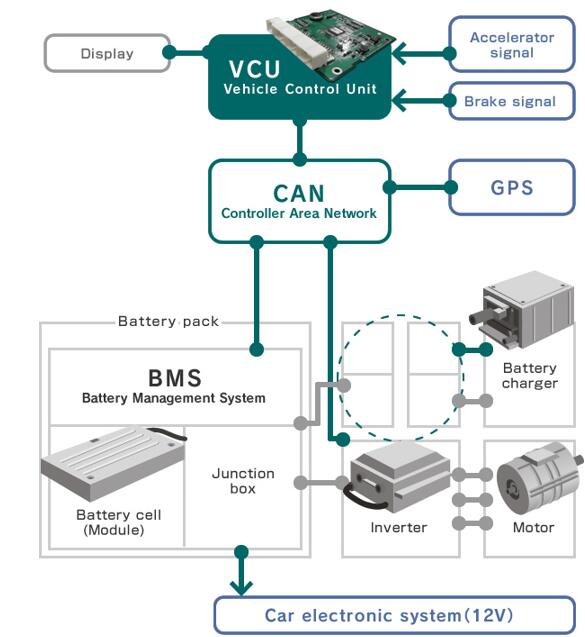
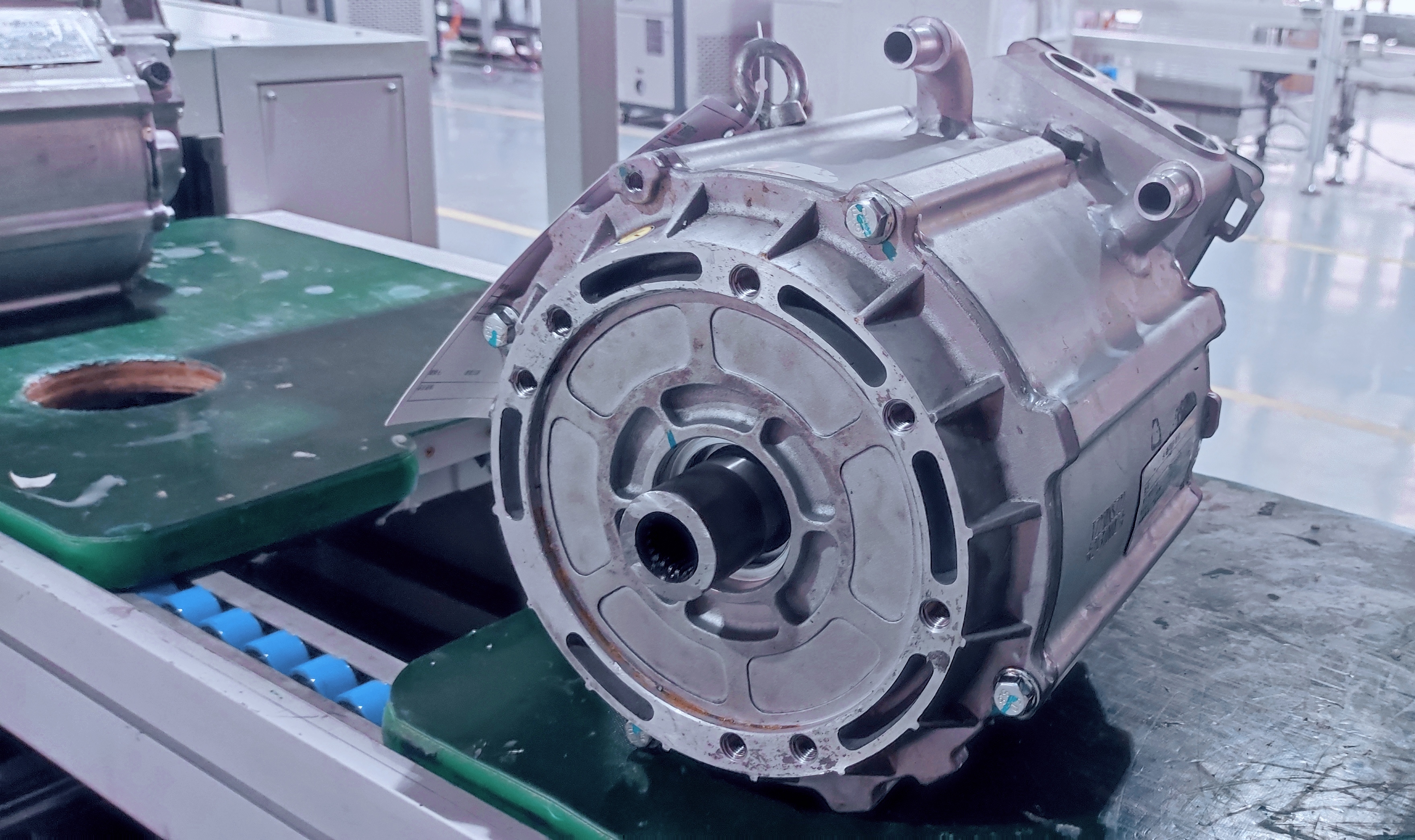
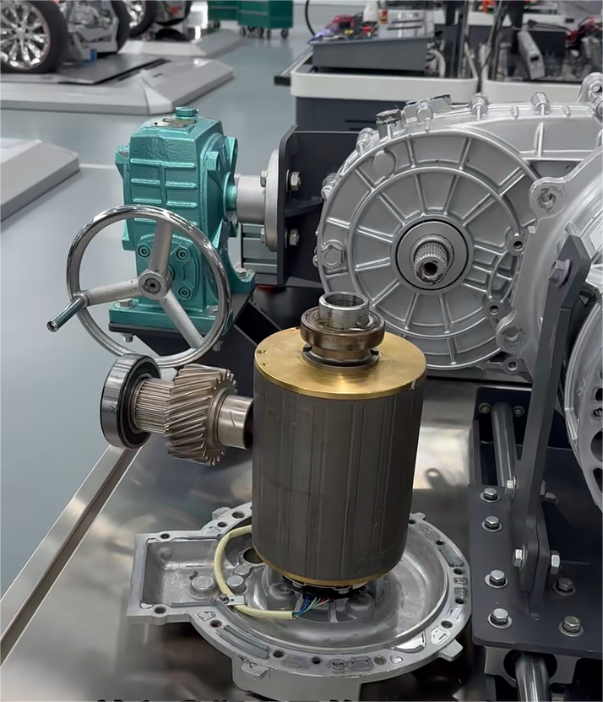
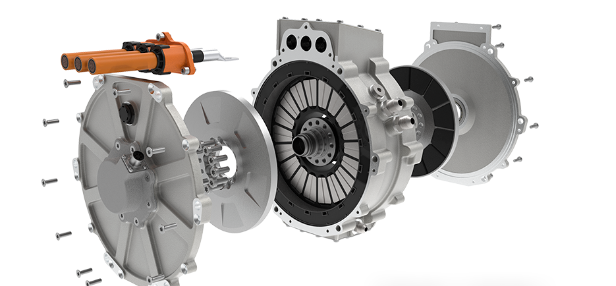
EV Drive Motors:
Why choose flat wire? High slot fill rate → boosts power density, meeting EV demands for range and performance.
Case studies: Tesla Model 3/Y, BYD Han, and other models adopt flat wire motors at scale.
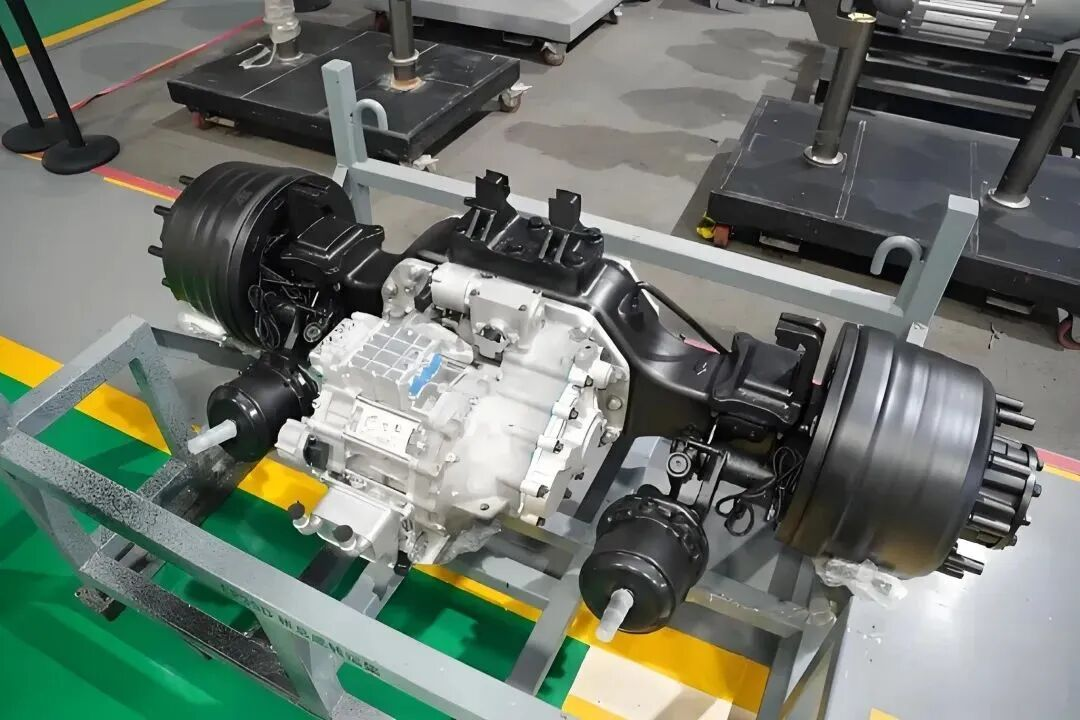
Industrial Motors:
Energy efficiency: Reduces copper loss, aligning with industrial cost-saving goals.
Compact design: Fits space constraints in robots, CNC machines, etc.
Home Appliance & Consumer Electronics Motors:
Miniaturization trend: Air conditioner compressors, washing machine motors shrink size and improve energy ratings via flat wire.
Aerospace & Defense:
Lightweight + reliability: Flat wire reduces weight while withstanding high temperatures/vibrations for harsh environments.
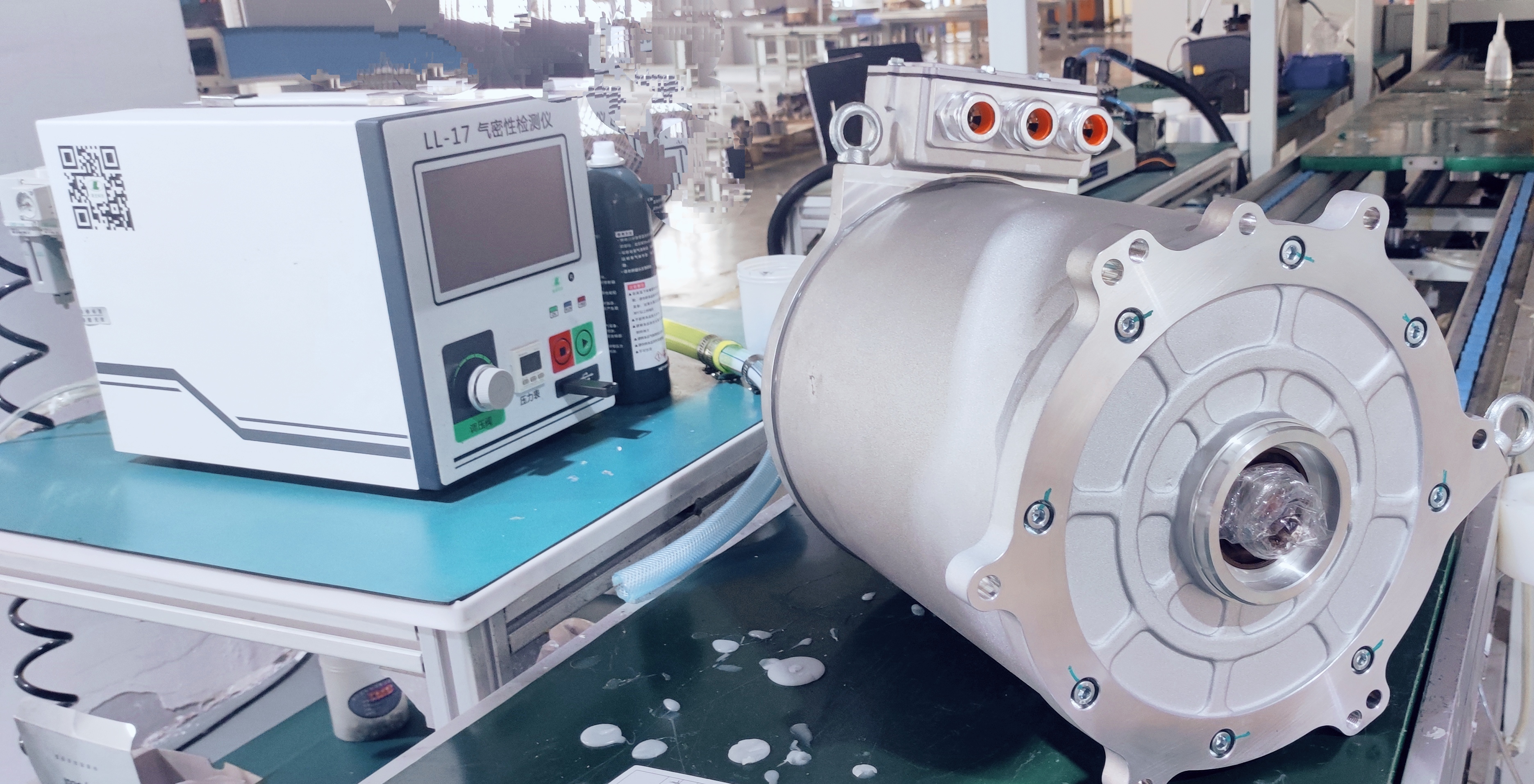
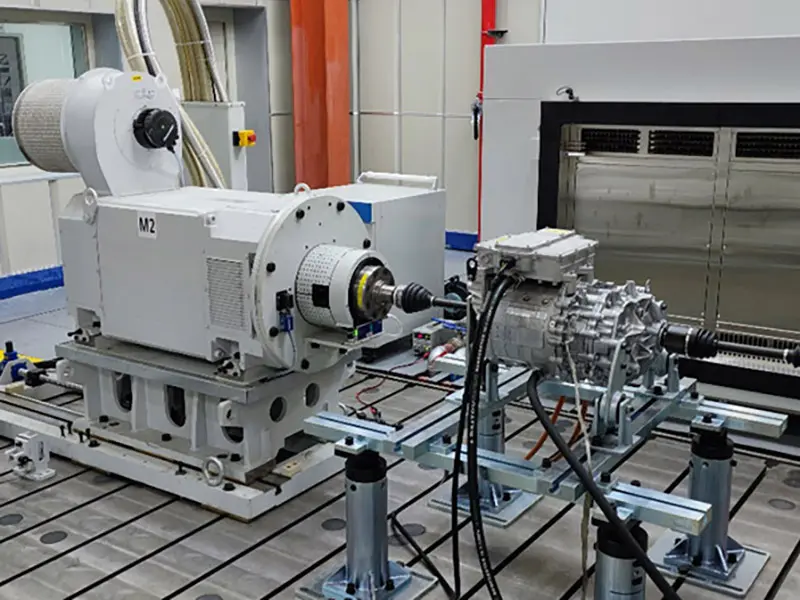
3. Why Choose Flat Wire Motors? Core Advantages Explained
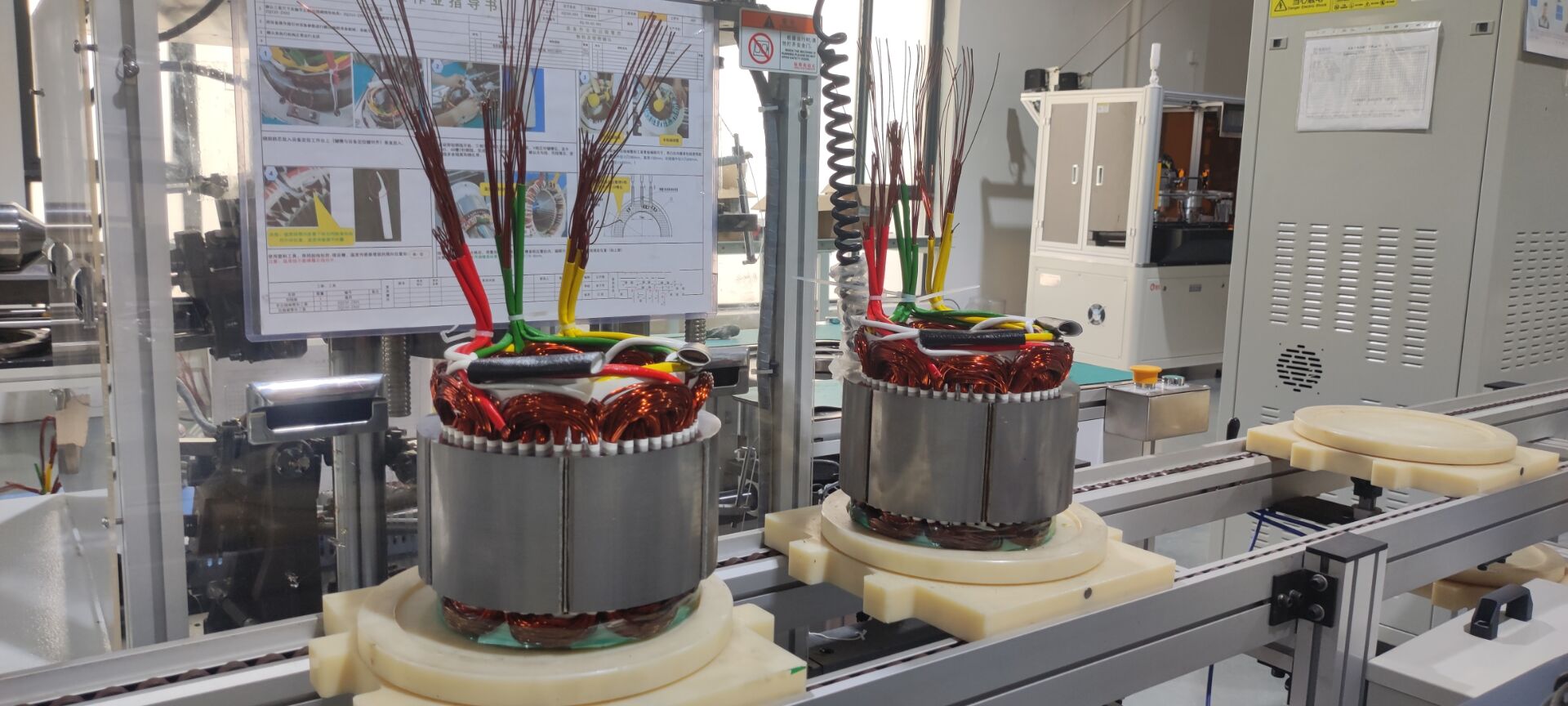
Higher Power Density: Tighter windings deliver 20%-30% higher output power in the same volume (cite industry data).
Better Heat Dissipation: Flat profile increases surface area, accelerating heat diffusion and extending motor life.
Lower Energy Loss: Reduced copper loss (due to consistent cross-section vs. bent round wire), achieving >97% efficiency.
Flexible Design: Supports high-speed motors (e.g., 20,000rpm+), ideal for EVs and high-speed pumps.
4. Flat Wire vs. Round Wire: Key Differences
Winding complexity: Flat wire requires precision automation (e.g., hairpin winding); round wire uses traditional methods.
Cost comparison: Higher initial cost, but lower total cost of ownership (TCO) long-term due to efficiency/lifespan gains.
Use cases: Flat wire → high-power/high-speed/compact needs; round wire → low-power/cost-sensitive/low-speed scenarios.
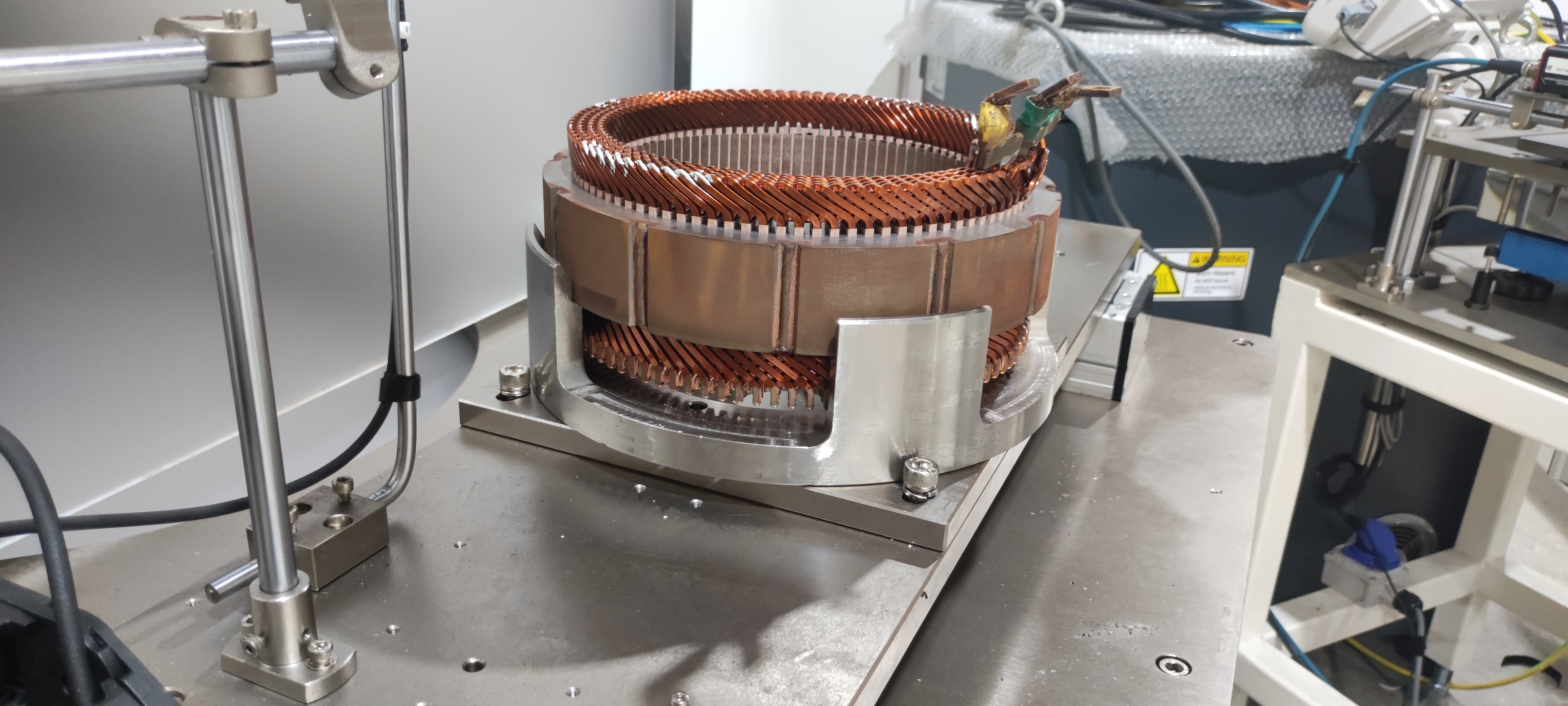

5. Industry Trends: The Rise of Flat Wire Motors
EV boom driving demand: Global EV sales growth → surging flat wire motor requirements (cite MarketsandMarkets projections).
Tech breakthroughs: Mature automated winding → lower production costs, accelerating adoption.
Future outlook: Expanding into emerging areas like electric aircraft and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
6. FAQ: Common Questions About Flat Wire
Q1: Are flat wire motors more expensive than round wire ones?
Q2: Is maintenance harder for flat wire motors?
Q3: Which brands use flat wire motors extensively?
Conclusion
Summarize key applications and advantages, emphasizing flat wire’s irreplaceability in efficient, compact motor design.
Future outlook: As tech advances, flat wire motors will replace round wire in more sectors, becoming critical to "green energy" and "smart manufacturing."
CTA: Learn more about flat wire motor technology or request custom solutions—contact us today!