Impact of China’s New Export Control on Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Motors
On October 9, 2025, the Chinese Ministry of Commerce announced new export control regulations targeting key rare earth technologies. The policy covers not only mining and refining but also the entire production chain of rare earth permanent magnets, including advanced separation, alloy processing, and magnet manufacturing technologies. This regulatory move aims to safeguard national security, protect strategic resources, and strengthen control over critical global supply chains.
Scope and Technical Focus
Unlike previous policies that mainly targeted physical exports, this regulation emphasizes technology control. It applies to high-performance elements such as neodymium (Nd), dysprosium (Dy), terbium (Tb), and samarium (Sm), as well as to production processes essential for NdFeB and other permanent magnets used in electric vehicle (EV) motors, wind turbines, robotics, and other high-tech applications.
The policy also introduces a "Chinese content" traceability requirement, meaning that even products processed abroad containing more than a minimal percentage of Chinese-sourced material now require official approval.
Short-Term Impact on the Industry
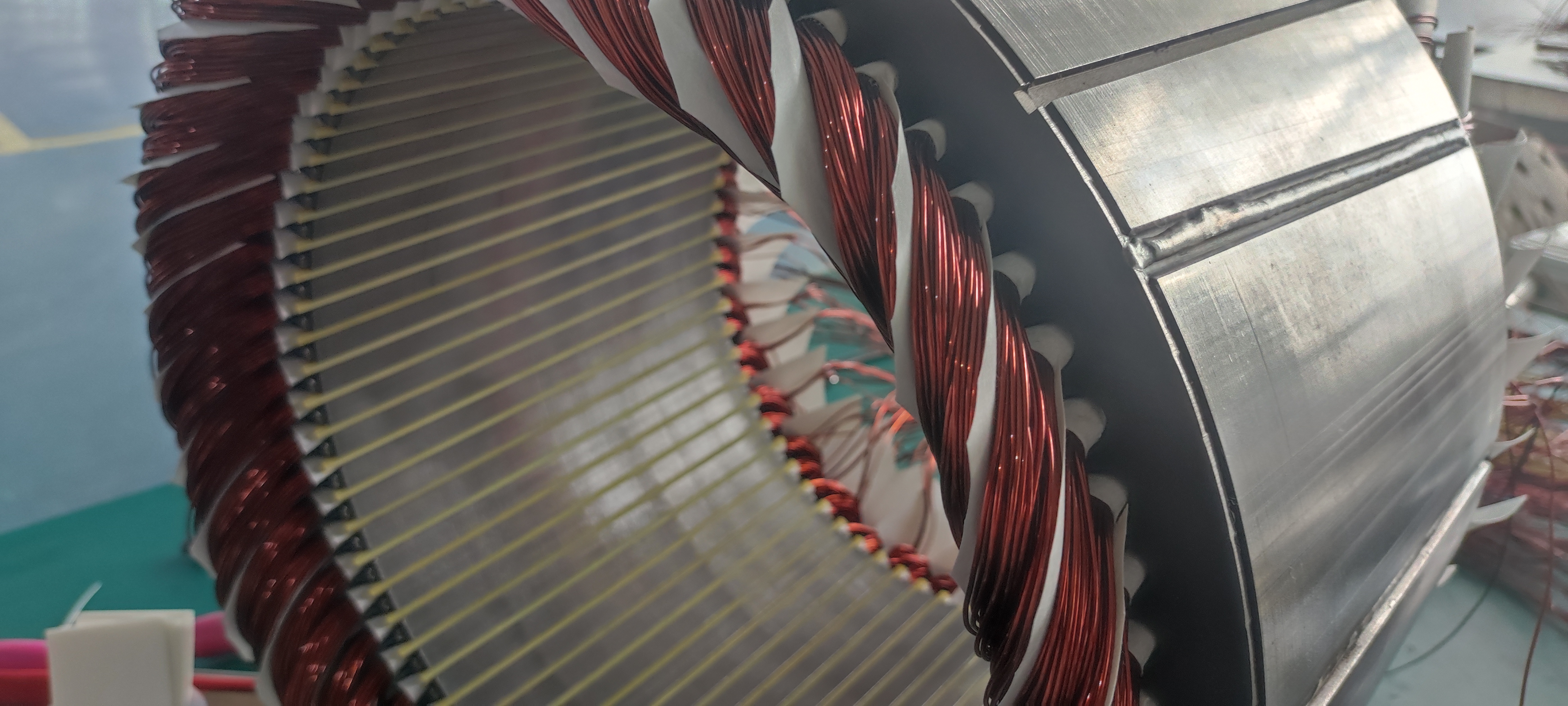
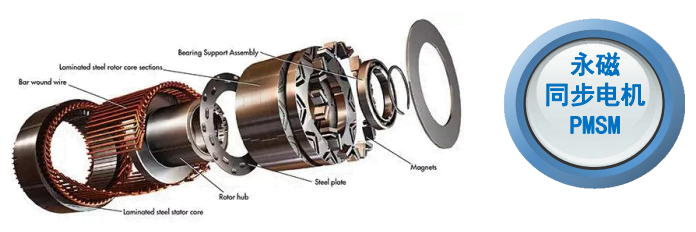
Permanent magnet motors, which rely on high-quality rare earth magnets, are particularly affected. These motors are widely used in EV drive systems, industrial automation, and defense equipment.
Short-term implications include:
1.Supply delays for high-performance NdFeB magnets, potentially affecting global EV production schedules.
2.Rising material costs, as manufacturers adjust procurement under the new export licensing requirements.
3.Production bottlenecks for manufacturers lacking alternative sources or domestic processing capabilities.
Each EV traction motor typically requires 2–3 kg of NdFeB magnets, and a significant portion of the global supply originates from China. As a result, the new policy directly influences delivery times and costs for international EV manufacturers.
Mid- to Long-Term Implications
The regulation is expected to drive a structural shift in the global permanent magnet supply chain:
1.Overseas localization efforts will accelerate, including investments in mining and refining capabilities outside China.
2.Technological barriers remain high, as efficient rare earth separation and high-purity magnet production require advanced knowledge and strict environmental compliance.
3.Chinese firms may gain pricing and technological leverage, consolidating their position in high-value segments.
4.Research into alternative materials (e.g., ferrite or rare-earth-reduced magnets) will intensify, though current substitutes do not match the performance of NdFeB magnets.
Strategic Significance
By controlling both materials and technology, China is shifting from being a supplier of raw resources to a leader in industrial standards and technological control. This strategic approach not only ensures long-term security of domestic industries but also strengthens influence over global high-tech manufacturing.
Recommended Strategies for Companies
Global manufacturers and suppliers affected by the new regulation may consider the following measures:
1.Compliance systems: Implement export control and traceability mechanisms to ensure timely approval.
2.Upstream resource planning: Secure stable supplies of rare earth materials through long-term contracts or strategic partnerships.
3.Alternative technologies: Accelerate R&D on rare-earth-reduced magnets and design optimizations to reduce dependency.
4.Localized production and partnerships: Collaborate with compliant overseas partners to maintain market presence while protecting intellectual property.
5.Industry collaboration: Engage with regulatory agencies and industry associations to facilitate smooth licensing and compliance procedures.
Conclusion
China’s new export control on rare earth technologies represents a strategic shift with far-reaching consequences for the permanent magnet motor industry. By regulating both materials and high-value production technologies, the policy enhances domestic technological leadership and introduces supply chain challenges for international manufacturers. Companies that proactively manage compliance, diversify resources, and invest in alternative technologies will be better positioned to navigate the evolving global landscape.