Comparison of NVH Performance Advantages and Disadvantages Between Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors and Flat-Wire Motors
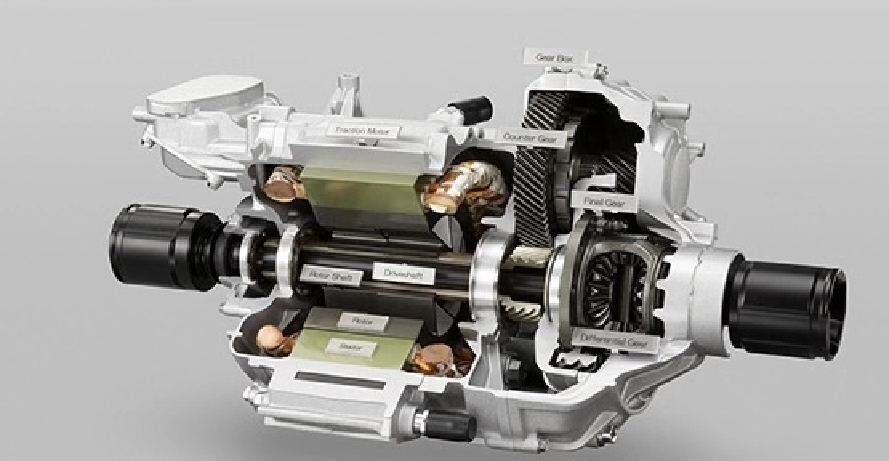
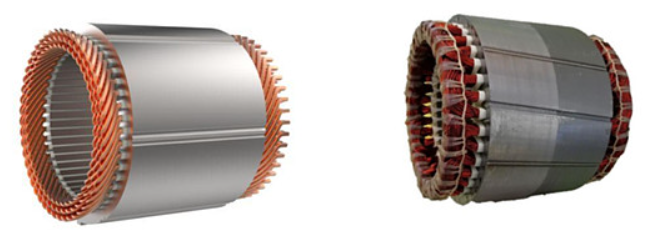
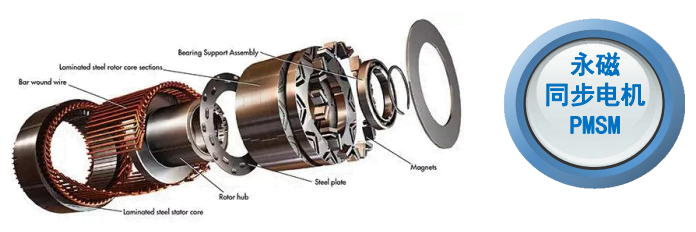
A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is a type of motor that utilizes permanent magnets in a synchronous motor structure. It consists of a stator, rotor, and permanent magnets. The working principle of a PMSM is based on electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic force laws. When the motor is energized, the current in the stator generates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnets in the rotor, thereby producing torque. The torque applied to the rotor causes it to rotate, enabling the motor to operate.
The noise generation mechanisms in PMSMs mainly include torque ripple and radial force waves. Torque ripple occurs due to instability in torque production, which can result from magnetic field inhomogeneity, instability in stator current, or rotor asymmetry. Torque ripple leads to motor vibration and noise.
Radial force waves are generated due to magnetic field inhomogeneity in the motor. During operation, uneven magnetic field distribution between the stator and rotor causes radial forces on the rotor. These radial forces induce vibration and noise.
Therefore, to reduce noise in PMSMs, it is essential to address torque ripple and radial force waves. This can be achieved by improving motor design and manufacturing processes to enhance torque stability and magnetic field uniformity. Additionally, appropriate selection of permanent magnet materials and reducing operating temperature can also help lower noise levels.
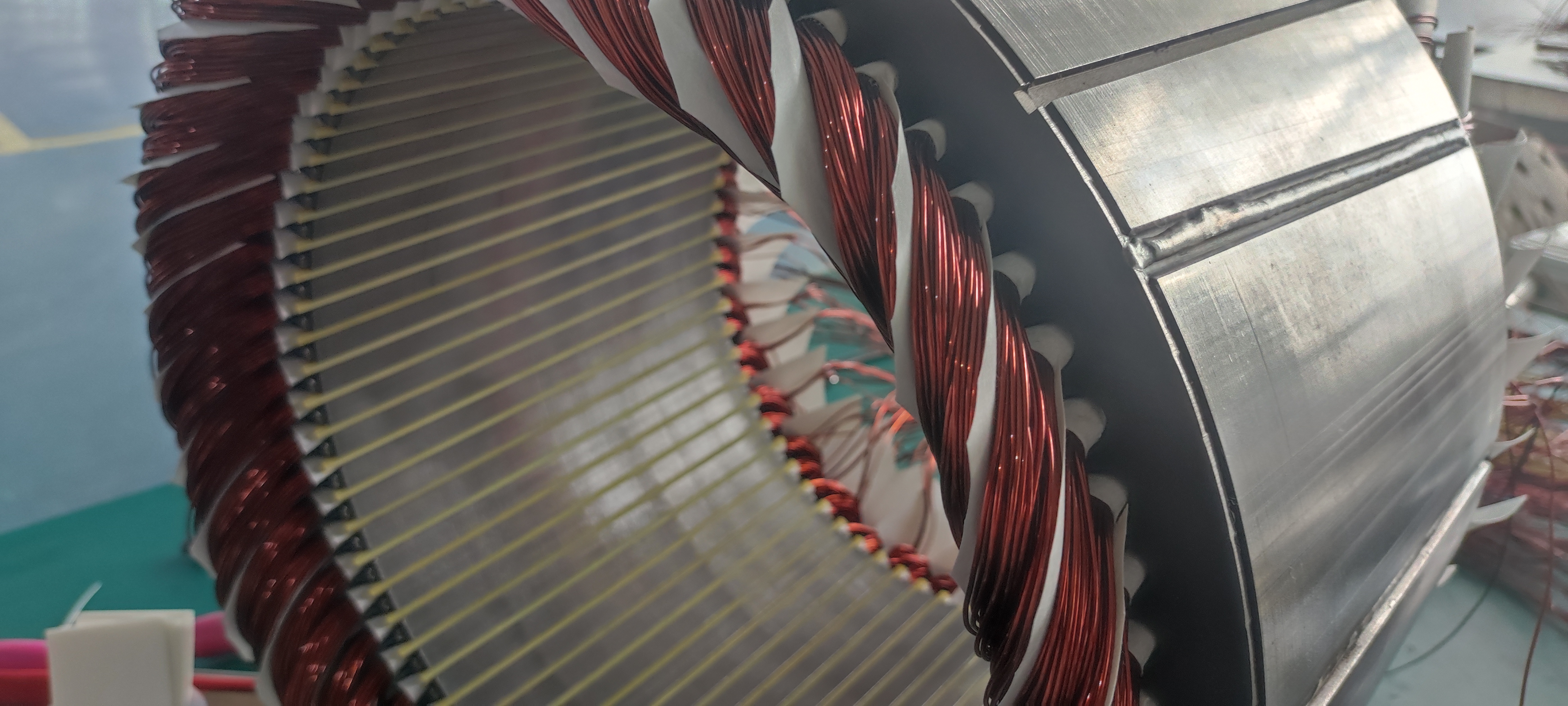
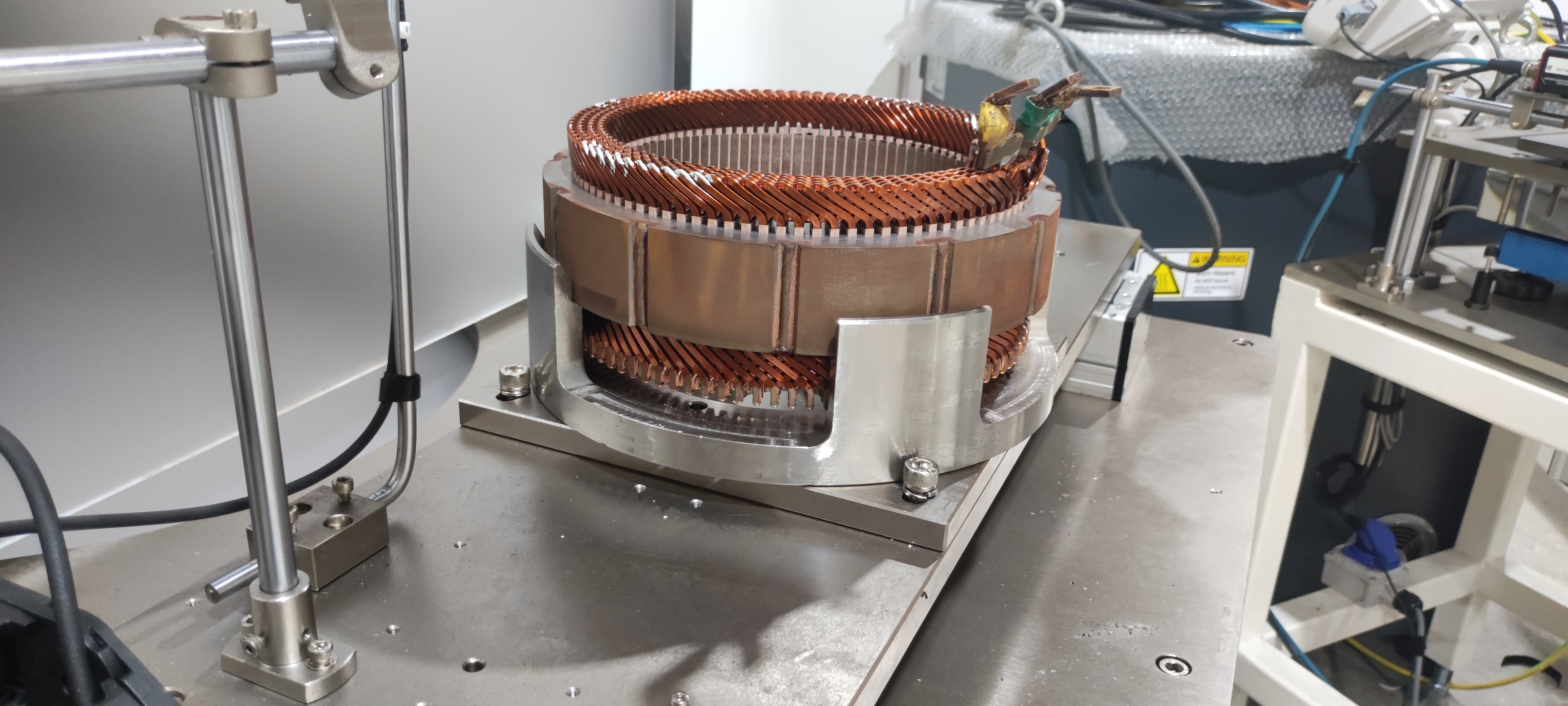
A flat-wire motor is a type of motor where the coils are wound in a planar configuration. It consists of a stator, rotor, and coils. The working principle of a flat-wire motor is also based on electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic force laws. When energized, the current in the stator generates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the coils in the rotor, producing torque. The torque applied to the rotor causes it to rotate, enabling the motor to operate.
The noise generation mechanisms in flat-wire motors similarly include torque ripple and radial force waves. Torque ripple arises from instability in torque production, which may be caused by magnetic field inhomogeneity, coil current instability, or rotor asymmetry. Torque ripple leads to motor vibration and noise.
Radial force waves are generated due to magnetic field inhomogeneity in the motor. During operation, uneven magnetic field distribution between the stator and rotor causes radial forces on the rotor, resulting in vibration and noise.
To reduce noise in flat-wire motors, it is necessary to address torque ripple and radial force waves. This can be achieved by improving motor design and manufacturing processes to enhance torque stability and magnetic field uniformity. Additionally, appropriate selection of coil materials and reducing operating temperature can help lower noise levels.
Compared to PMSMs, flat-wire motors offer the following advantages in terms of NVH (Noise, Vibration, and Harshness):
-
Lower Noise: Due to their unique structural design, flat-wire motors can reduce electromagnetic noise generation. They produce less electromagnetic noise during operation compared to PMSMs.
-
Lower Vibration: The structural design of flat-wire motors minimizes mechanical vibration. They exhibit lower levels of mechanical vibration compared to PMSMs.
-
Higher Stiffness: Flat-wire motors have higher structural stiffness, which reduces the transmission and propagation of mechanical vibrations. They demonstrate better structural stiffness during operation compared to PMSMs.
-
Better Low-Speed Performance: Flat-wire motors perform well at low speeds, reducing noise and vibration during operation.
It is important to note that these advantages are relative and do not imply that flat-wire motors are superior to PMSMs in all aspects. In practical applications, the performance differences between flat-wire motors and PMSMs should be comprehensively evaluated based on actual requirements and system needs to select the appropriate motor type.