Flat Wire Motor vs Hairpin Motor: What’s the Difference & Which Is Better for EVs?
1. Introduction: The Technological Revolution of EV Motors and Core Choices
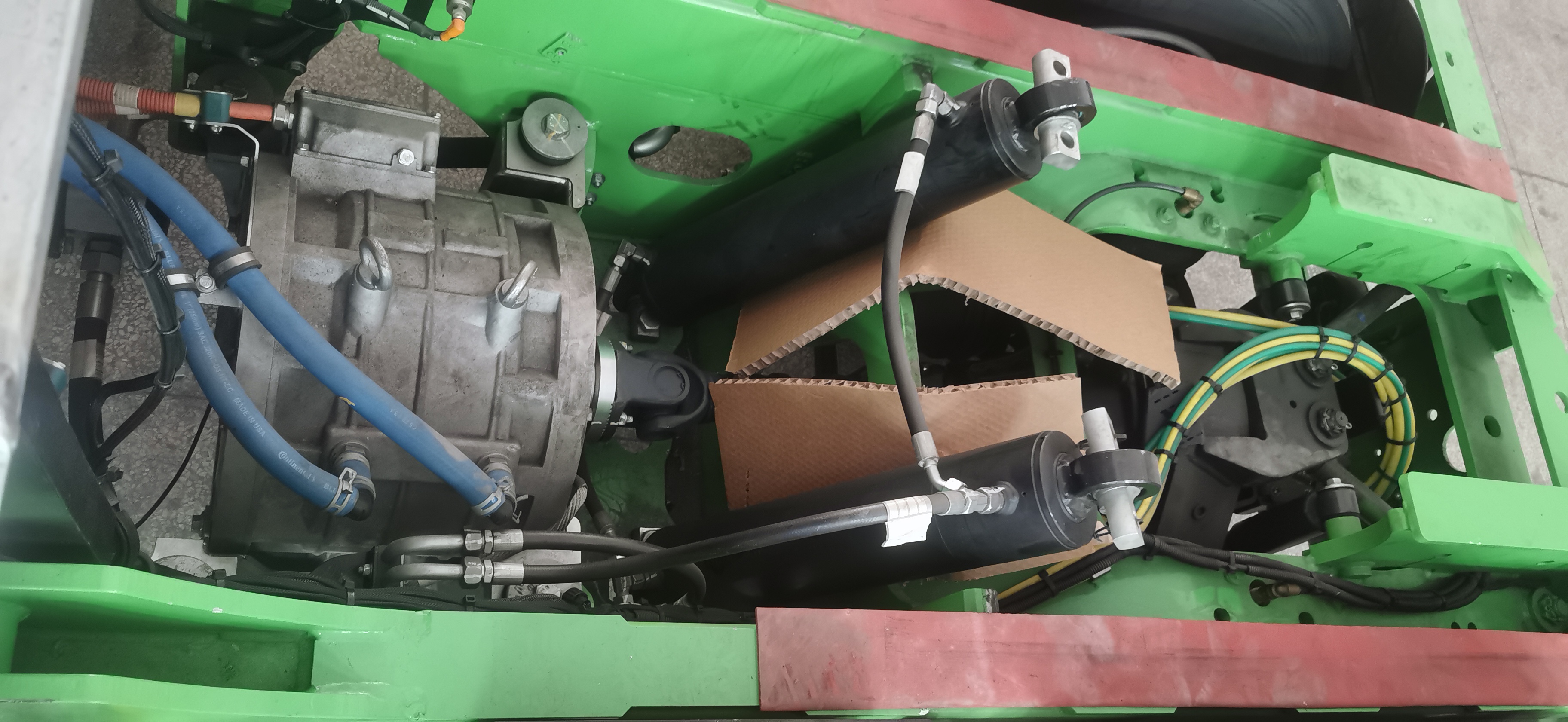
The global shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) has driven rapid innovation in motor technology. Two leading contenders—Flat Wire Motors and Hairpin Motors—are reshaping how EVs balance performance, efficiency, and cost. While both aim to optimize power output and reduce energy loss, their structural designs and manufacturing approaches create distinct trade-offs. This article breaks down their differences across key metrics to help engineers, automakers, and EV enthusiasts make informed decisions.
2. Technical Foundation: The Structures and Principles of the Two Motors
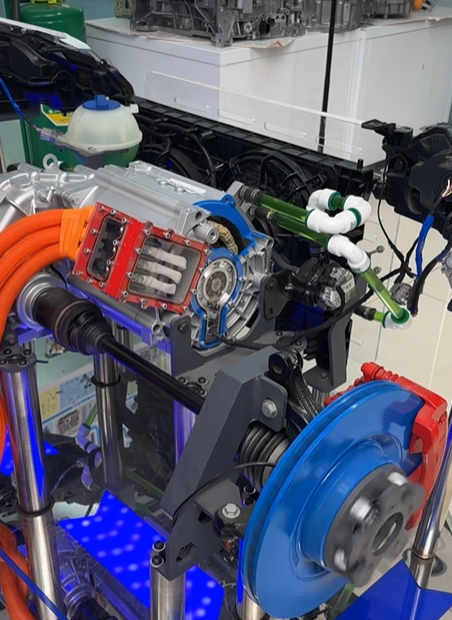
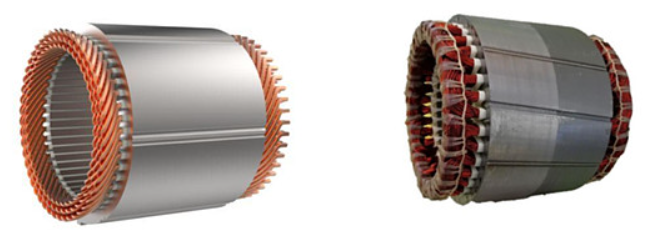
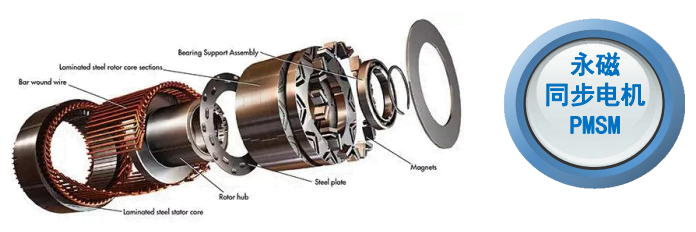
2.1 Flat Wire Motor
Structural Features:
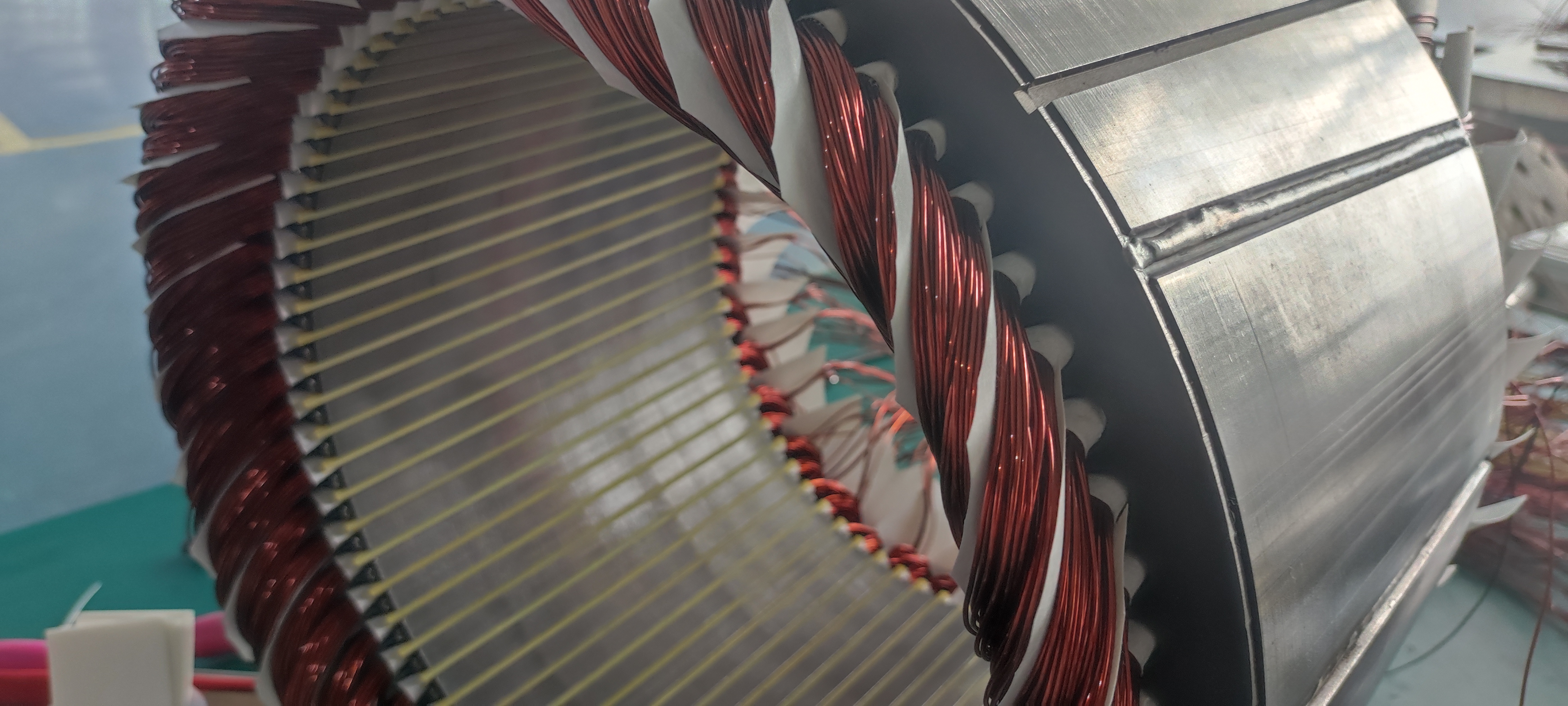
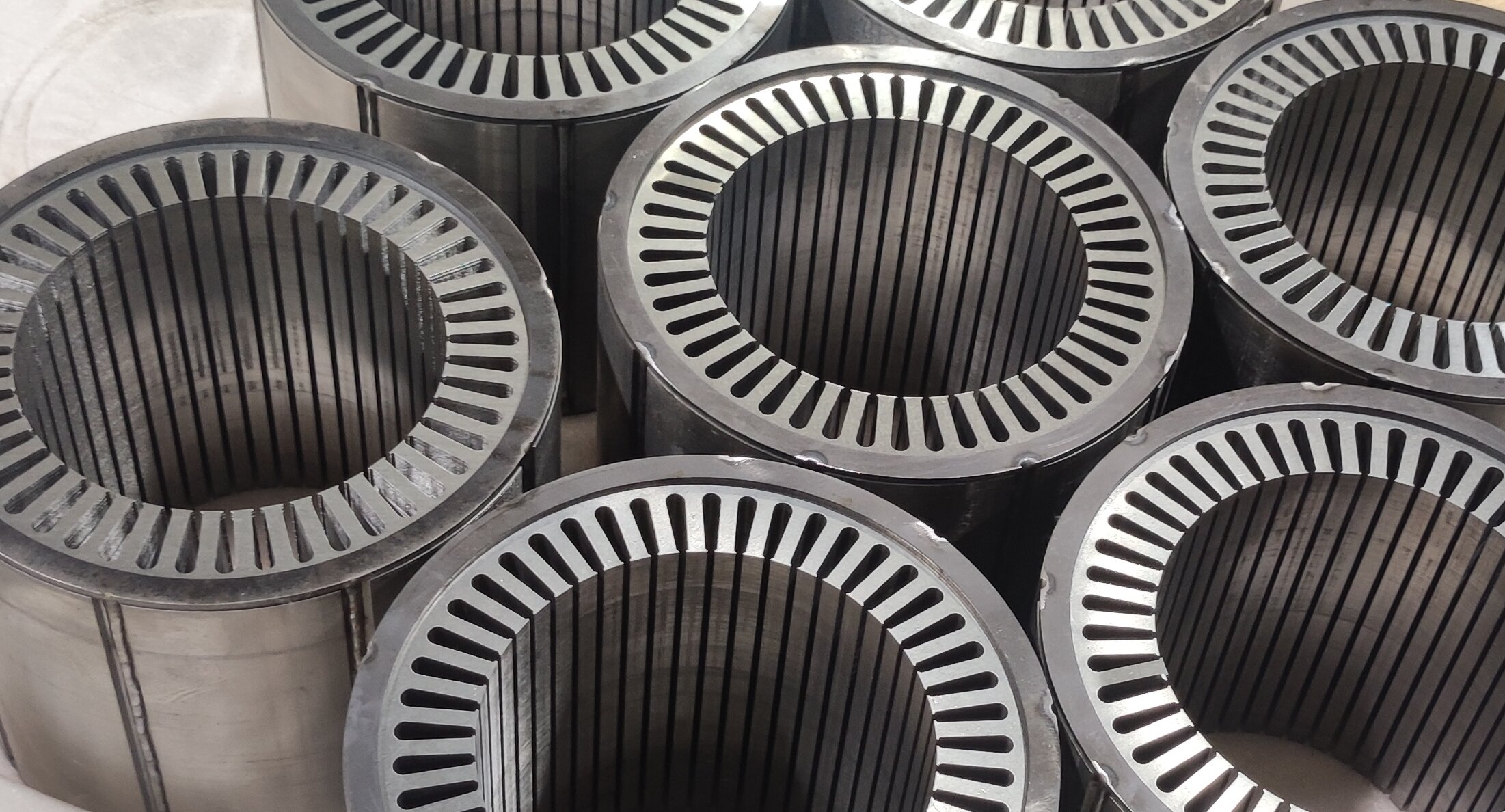
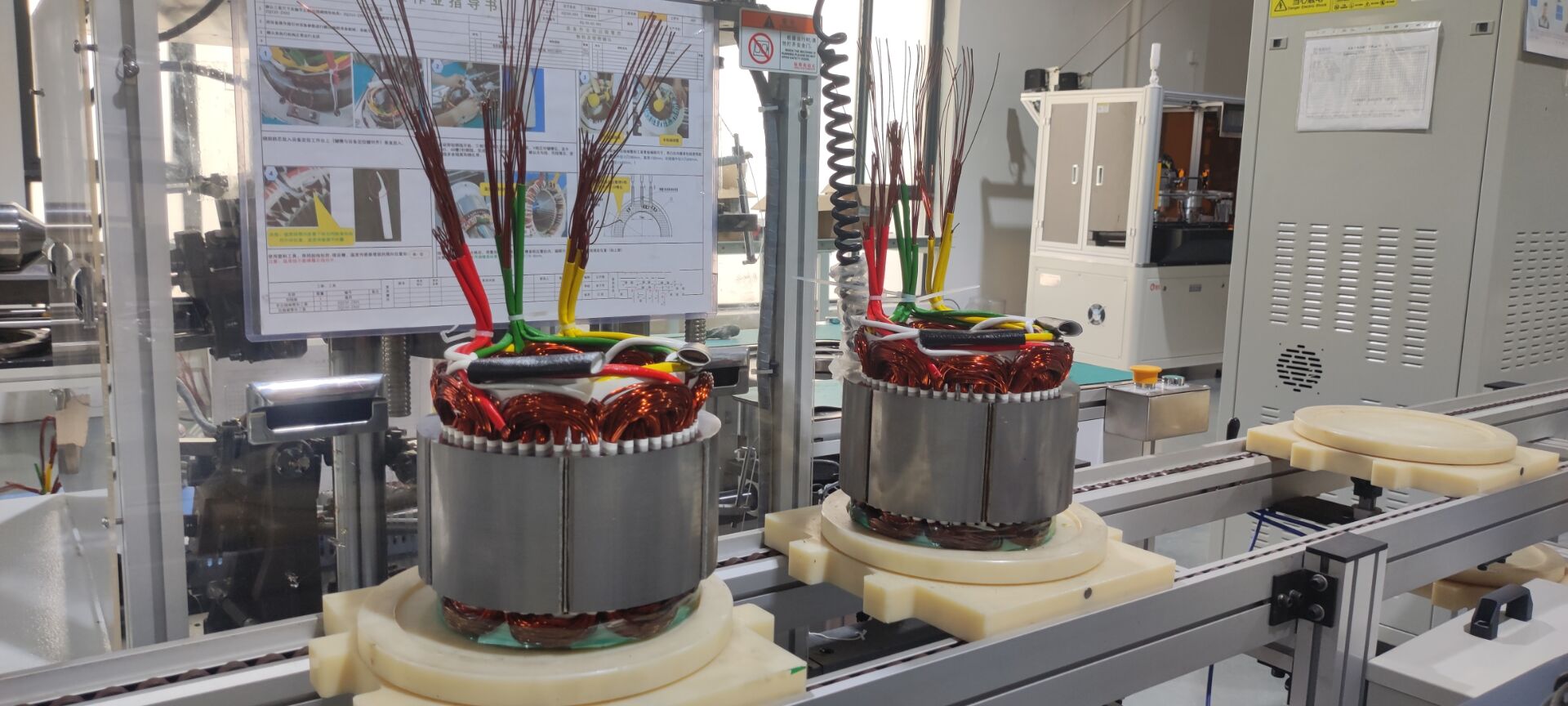
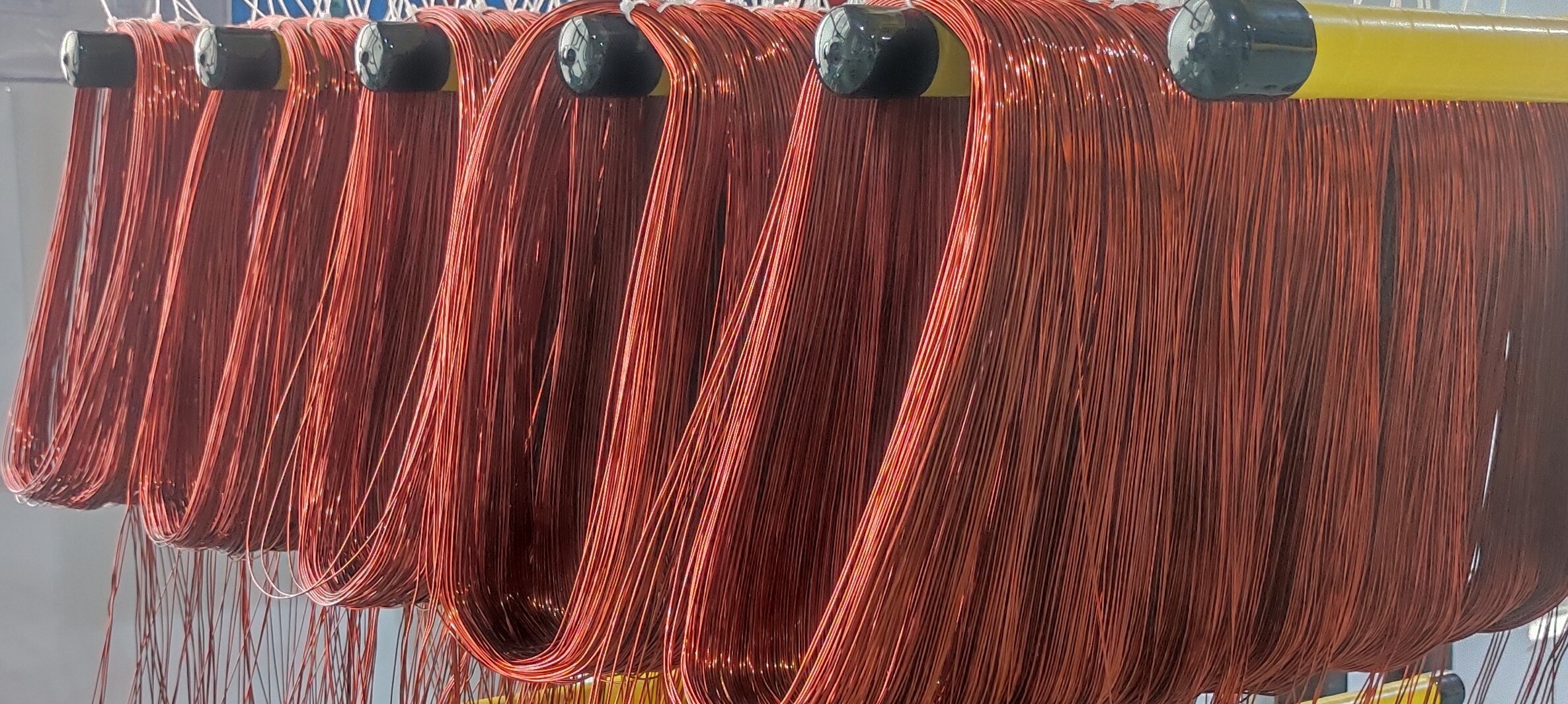
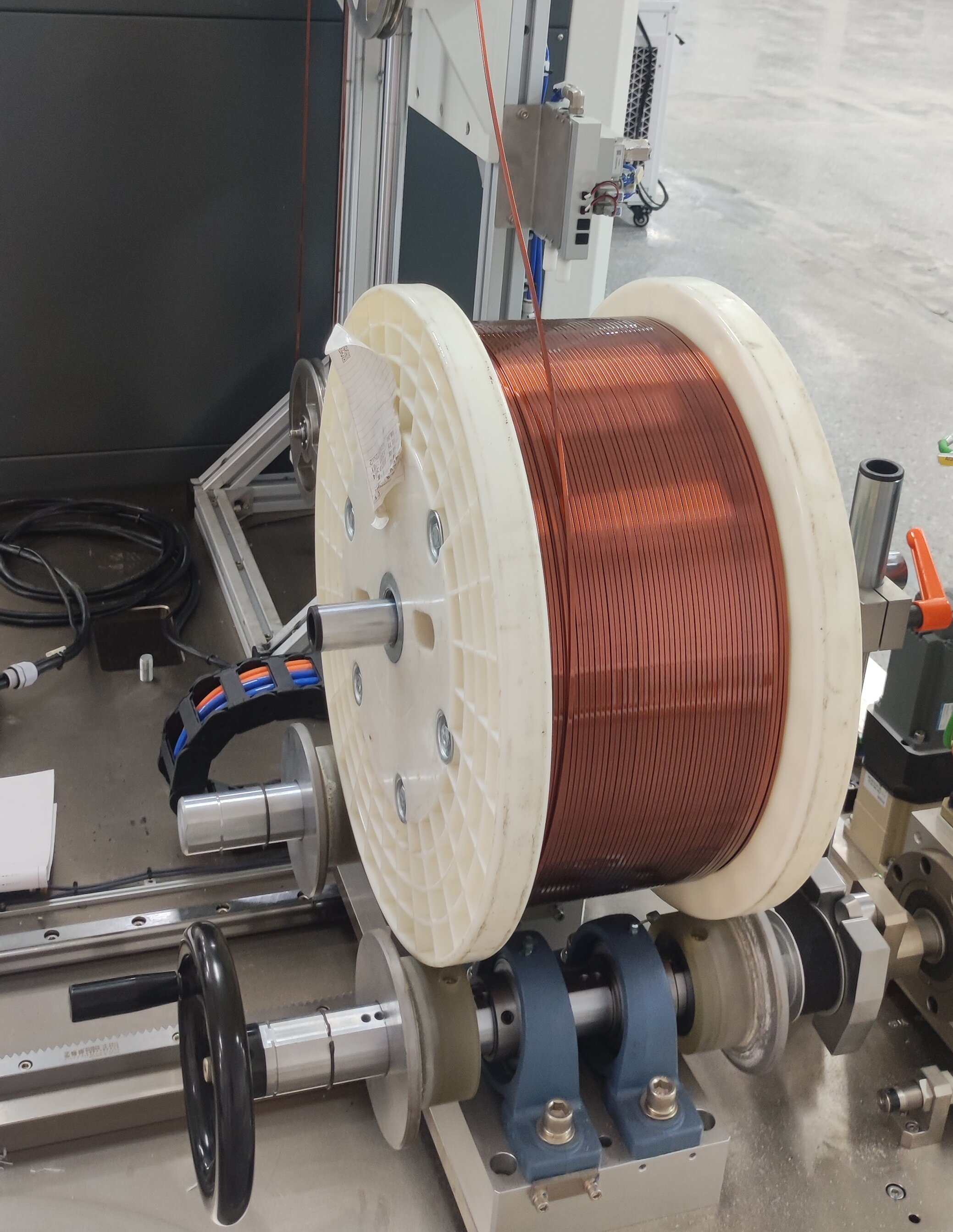
Flat Wire Motors use rectangular copper wires (instead of traditional round wires) wound tightly into stator slots. This design increases slot fill factor (up to 75% vs. 45% for round wires), enabling more copper in the same space.
Working Principle:
The flat shape reduces skin effect (current crowding at high frequencies), lowering copper losses. Paired with oil or water cooling, this motor excels in high-torque, low-speed applications like urban driving.
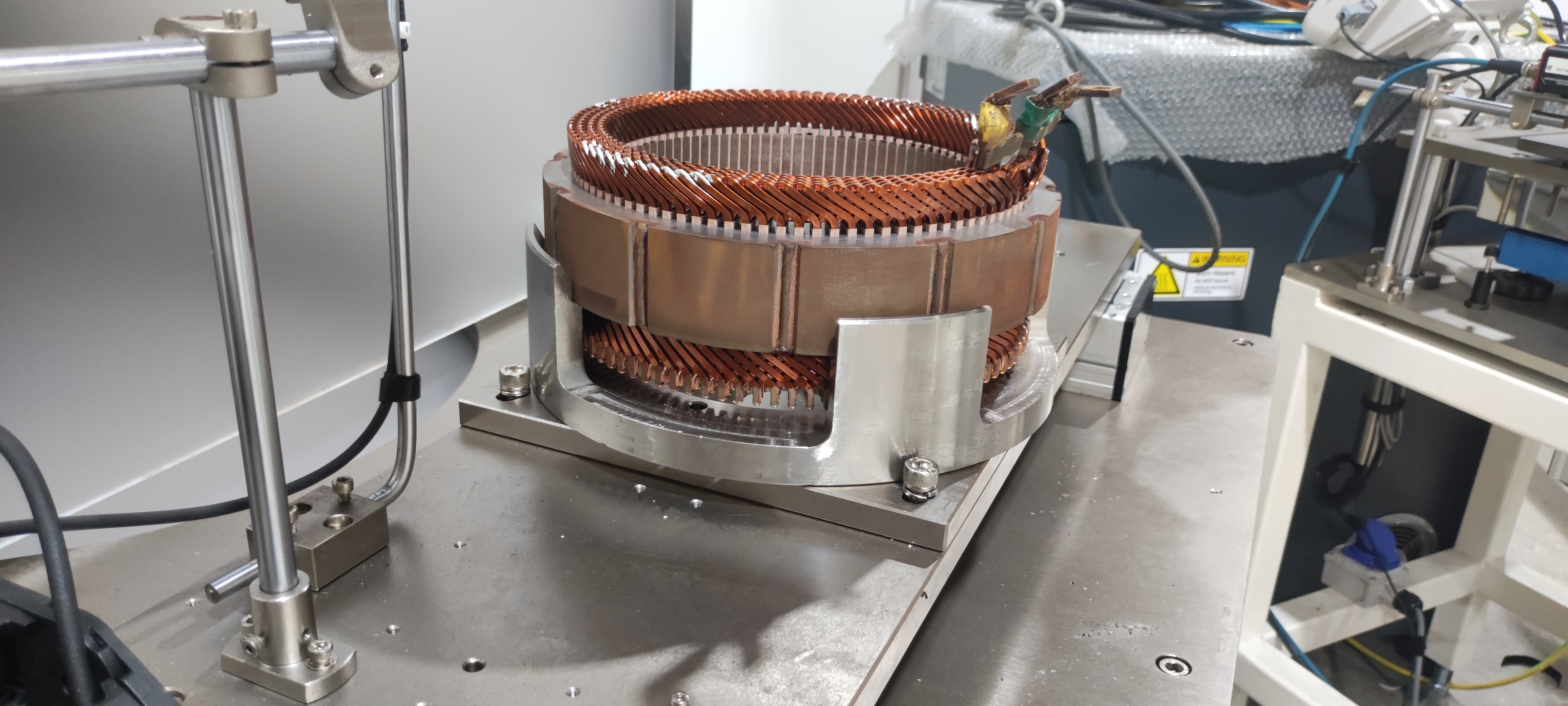
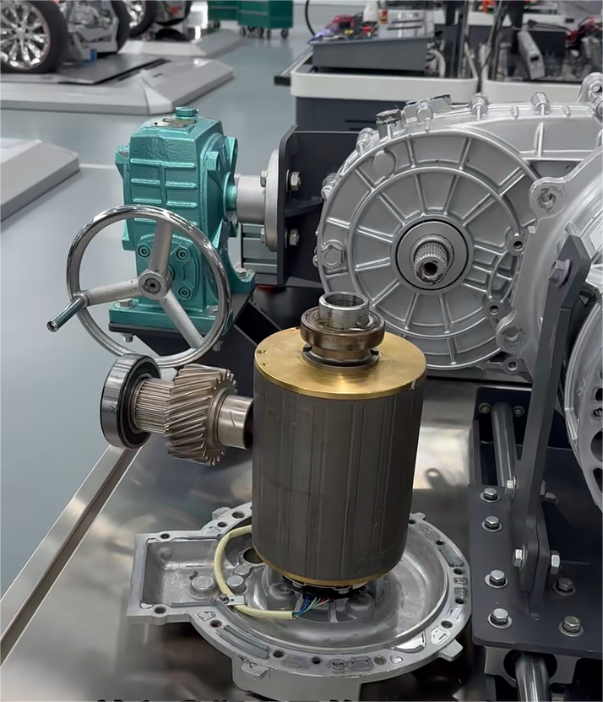
2.2 Hairpin Motor
Structural Features:
Hairpin Motors use U-shaped copper bars (resembling hairpins) inserted into stator slots and welded at the ends. This modular design simplifies automation and improves power density.
Working Principle:
The hairpin shape minimizes end-winding length, reducing resistance and improving efficiency at high speeds. Its compact structure also supports oil-cooled integration for thermal management.
3. Performance Comparison: Efficiency, Power Density, and Heat Dissipation
3.1 Efficiency Performance
Flat Wire Motor:
Peak efficiency: 97%+ at low-to-mid speeds (e.g., city driving).
Weakness: Higher iron losses at high RPMs due to thicker wire stacks.
Hairpin Motor:
Peak efficiency: 96–97% at high speeds (e.g., highway cruising).
Weakness: Slightly lower efficiency at low speeds due to welding joint losses.
3.2 Power Density
Flat Wire Motor:
Higher torque density (Nm/kg) due to compact winding, ideal for heavy-duty EVs (e.g., SUVs, trucks).
Hairpin Motor:
Higher power-to-weight ratio, suited for lightweight EVs (e.g., compact cars, sports cars).
3.3 Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
Flat Wire Motor:
Larger surface area for heat dissipation, but relies on external cooling systems.
Hairpin Motor:
Oil-cooled stators directly transfer heat from hairpin ends, enabling higher continuous power output.
4. Cost and Manufacturing: Challenges of Large-Scale Production
4.1 Material Costs
Flat Wire Motor:
Rectangular copper wire is 20–30% more expensive than round wire, but it offsets these costs through higher efficiency.
Hairpin Motor:
Standardized hairpin bars reduce material waste, but welding processes add 5–10% to production costs.
4.2 Production Process
Flat Wire Motor:
Manual winding is complex; automation requires high-precision machinery (e.g., laser welding).
Hairpin Motor:
Mass-producible via robotic insertion and laser welding, lowering labor costs.
4.3 Quality Rate and Maintenance
Flat Wire Motor:
Lower fault rates in controlled environments, but harder to repair due to tight windings.
Hairpin Motor:
Modular design simplifies field repairs, but it requires strict quality control to prevent welding defects.
5. Application Scenarios: Compatibility of Different EV Models
5.1 Passenger Vehicles (BEV/PHEV)
Flat Wire Motor:
Best for luxury EVs prioritizing quiet operation and instant torque (e.g., Lucid Air).
Hairpin Motor:
Dominates mainstream EVs like the Tesla Model 3 for its cost-efficiency and scalability.
5.2 Commercial Vehicles (Logistics Vehicles/Buses)
Flat Wire Motor:
Handles frequent stop-and-go driving in delivery vans with durable thermal performance.
Hairpin Motor:
Optimized for long-haul buses requiring sustained high-speed efficiency.
5.3 Performance Cars and Supercars
Flat Wire Motor:
Delivers explosive acceleration for hypercars like the Rimac Nevera.
Hairpin Motor:
Enables multi-motor layouts (e.g., Porsche Taycan’s rear-axle hairpin motors) for agile handling.
6. Industry Trends: Technological Iteration and Future Directions
6.1 Material Innovation
Flat Wire Motors: Adopting ultra-thin enamel coatings to reduce winding thickness.
Hairpin Motors: Exploring aluminum hairpins to cut costs (though at the expense of conductivity).
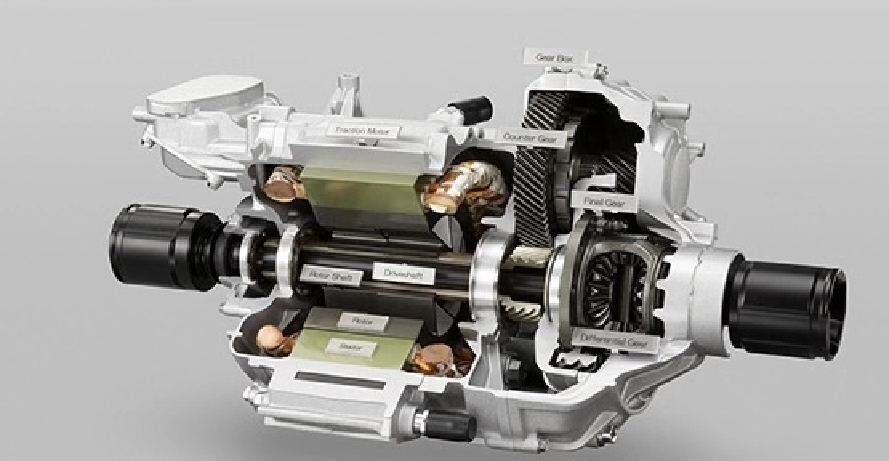
6.2 Integrated Design
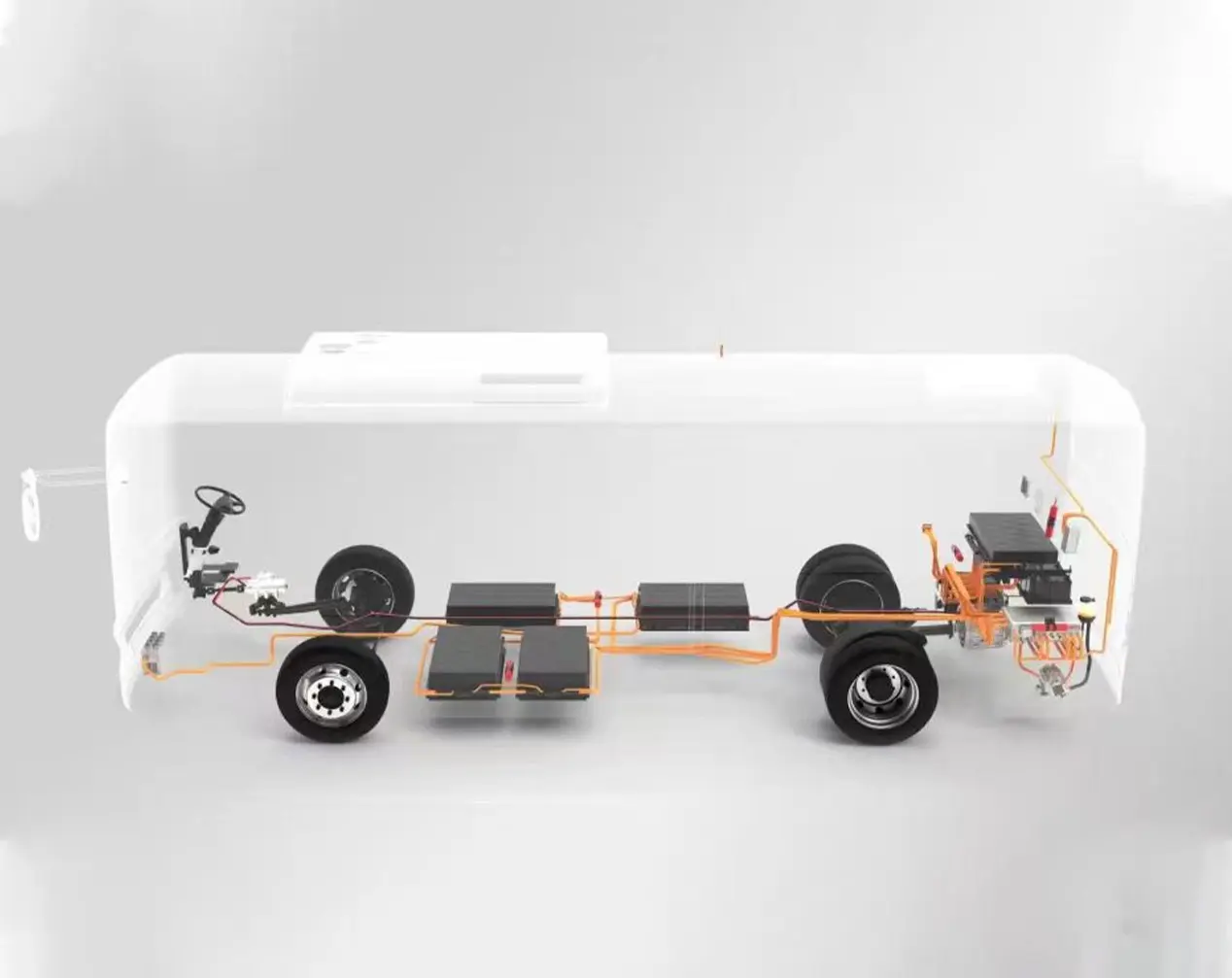
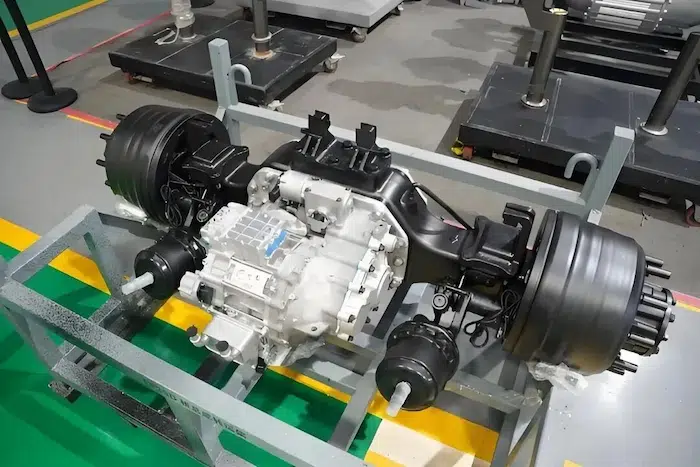
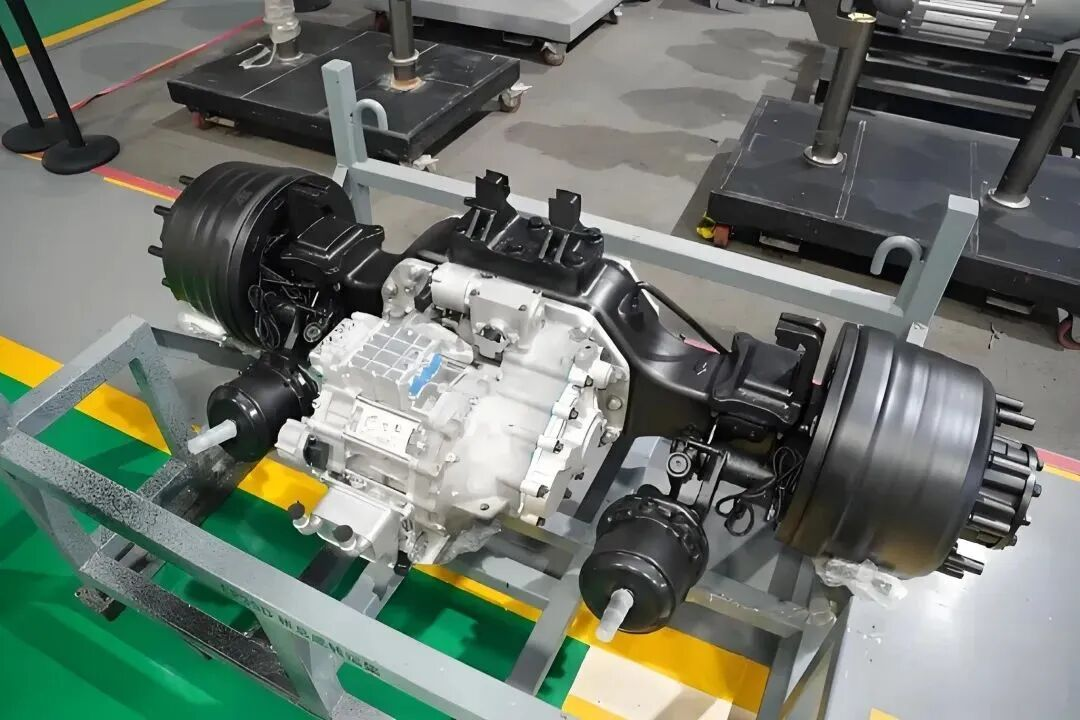
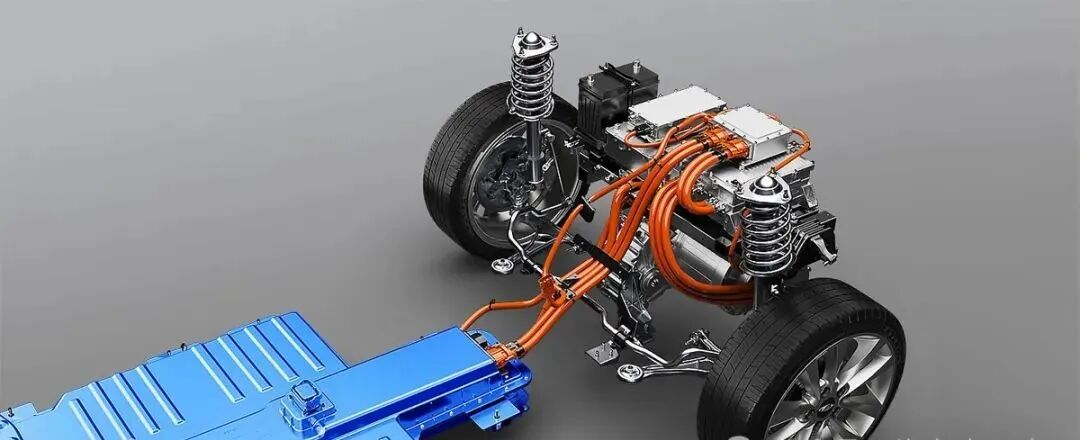
Both technologies are merging with inverters and gearboxes into compact “e-axles” (e.g., BYD e-Platform 3.0).
6.3 Intelligent Control
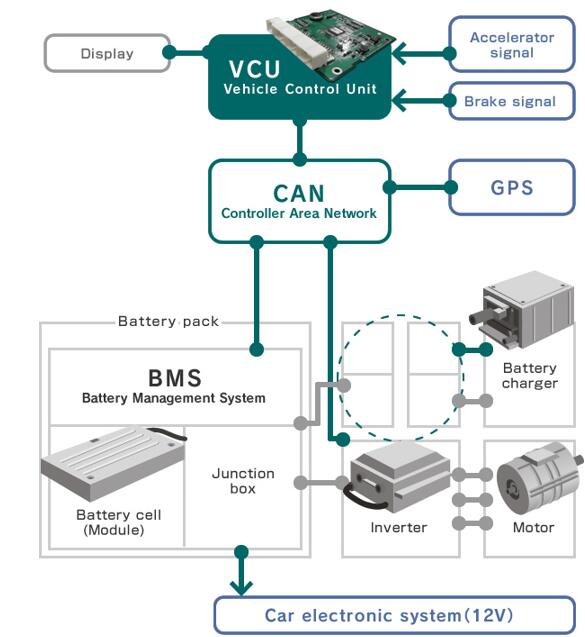
AI-driven thermal prediction algorithms optimize efficiency in real-time for both motor types.
7. Conclusion: How to Choose? Key Decision Factors
Pick Flat Wire Motors if:
Your EV needs high torque at low speeds (e.g., urban SUVs, heavy trucks).
You prioritize long-term efficiency gains over upfront costs.
Pick Hairpin Motors if:
Your EV targets high-speed cruising (e.g., sedans, crossovers).
You require scalable, low-cost production for high-volume markets.
About Pumbaa: Your Trusted PMSM Motor Supplier
Pumbaa specializes in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) for EVs, offering both Flat Wire and Hairpin motor solutions tailored to your needs. With a focus on high efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness, Pumbaa’s motors power everything from passenger cars to commercial fleets.