Ev motors and controllers: The Core of High-Power Electric Mobility Systems
Fast-emerging electric mobility is a game-changer for many different industries that require high-powered, efficient propulsion systems-from logistics trucks and city buses to sanitation trucks and electric ships. High-power electric mobility solutions are redesigning how heavy-duty transportation works. Sitting at the very core of such transformation are Ev motors and controllers-those very building blocks that convert electrical energy into movement with an assurance of high-level performance. How these systems interface, integrate, and power modern electric vehicles is key to the next step in developing the future of efficient transportation.
1. Introduction: Powering the Future of Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles
More than the shift to other sources of energy, a transition towards electric propulsion from fossil fuels forms a sea change in design, control, and performance. Heavy-duty electric vehicles demand high torque, continuous operation, and dynamic energy management. Unlike light passenger electric vehicles, these need higher power densities and reliable operations under tough conditions. A combination of highly efficient electric motors with intelligent controllers forms the backbone of these advanced mobility systems that enable sustainable and cost-efficient solutions for transportation.
2. The Role of Ev motors and controllers in Electric Vehicles
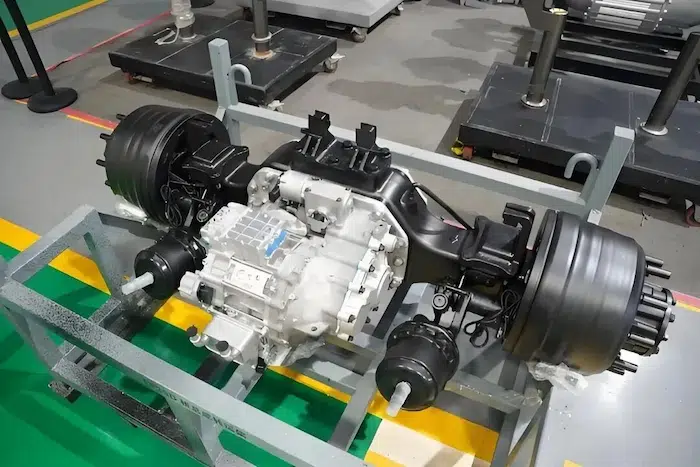
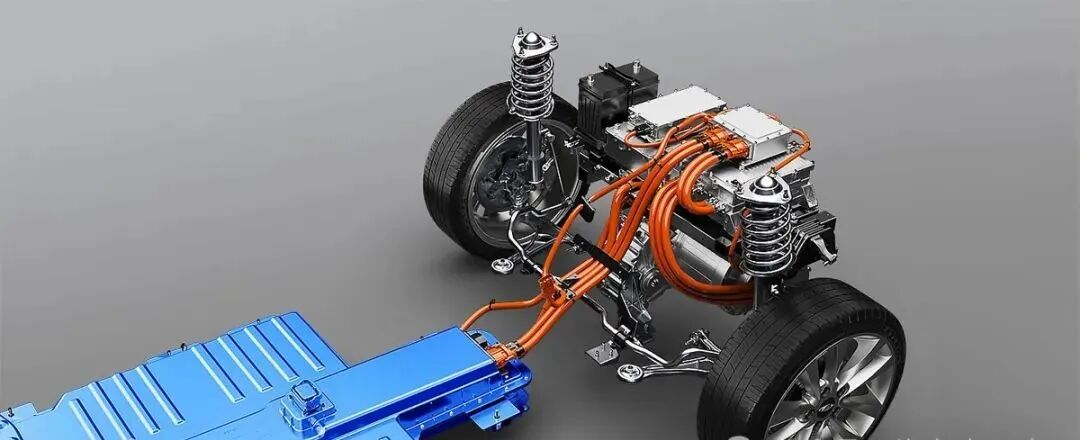
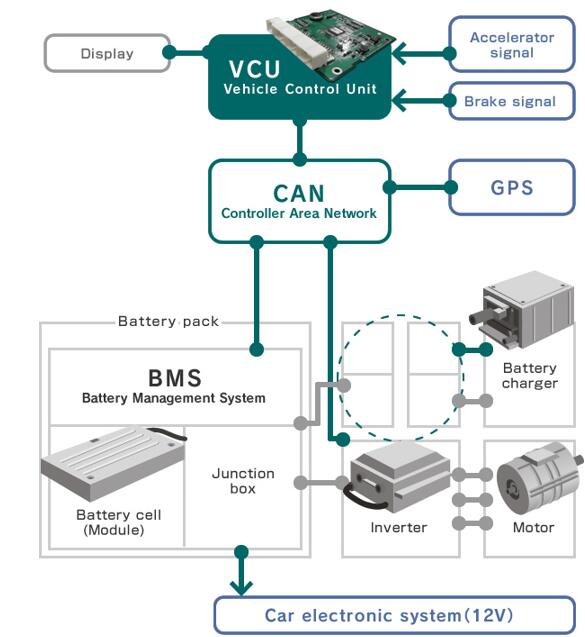
Motors in electric vehicles represent the mechanical hearts of EVs that, in essence, convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical motion. This, however, needs to be in a controlled fashion for attaining the best torque, speed, and energy efficiency. That is where the motor controllers come in. The electric motor controller acts like an intelligent intermediary between the power supply and the motor, controlling current flow, monitoring performance, and responding to real-time operating conditions based on variations in loads and heat. All these combined provide smooth acceleration, regenerative braking, and the highest possible efficiency over various driving conditions.
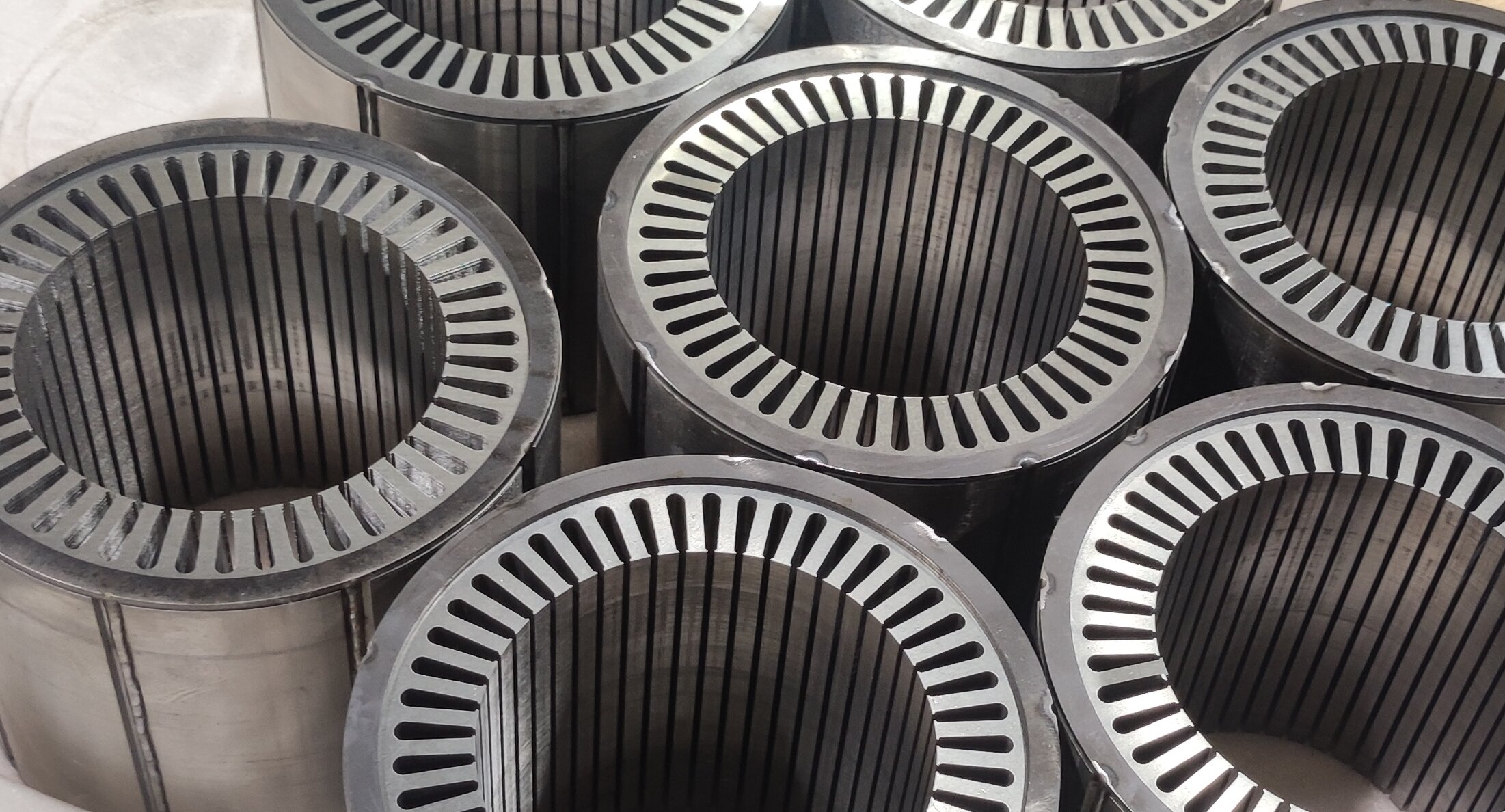
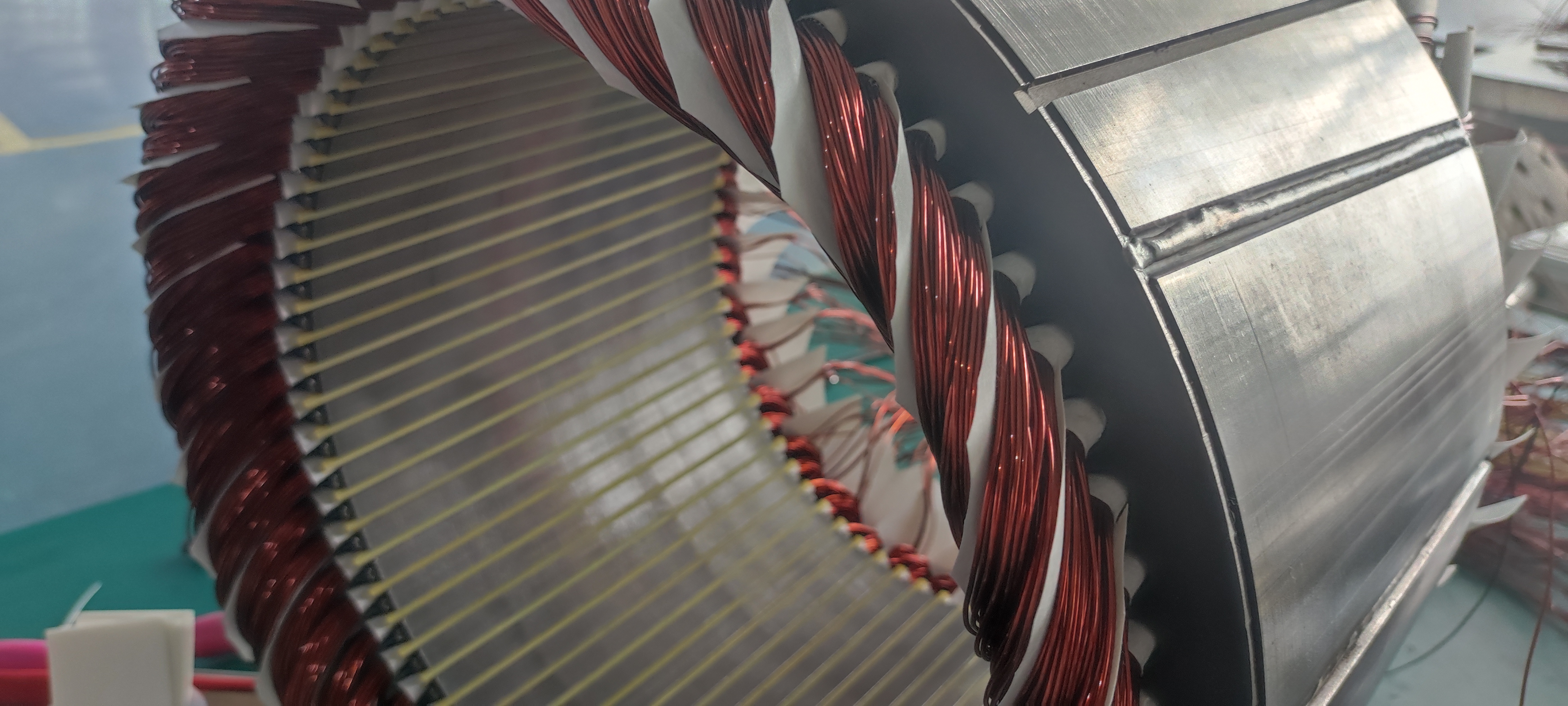
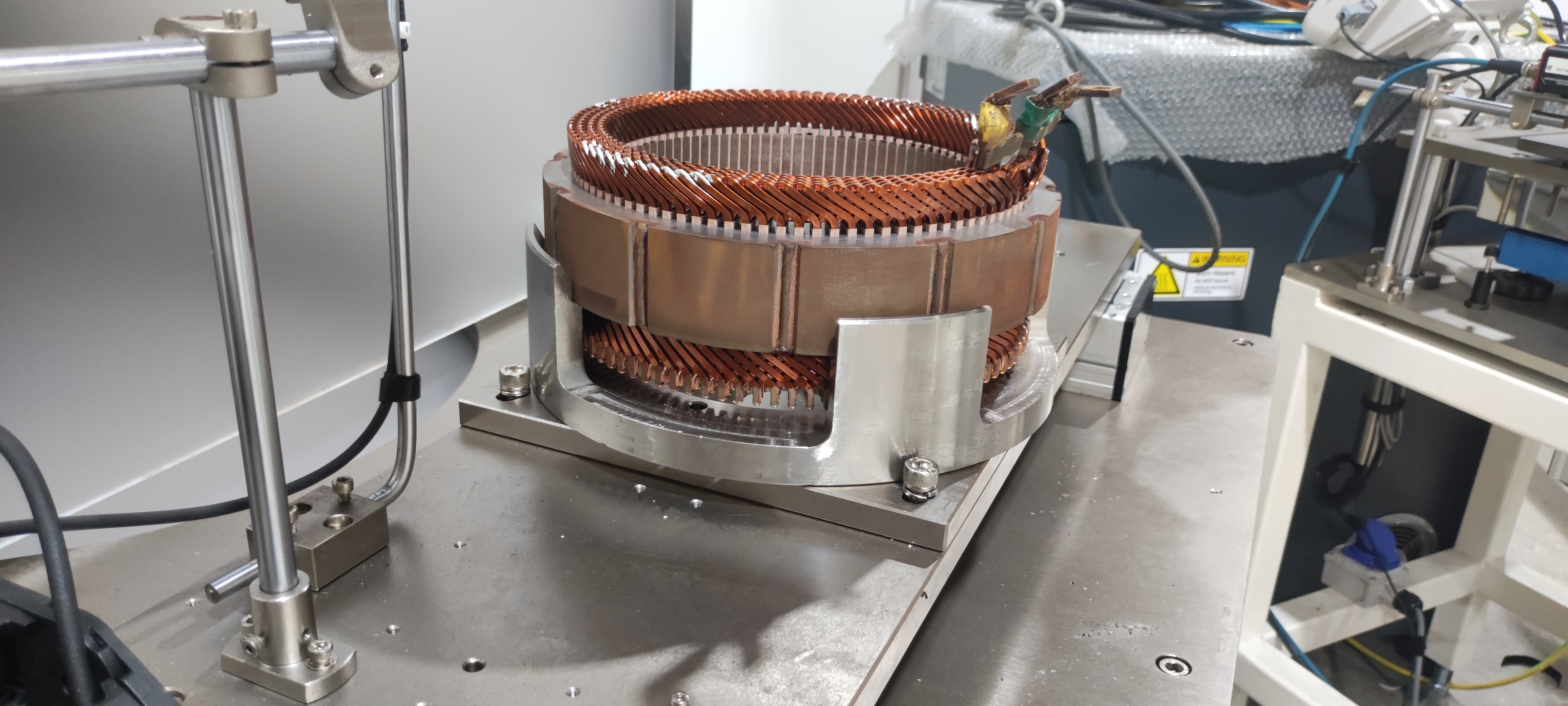
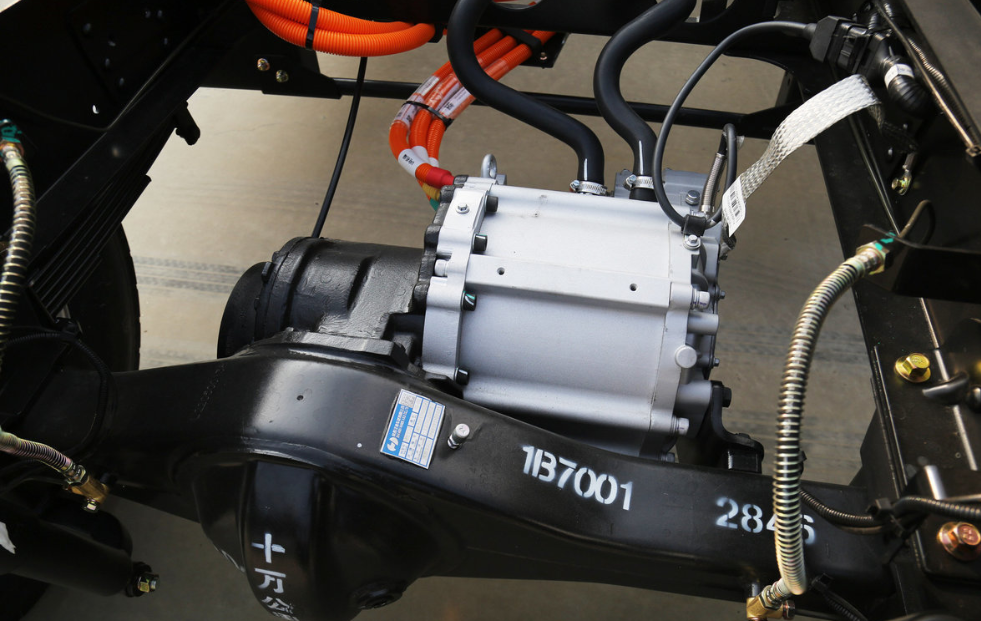
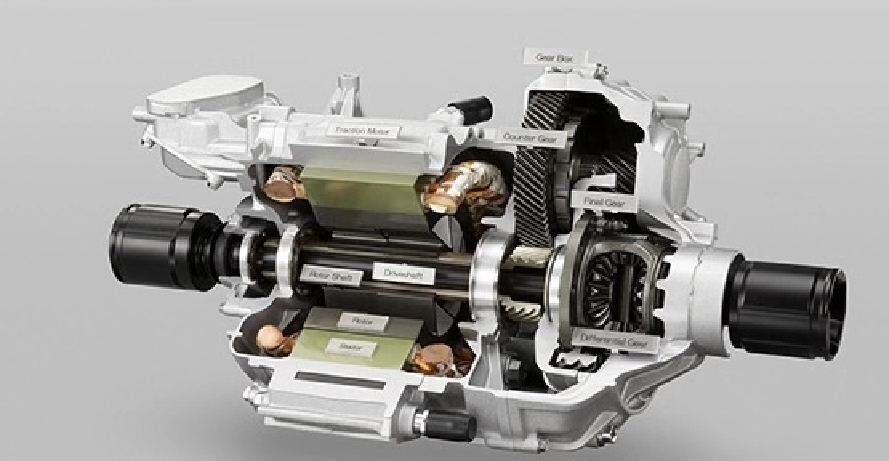
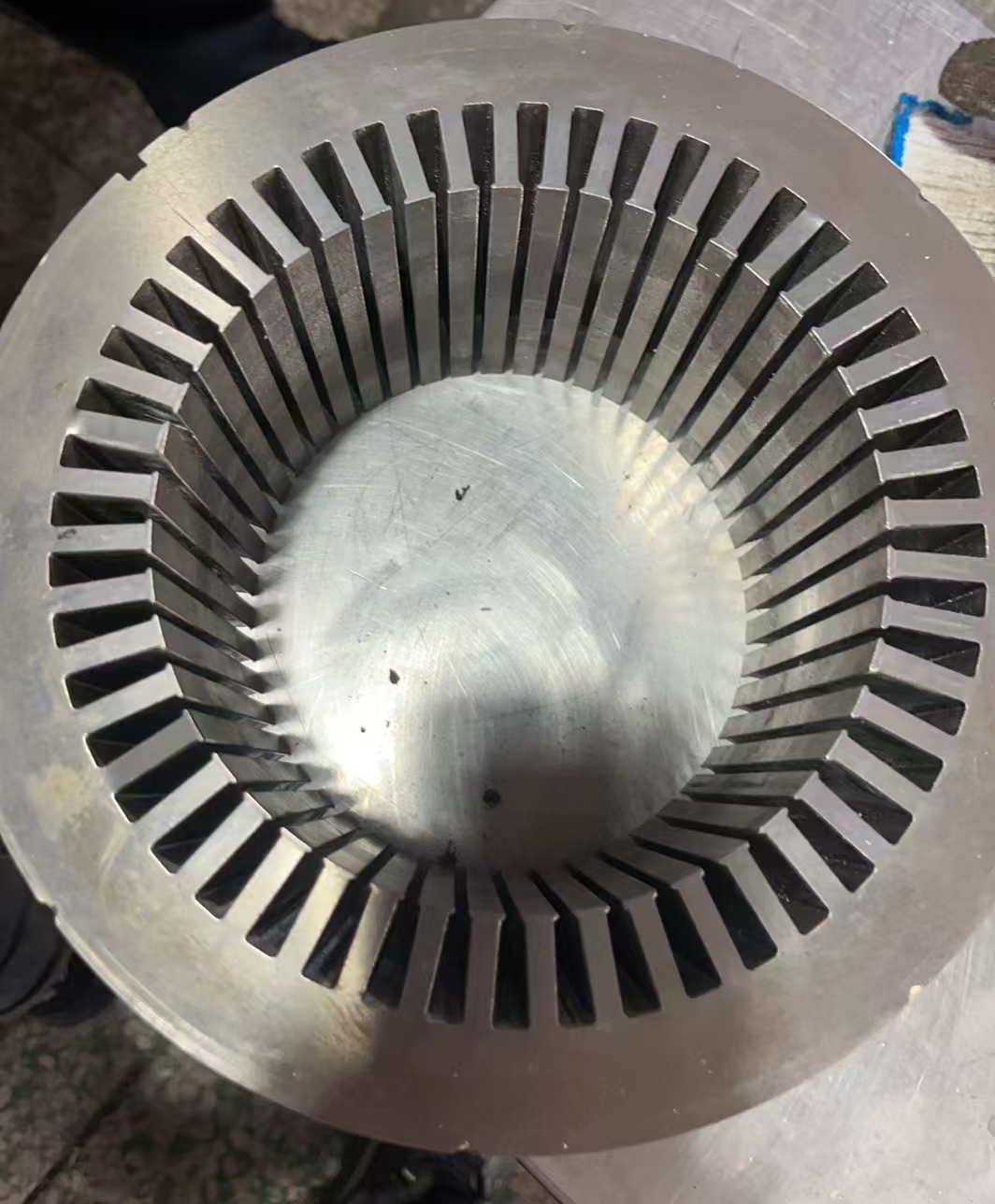
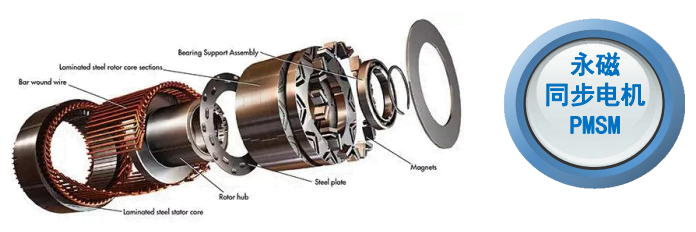
3. Understanding the Electric Motor: The Heart of Motion
The driving force of each EV is an electric motor; in heavy-duty applications, the kind of motor used-permanent magnet synchronous motors, induction motors, or switched reluctance motors-is a substantial factor. Permanent magnet synchronous motors have gained popularity due to their efficiency, compactness, and superior torque density. However, induction motors show advantages in robustness and cost. Whatever may be its type, torque delivery with performance and minimization of energy losses are directly related to vehicle range and reliability. Advanced cooling systems and optimized magnetic designs further raise the performance of these motors under demanding conditions, truly making them the heart of the motion in electric mobility.
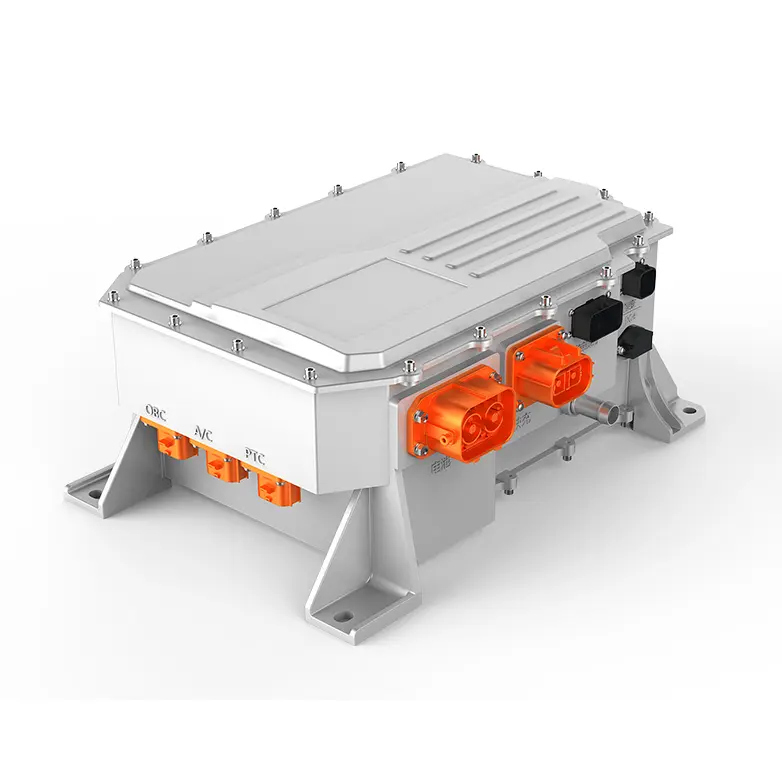
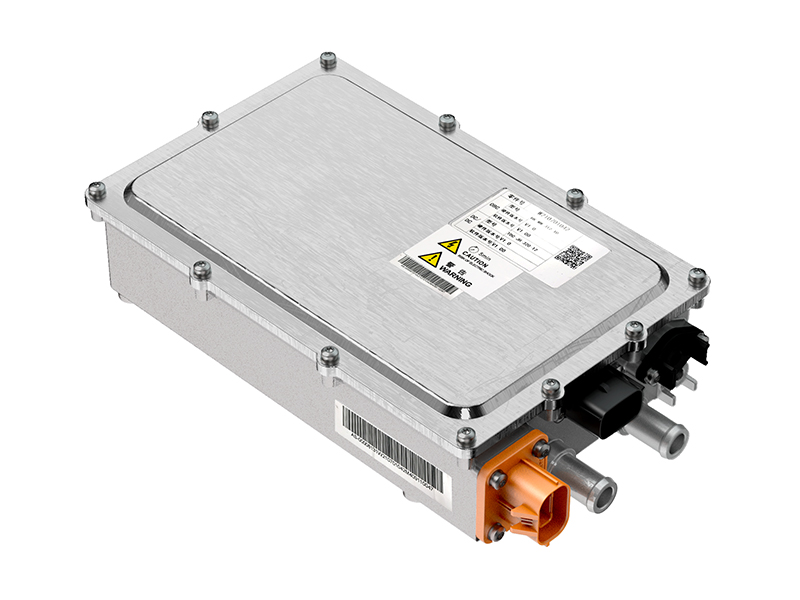
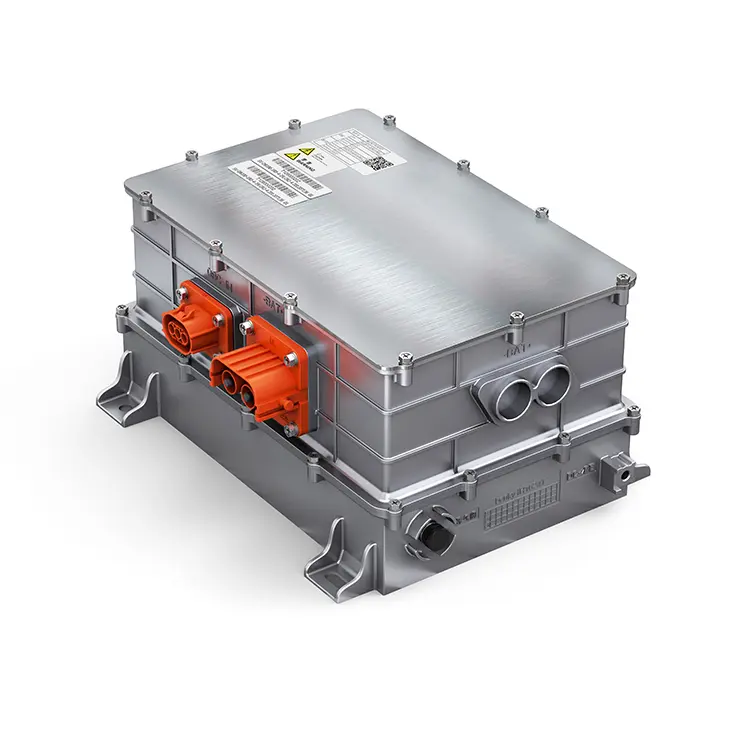
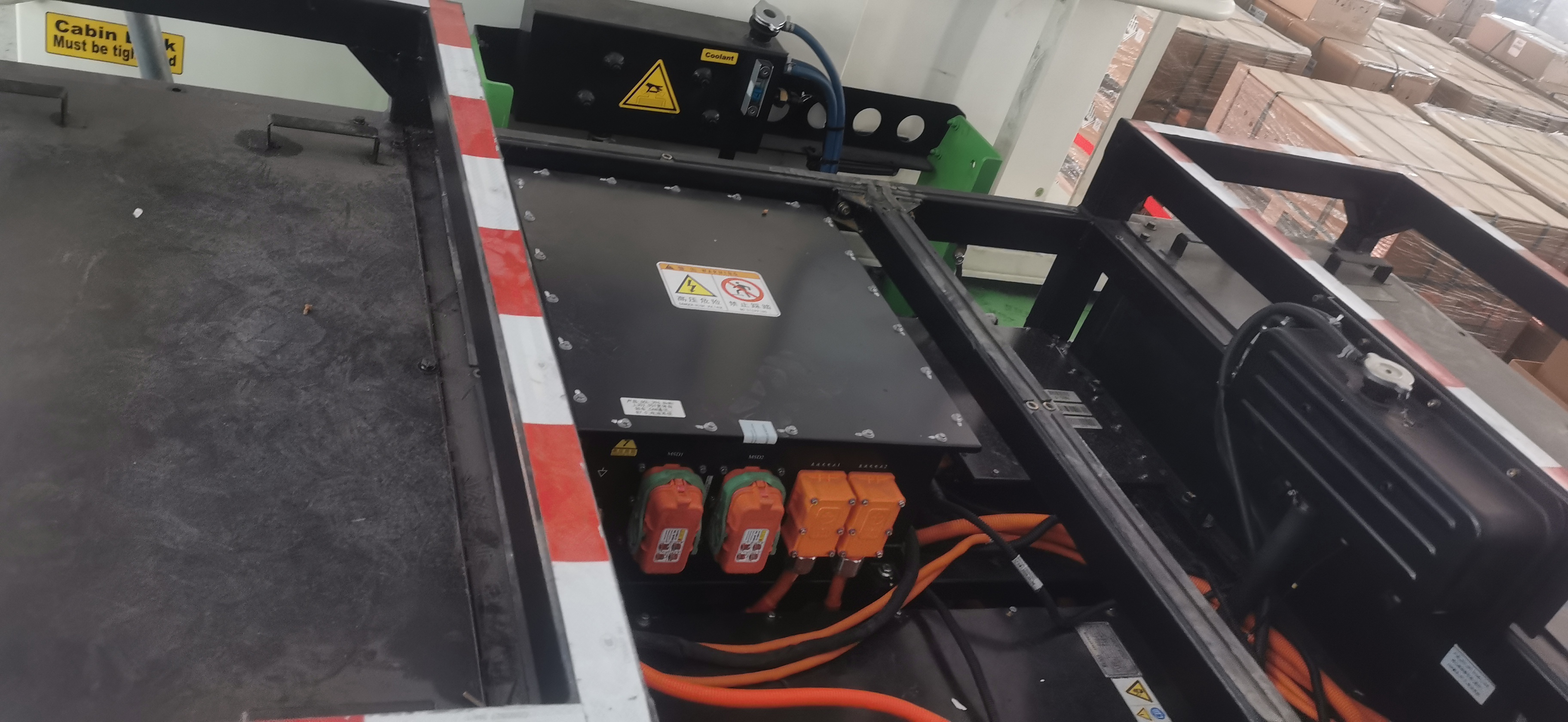
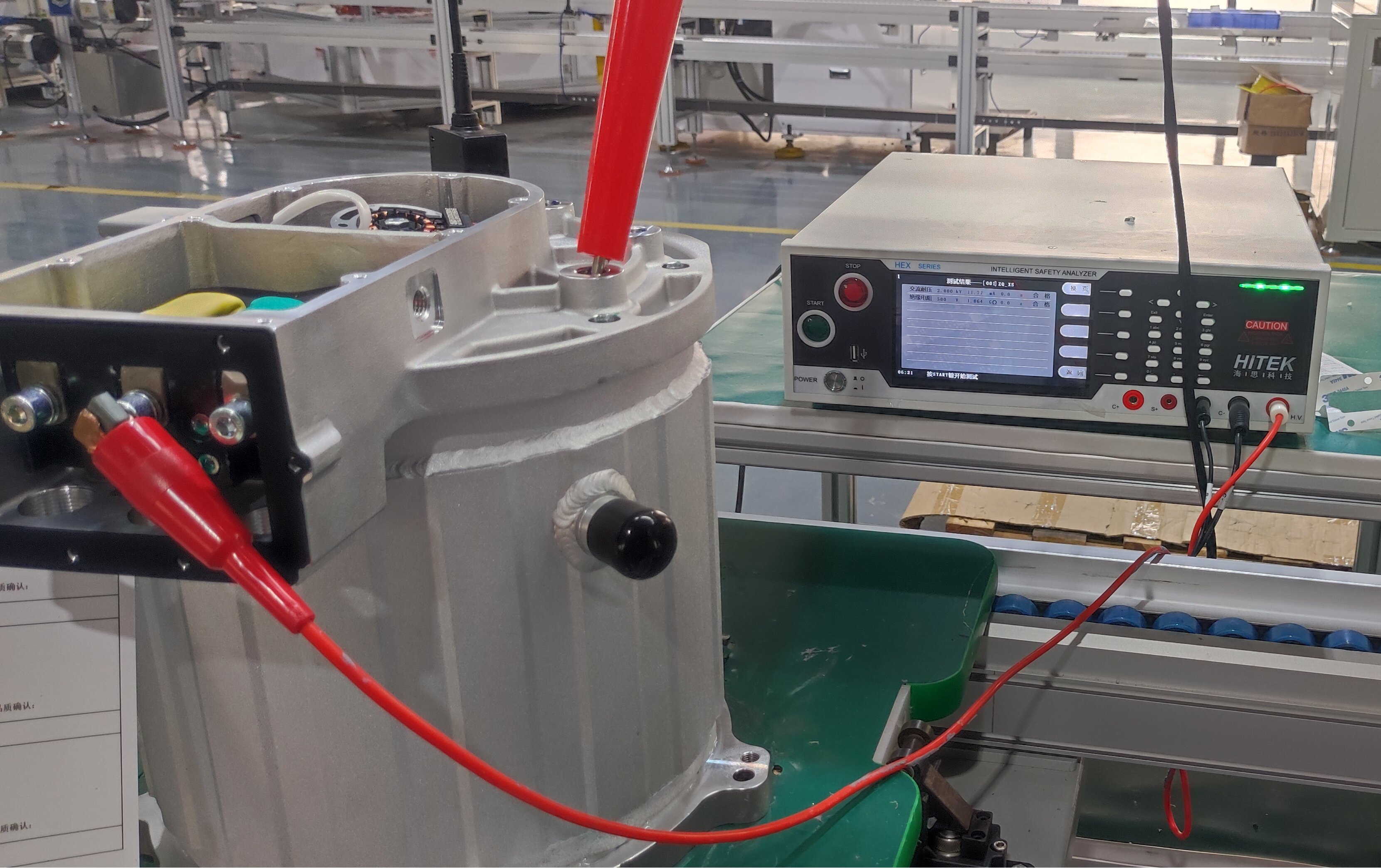
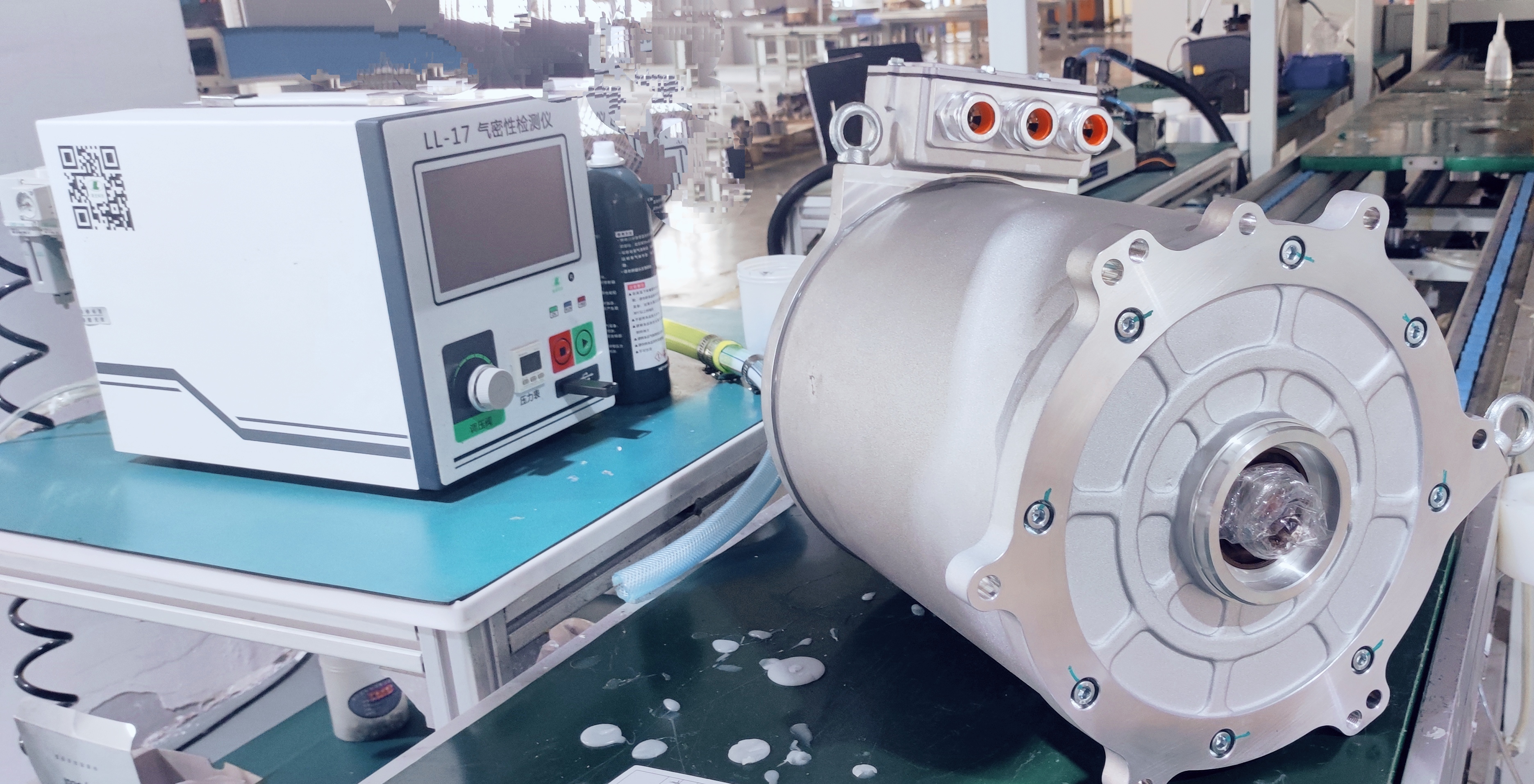
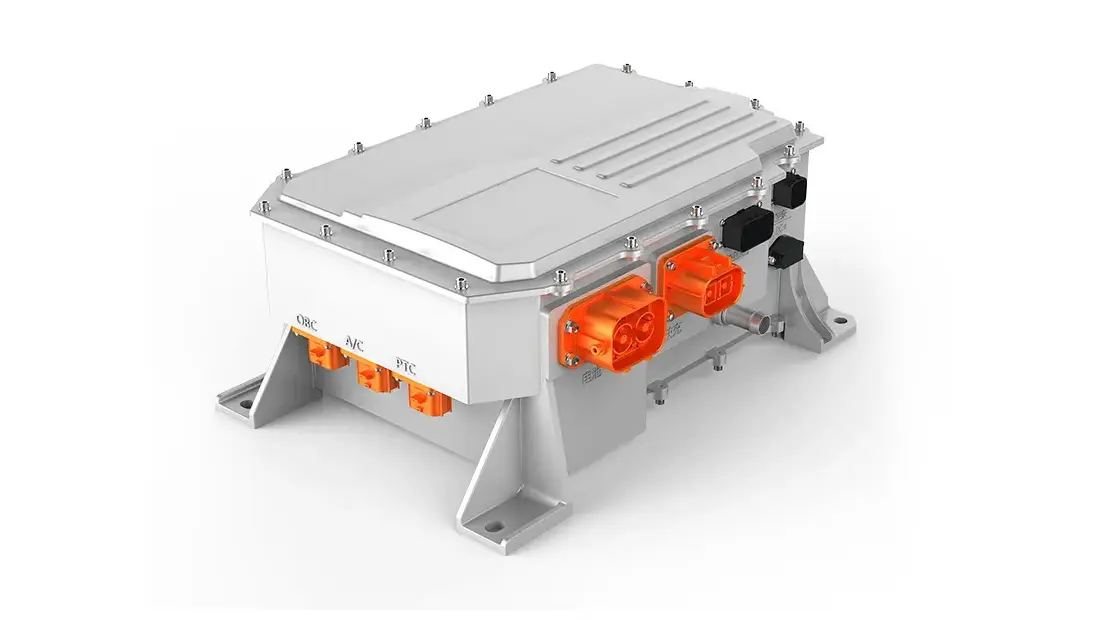
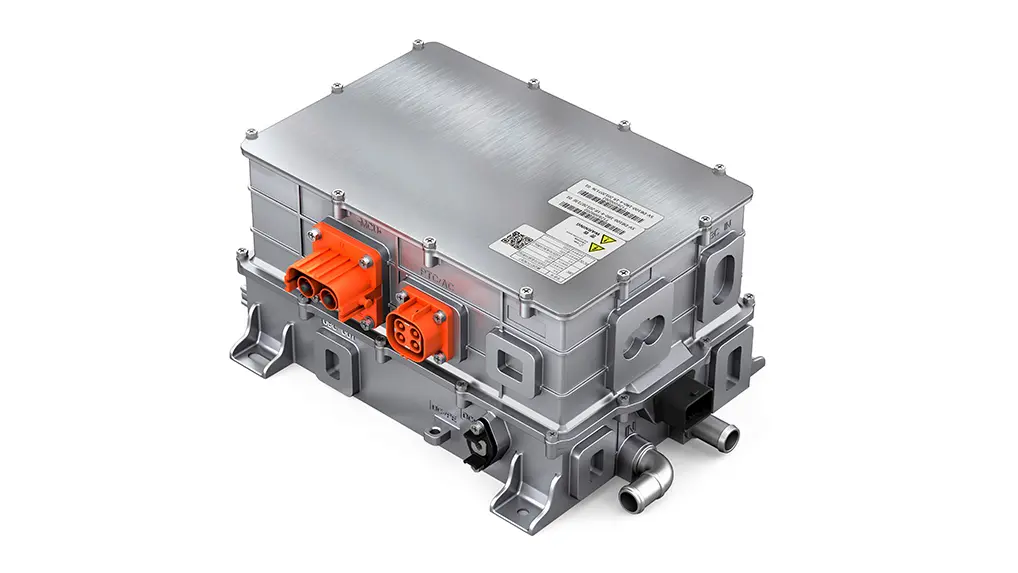
4. The Electric motor controller: the Intelligent Power Manager
The motor controller acts as the brain for the electric powertrain, and its main purpose is to convert DC from the battery into AC applied to the motor. This involves voltage, frequency, and current control in pursuit of target speed and torque. Field-oriented control and advanced algorithms have been implemented in state-of-the-art controllers, thereby enabling them to perform real-time performance management for smooth operation. They also implement safety features, diagnostics, and communication capabilities that interface with vehicle management systems. In heavy-duty applications, controllers need to handle high surges of power and maintain stability under variable loads; they need to be both reliable and durable under all conditions.
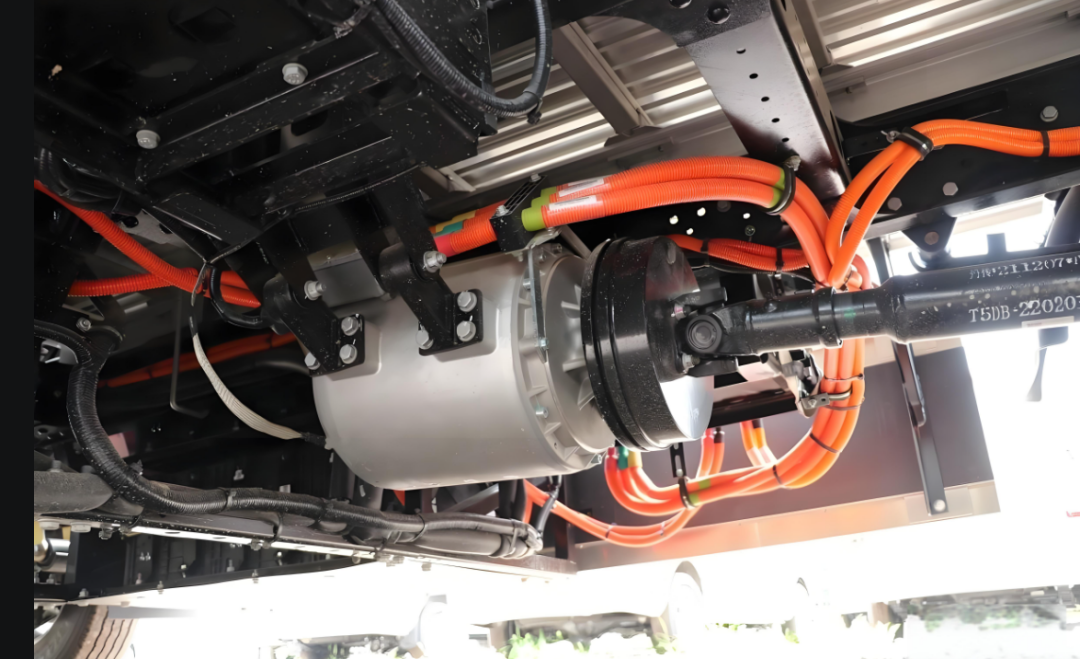
5. Power Supply System: Charging and Conversion Solutions
Efficiency of power is crucial in EVs, maintained by the efficient power supply systems onboard, which include chargers, DC-DC converters, and battery management systems for proper charging, voltage regulation, and energy distribution. High-power charging systems enable fast recharging, especially in the case of commercial vehicles operating on a tight schedule. Energy conversion technologies deliver clean, stable power to the motor and controller, thus optimizing the efficiency of the overall system and prolonging component life.
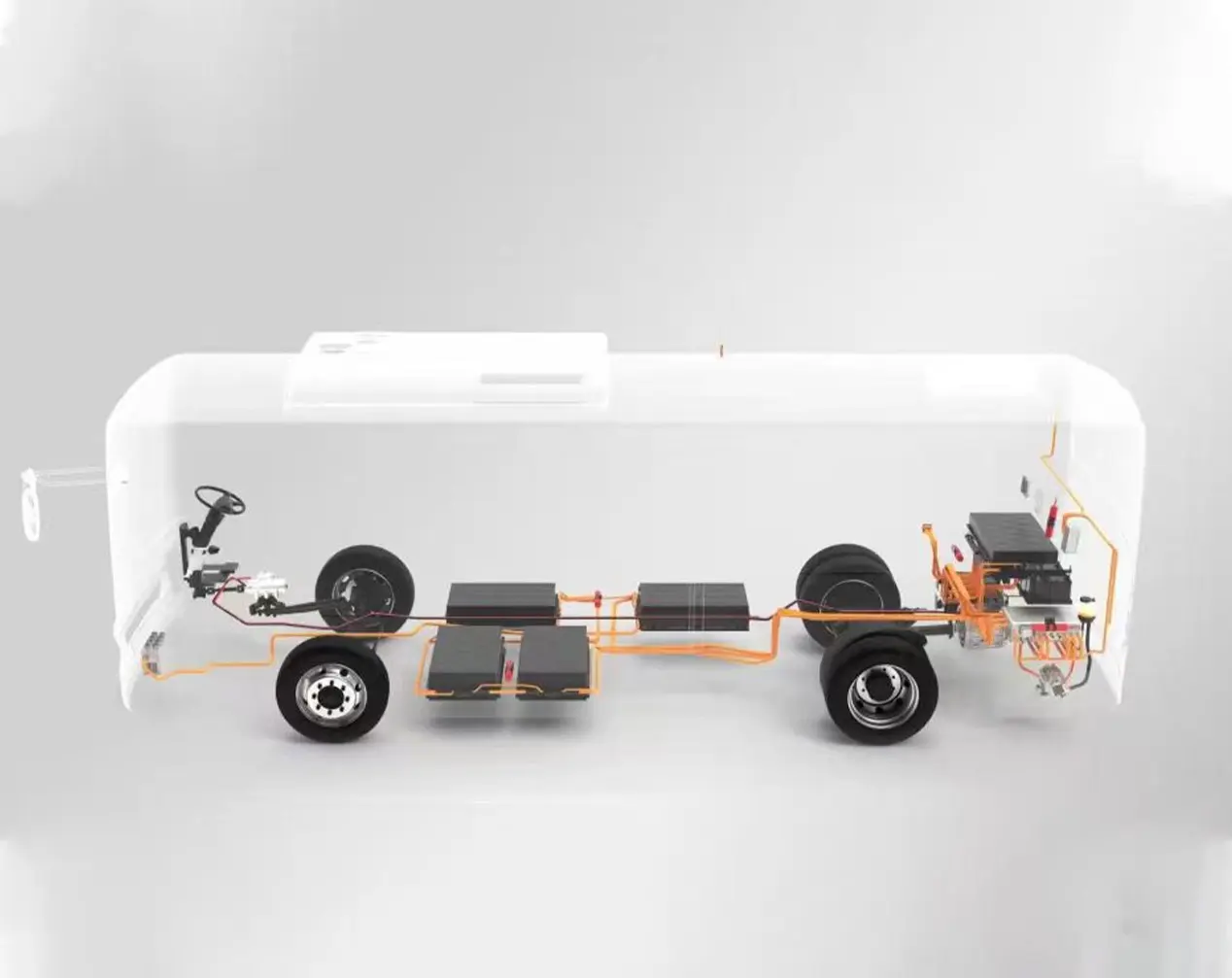
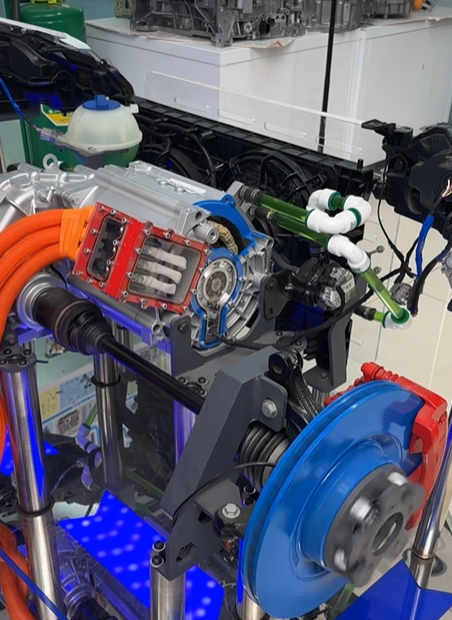
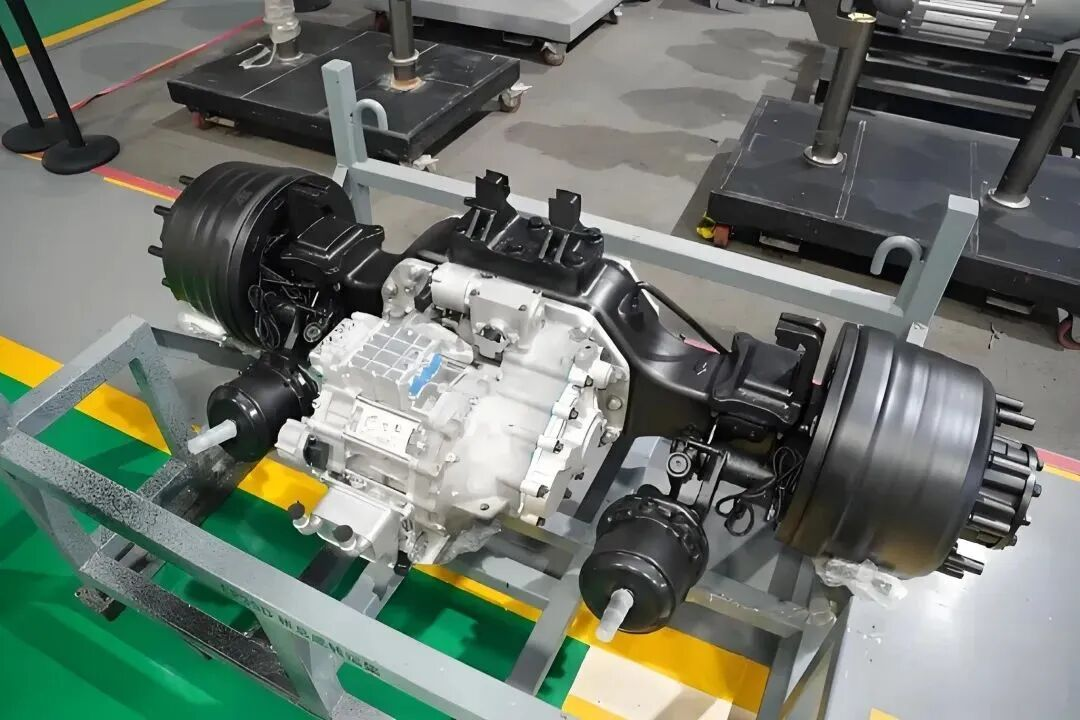
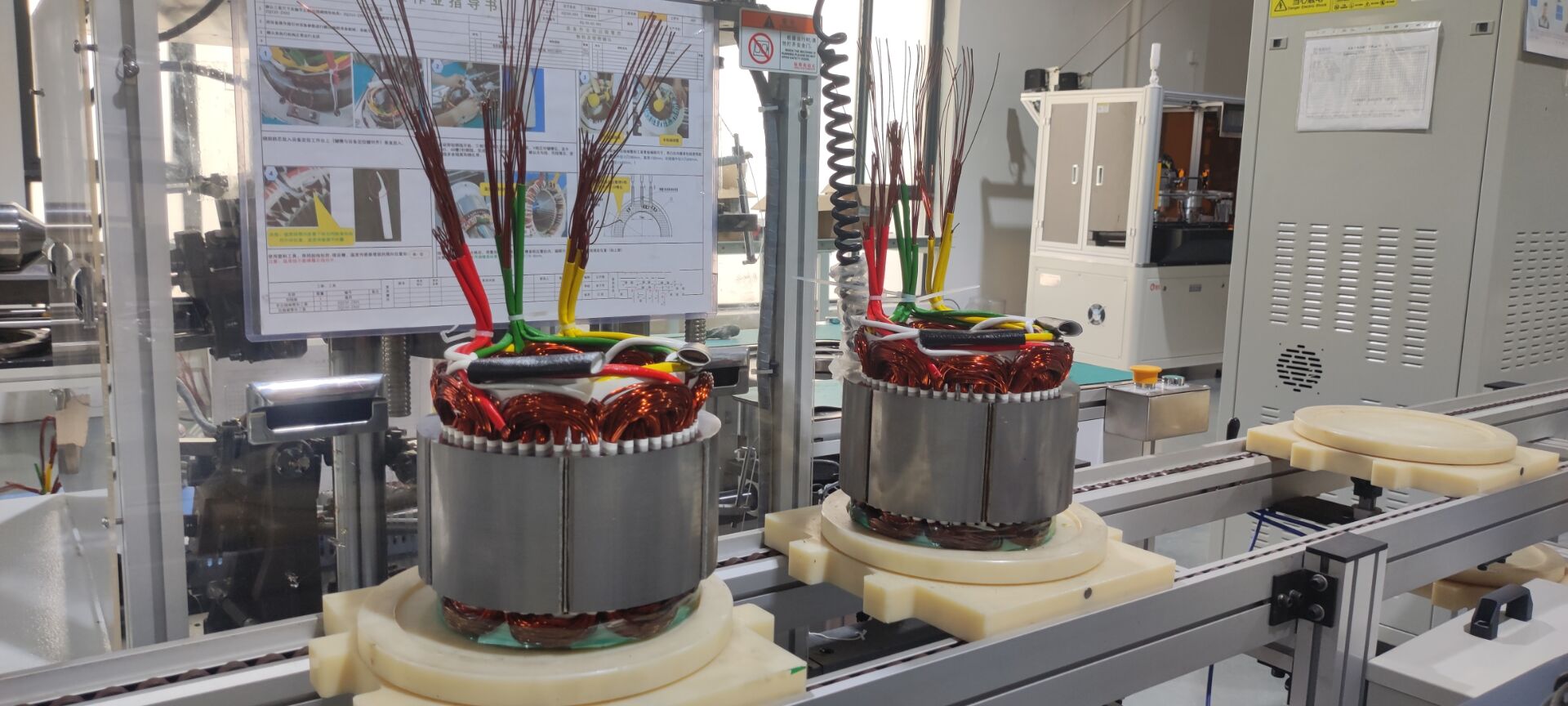
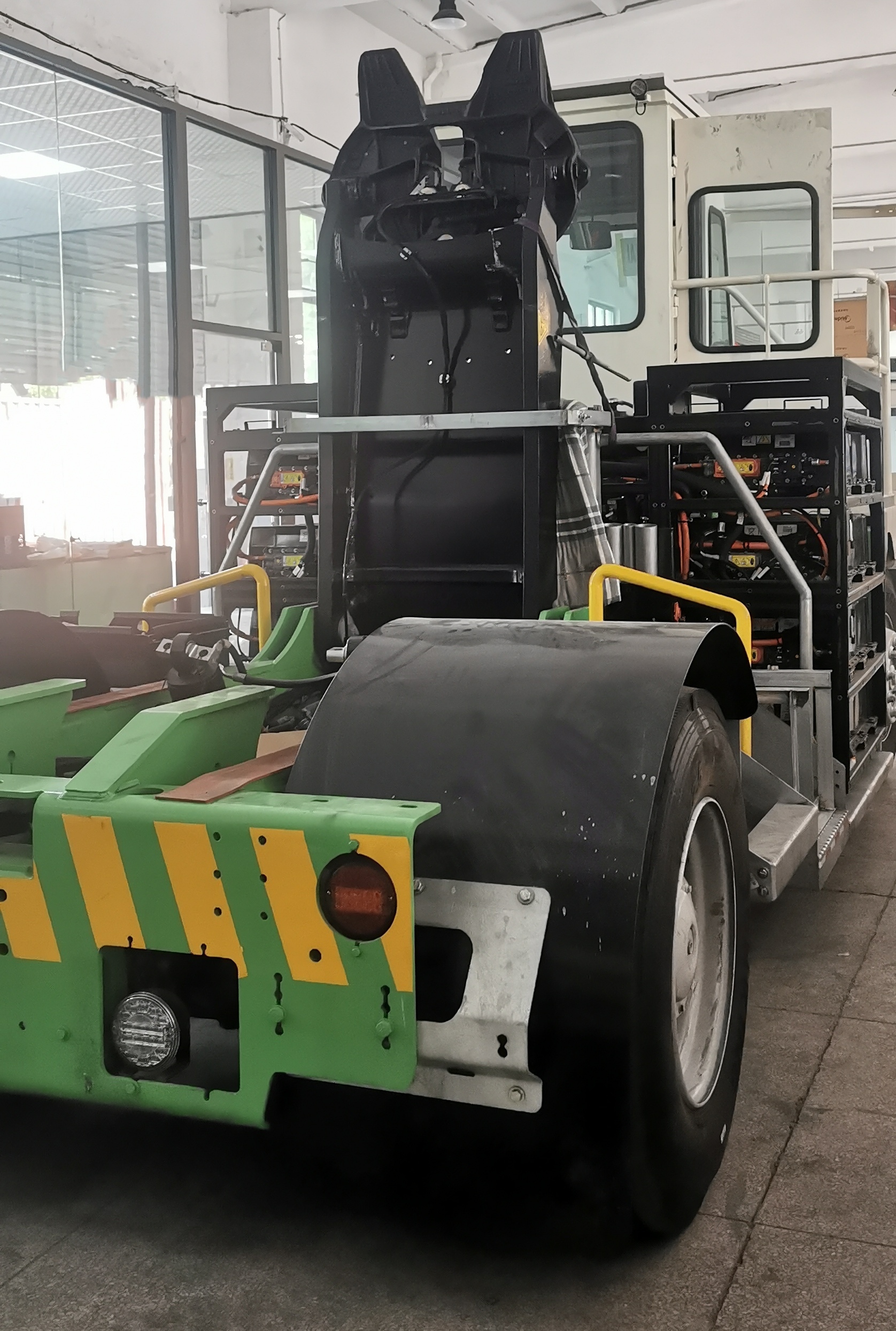
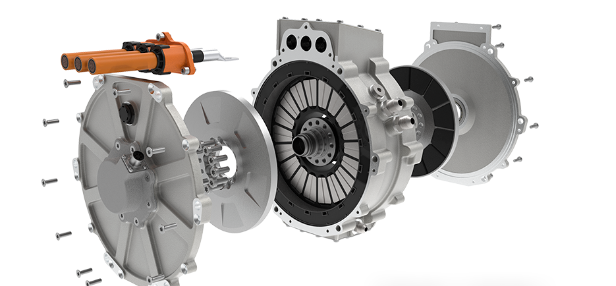
6. Integration of Motor, Controller, and Power Supply
The integration of motor, controller, and power supply holds the key to achieving compactness, efficiency, and reliability in high-power electric mobility systems. By integrating the motor, controller, and power supply into one unified component, manufacturers can cut cabling, reduce energy losses, and make the installation process easier. With such a design, cooling efficiency is better, fault tolerance is higher, and smarter control can be achieved through unified communication protocols. For electric buses and ships, such integration saves space and allows for better maintainability and system stability.
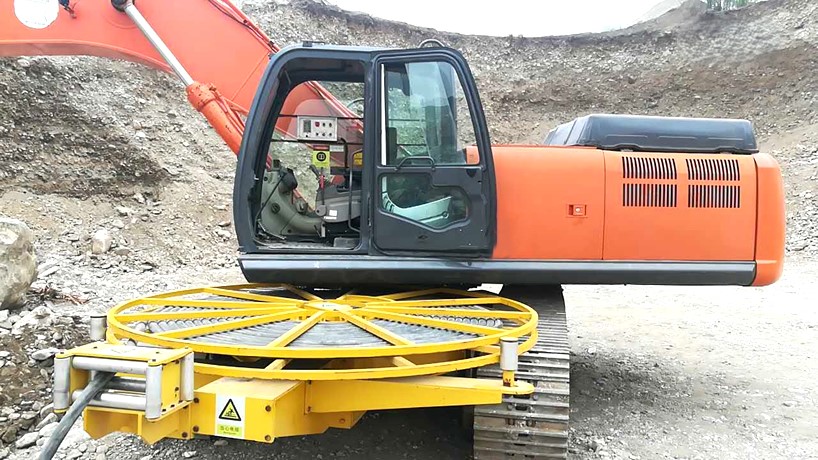
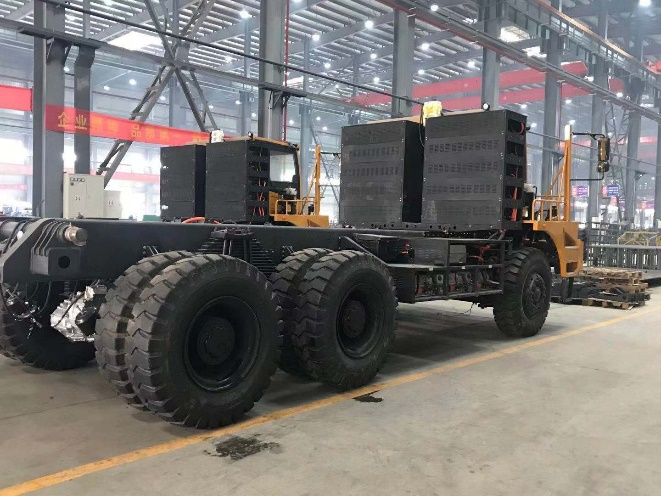
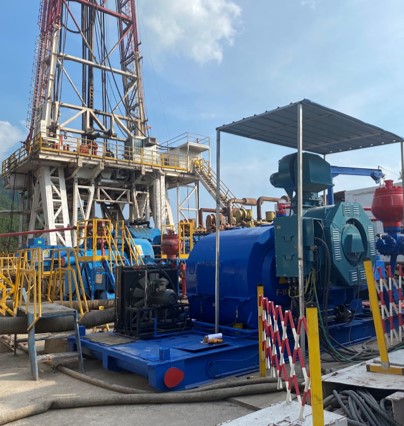
7. Heavy-Duty and Marine Electric Mobility Applications
Ev motors and controllers have long found their application not only in passenger cars but also as powerful torque providers in logistics trucks with heavy payloads, providing quiet, emission-free running in city buses, constant performance at low speeds and high load in sanitation trucks, while electric ferries and vessels operate high-torque, water-cooled motor systems in marine applications to provide stable propulsion with minimum environmental impact. Such versatility points to their ability to meet high demands across a number of industries in support of global sustainability goals.
8. The Benefits of Advanced EV Motor and Controller Solutions
Advanced EV motors, along with controllers, represent several benefits: increased efficiency, reduced maintenance, lower operating costs, and enhanced safety. Smart algorithms for control enable predictive maintenance and performance optimization along with integrated diagnostics. Energy recovery with regenerative braking further extends driving range, while improved thermal management ensures consistent operation even under extreme conditions. Fleet operators are assured of greater reliability, a reduced total cost of ownership, and adherence to increasingly strict environmental regulations.
9. Conclusion: Driving the Next Generation of Electric Power Systems
While humanity continues down the path toward zero-emission transportation, Ev motors and controllers continue at the top of innovation. Further development defines performance, reliability, and sustainability for future mobility systems. Integrating smart control into high-efficiency motors and robust solutions for power supply constitutes the backbone for the next generation of electric logistics vehicles, public transport systems, and marine vessels; by all means, it is not only powering heavy-duty EVs but driving the world toward cleaner, smarter, and more powerful electric mobility.