Variable Speed Motor and Controller & Direct Drive Electric Motor for Next-Generation Commercial EV Platforms
1. Market Shift: From Mechanical Drivetrains to Intelligent Electric Propulsion
Commercial transportation has entered a decisive phase of electrification. With global regulations promoting low-carbon logistics and public transportation, OEMs are transitioning from complex mechanical drivetrains to highly integrated electric propulsion systems. Trucks, buses, port tractors, industrial vehicles, and electric boats increasingly rely on variable speed motor and controller platforms and direct drive electric motor systems to deliver higher efficiency and better long-term reliability.
Unlike internal-combustion systems that depend on multi-stage transmissions, electric propulsion offers instant torque, precise power control, lower mechanical losses, and significantly reduced maintenance. This shift is redefining vehicle power density, operating costs, and long-term lifecycle performance, making intelligent electric propulsion the foundation of next-generation commercial EV platforms.
2. Variable Speed Motor and Controller as the “Brain” of Modern EV Platforms
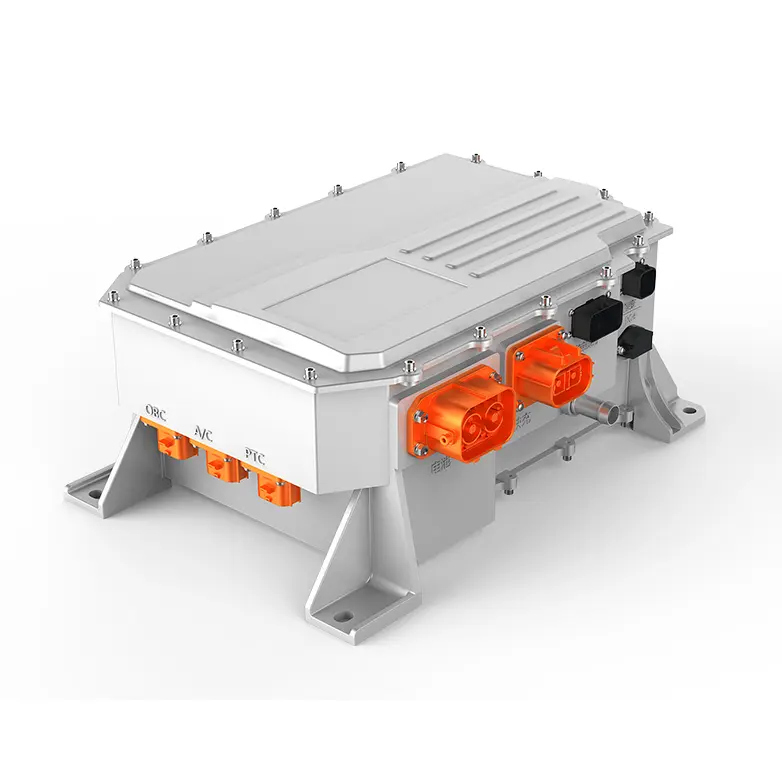
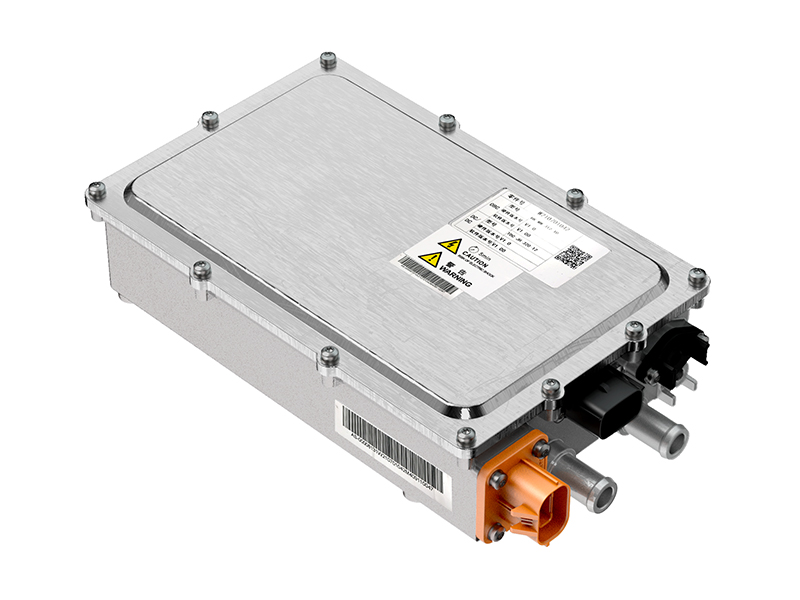
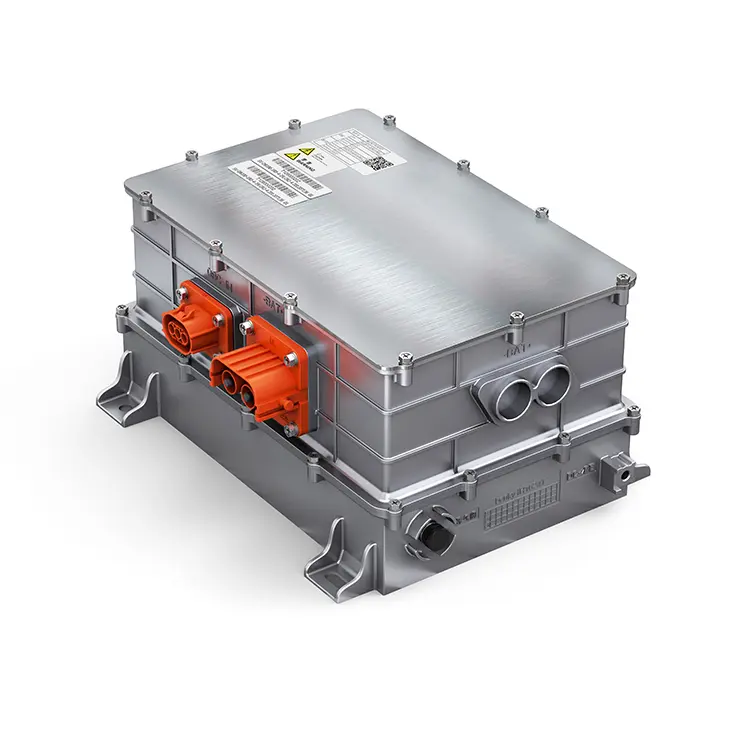
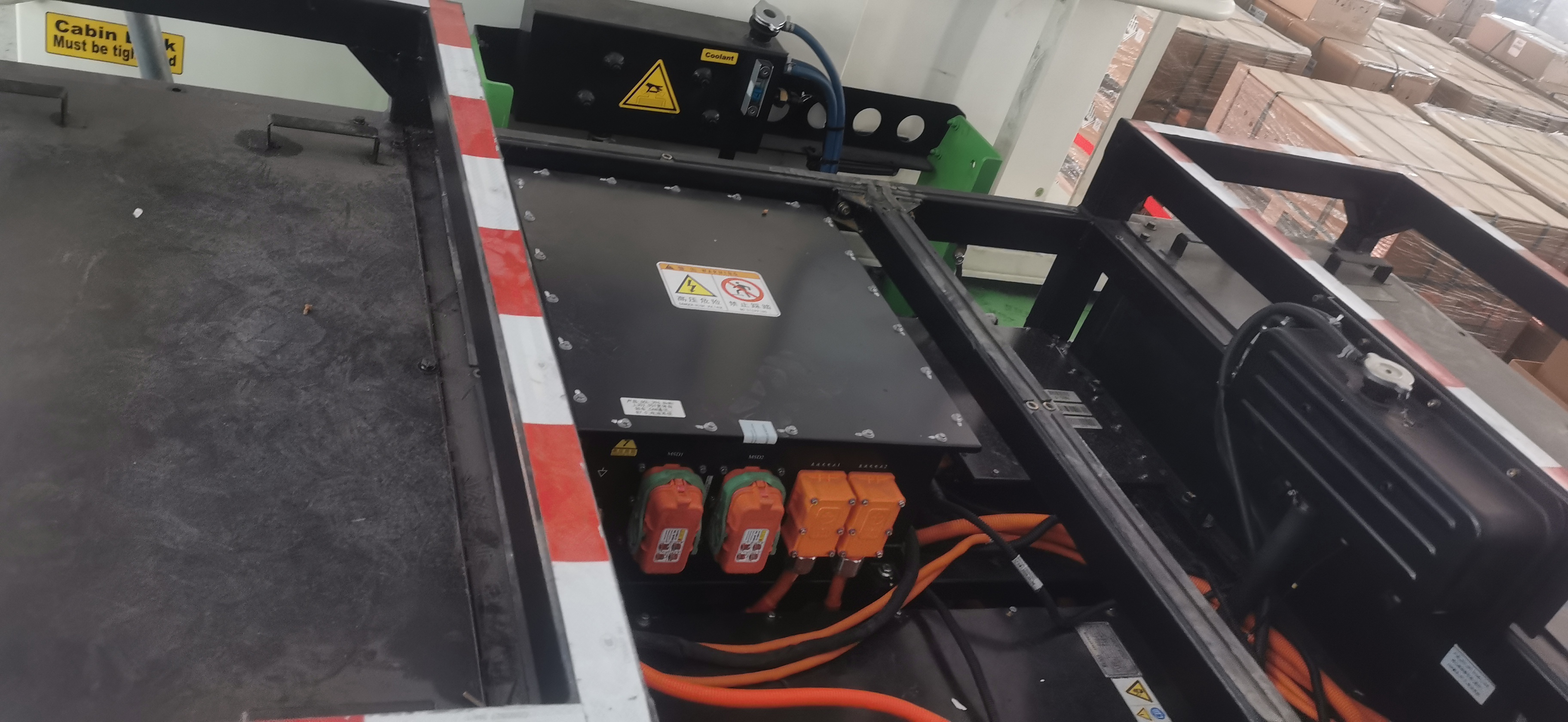
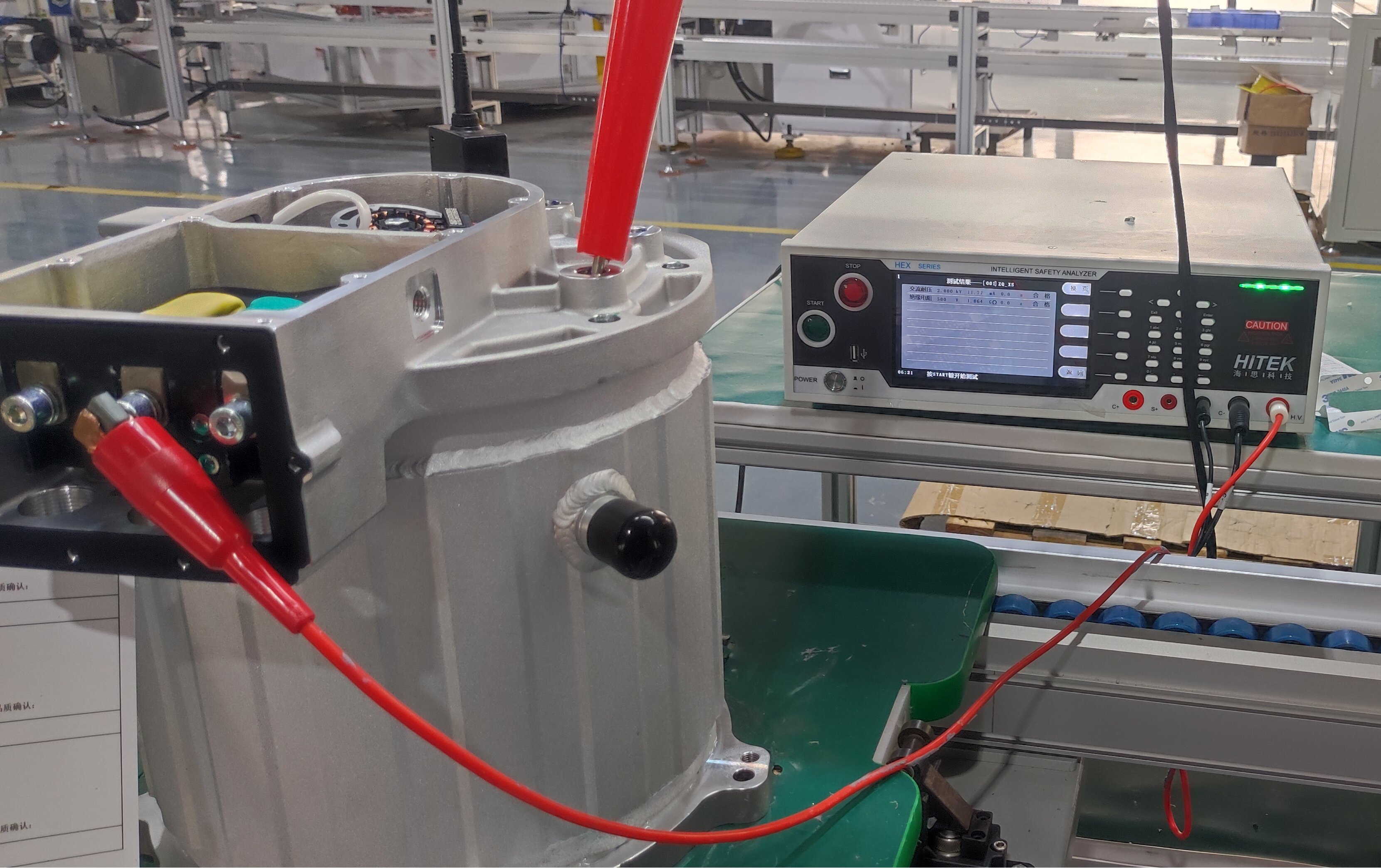
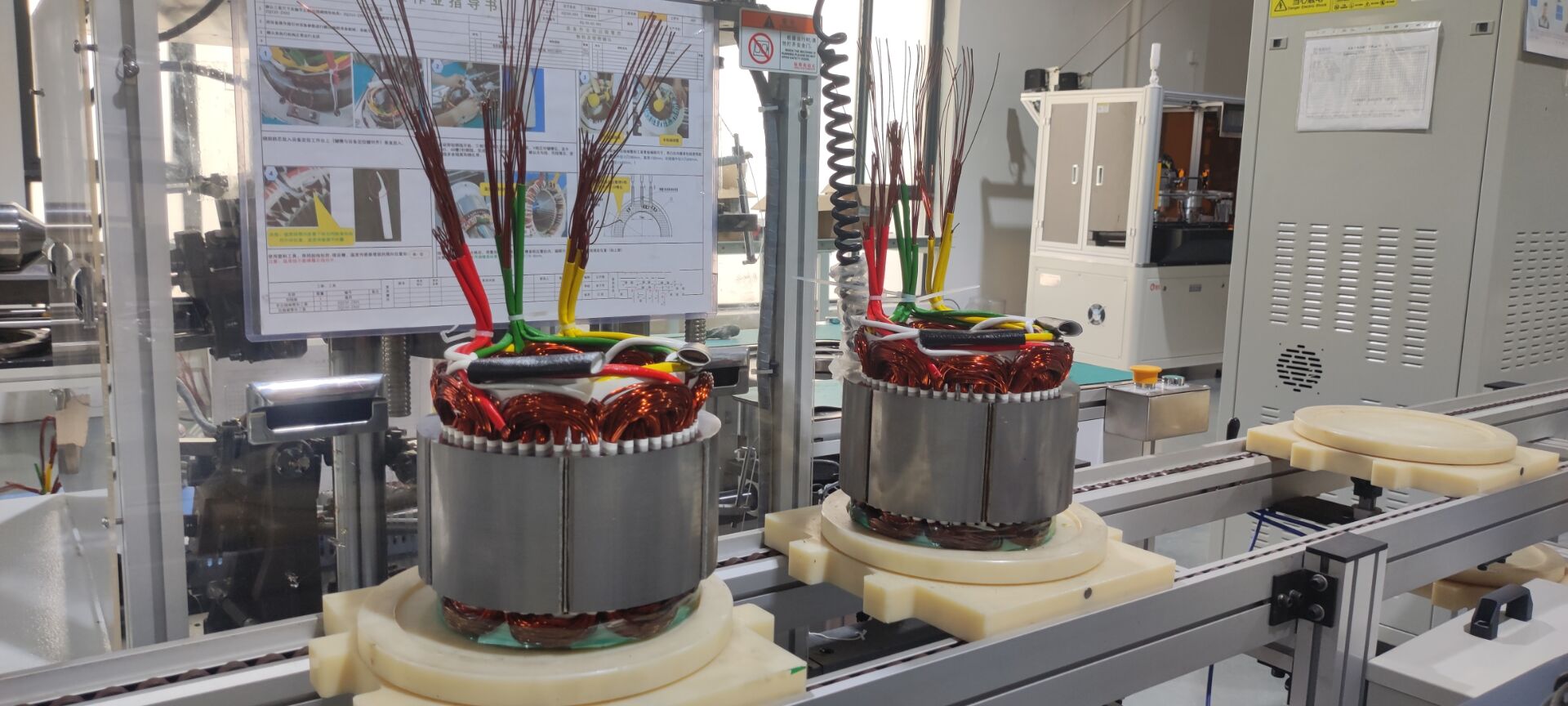
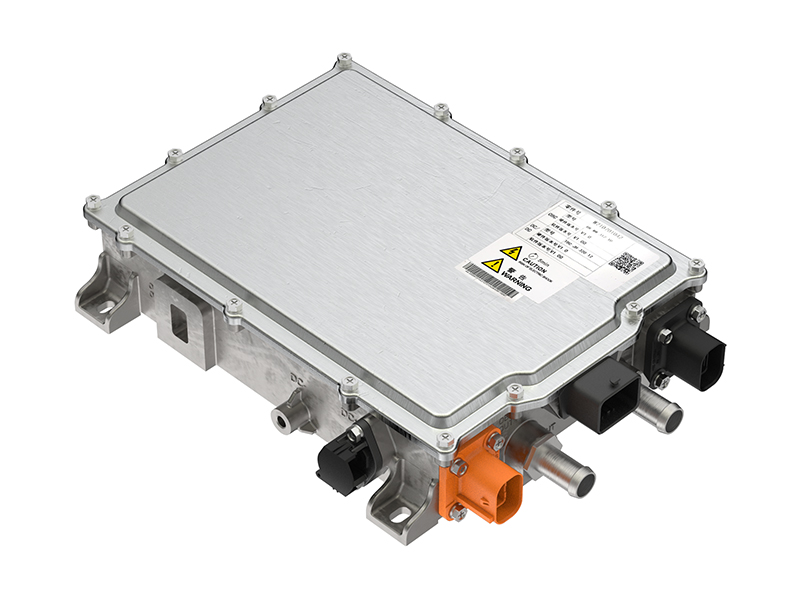
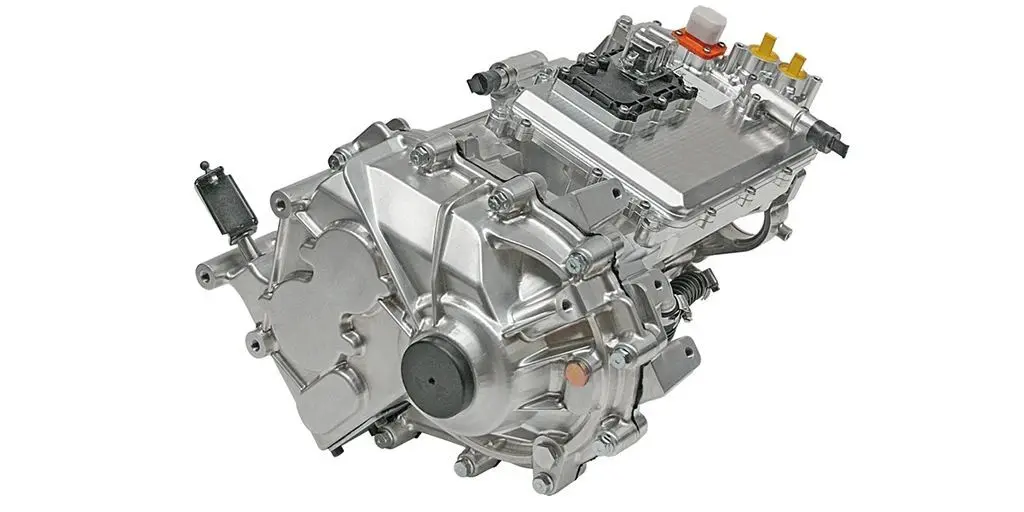
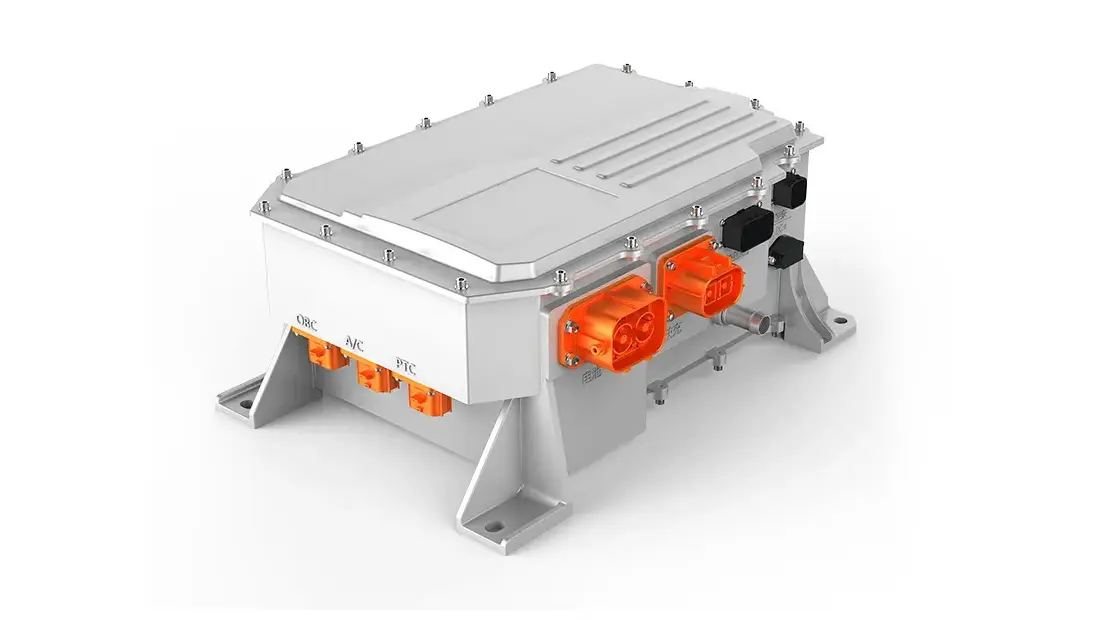
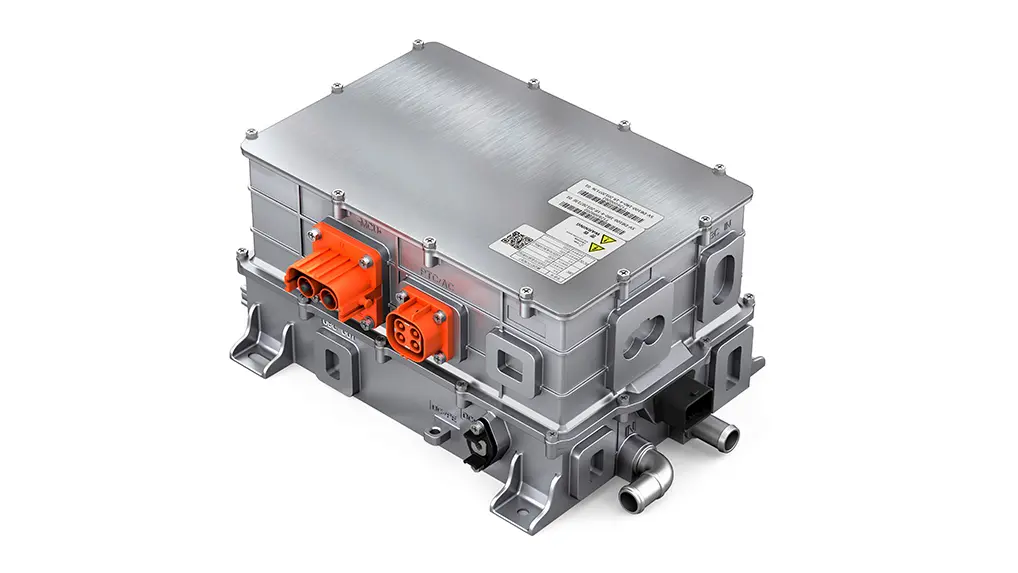
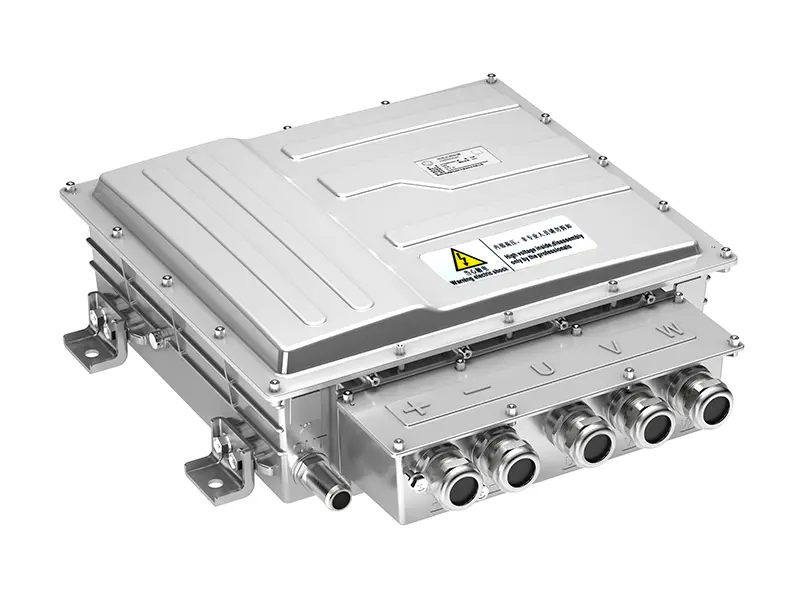
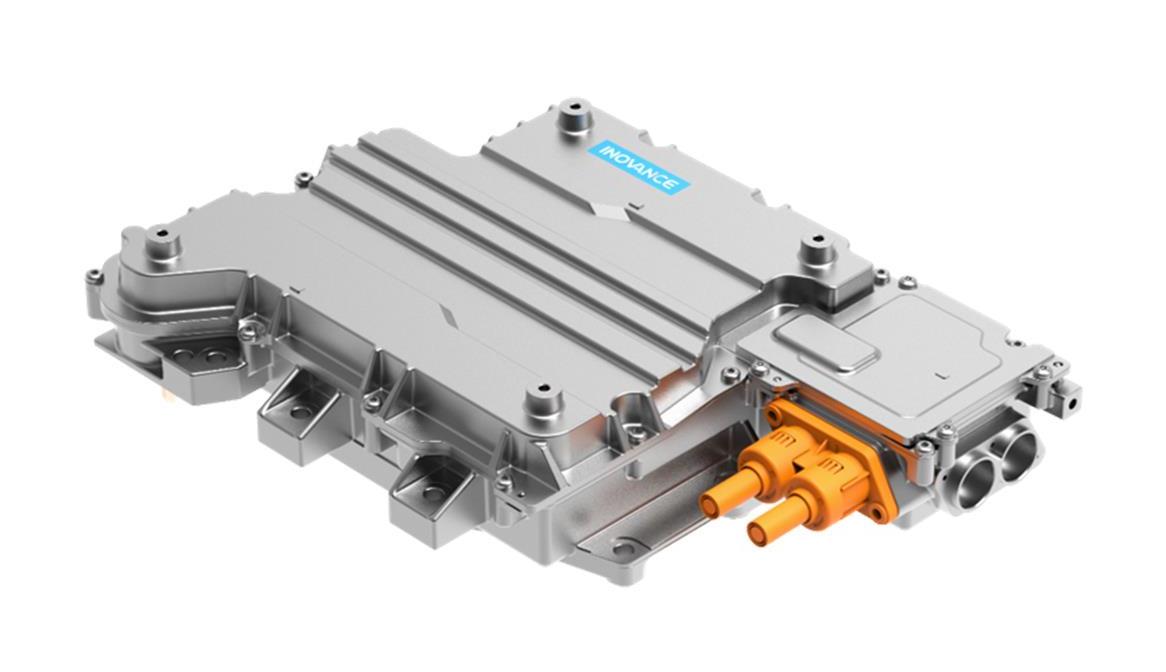
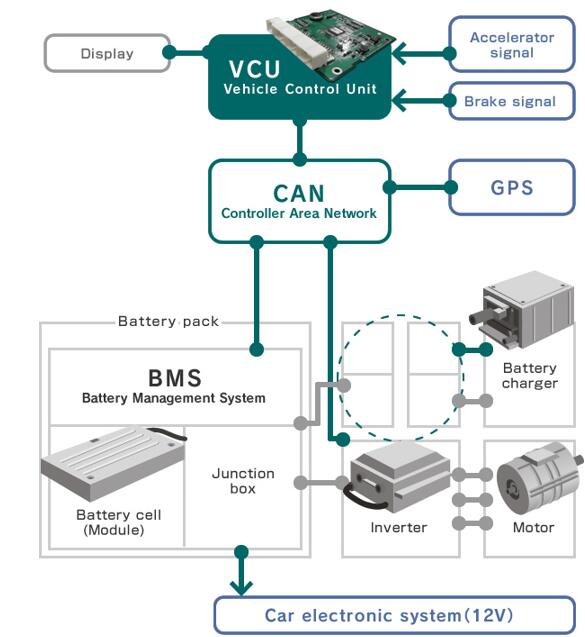
In modern commercial EVs, the variable speed motor and controller (inverter) acts as the central computing and power-management hub of the propulsion system. It continuously manages torque, speed, voltage, thermal behavior, and energy flow between motor, charging system, and onboard auxiliary power units.
Core value points include:
- Dynamic torque control for demanding start-stop conditions, gradients, and varying loads
- Optimized inverter efficiency, increasing usable range and reducing operating cost
- Programmable control algorithms enabling application-specific tuning (logistics trucks, city buses, marine propulsion)
- Integration of onboard chargers and DC–DC converters, reducing parts count and simplifying power electronics architecture
- Adaptive thermal protection for long-duration heavy-duty use
As commercial EV applications diversify, software-defined motor controllers allow OEMs to customize torque curves, acceleration behavior, regenerative braking intensity, and fault responses, giving manufacturers competitive differentiation without redesigning hardware.
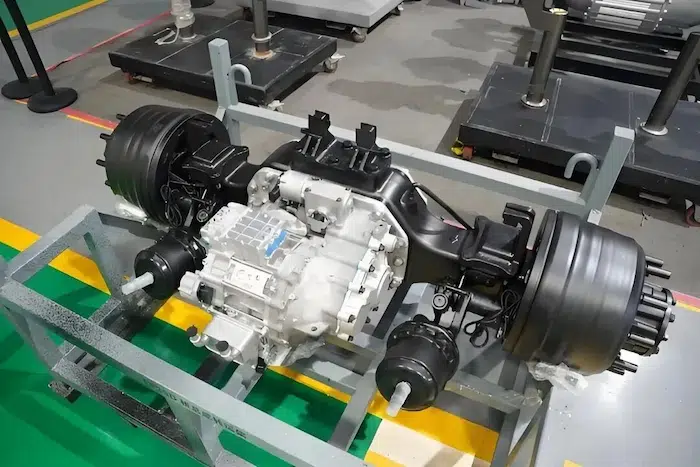
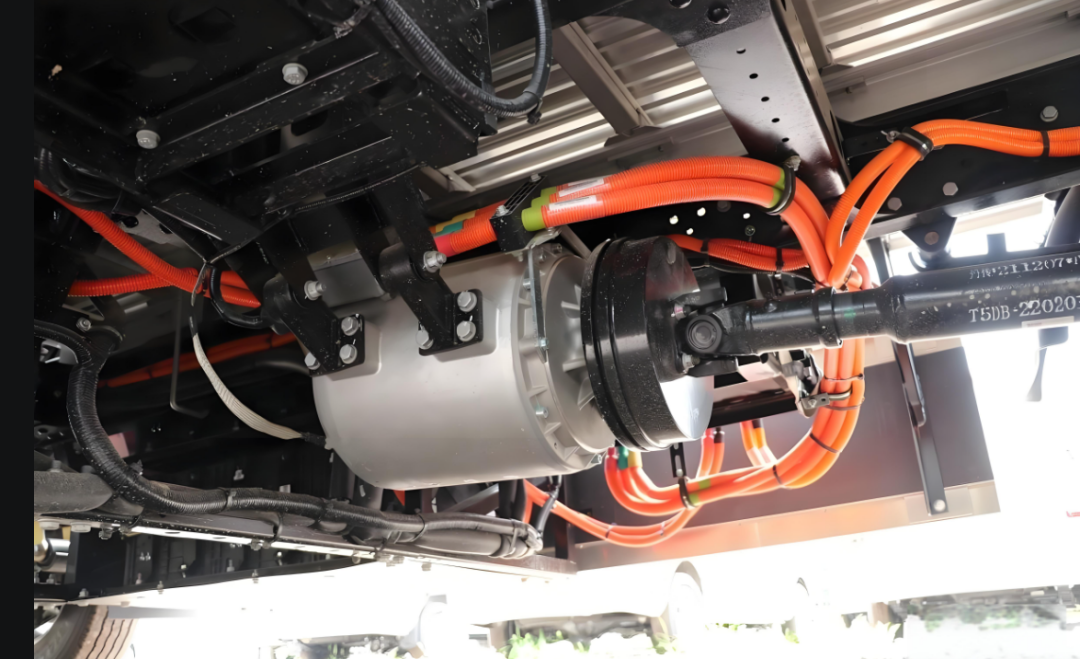
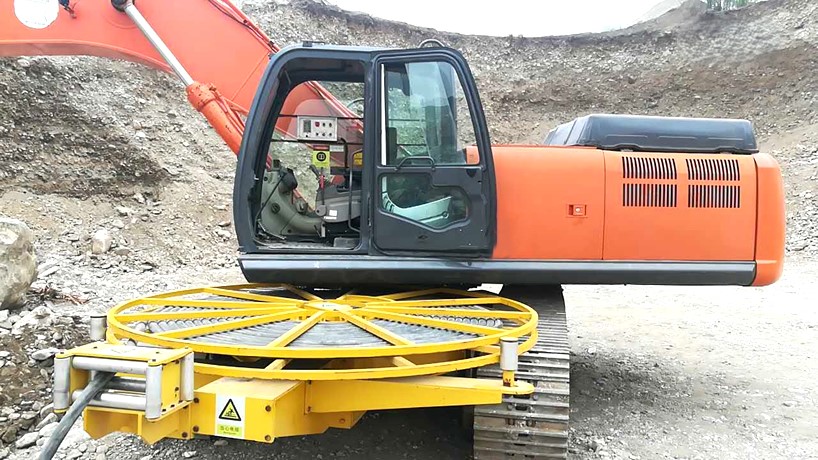
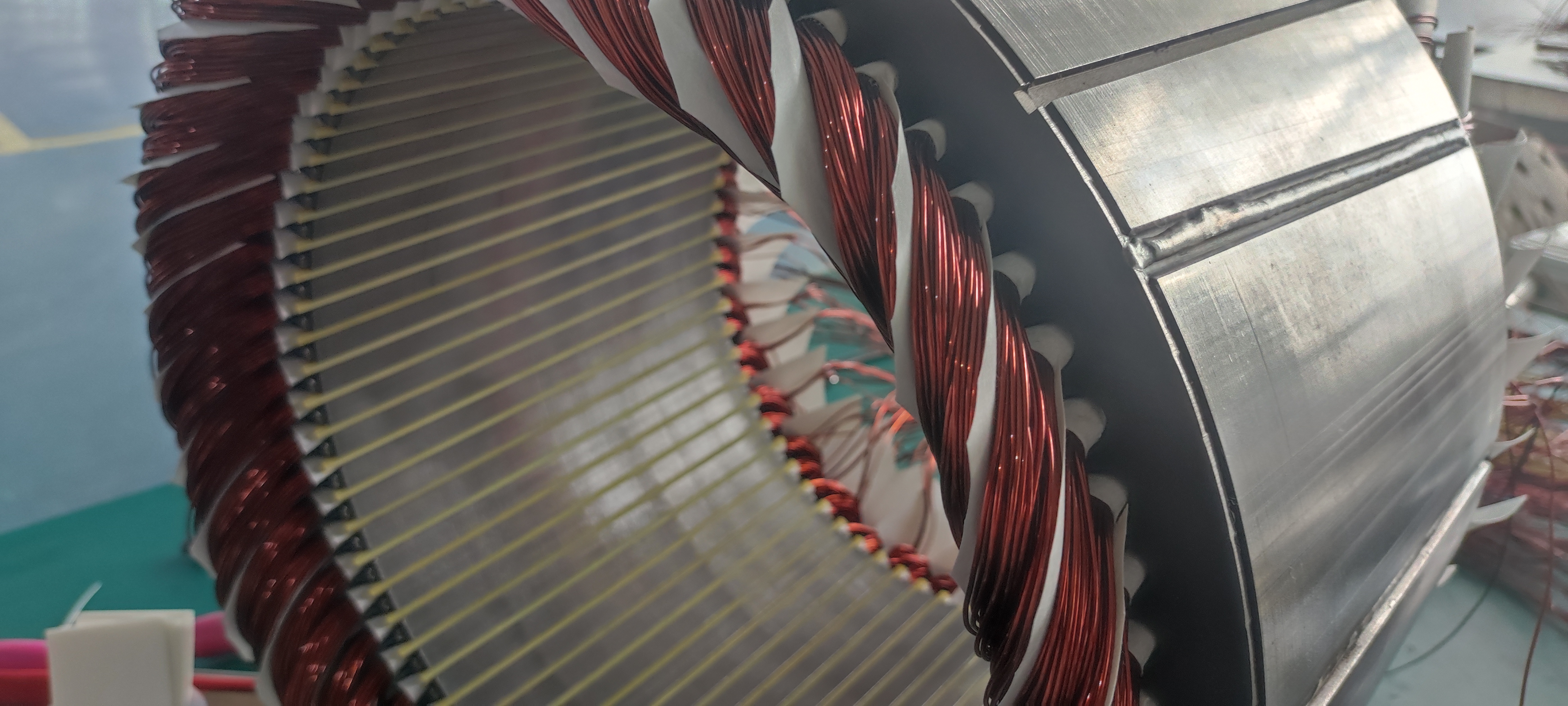
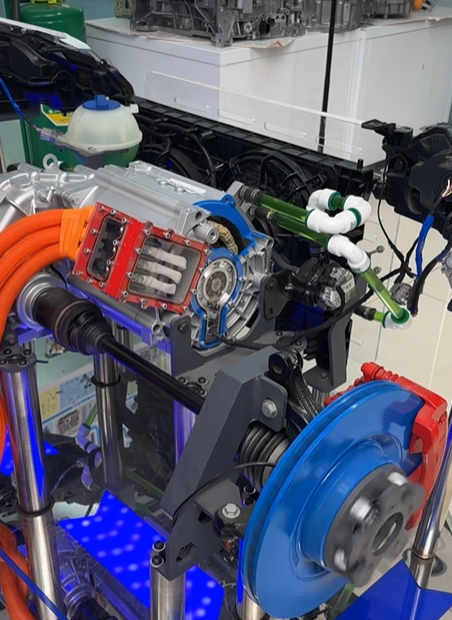
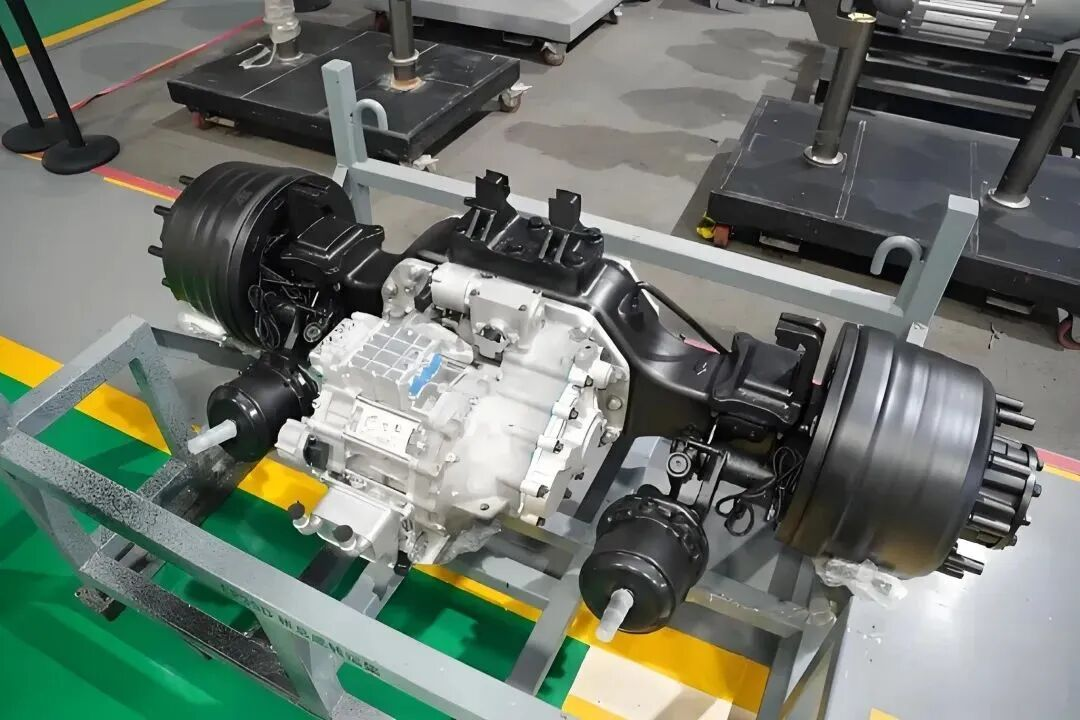
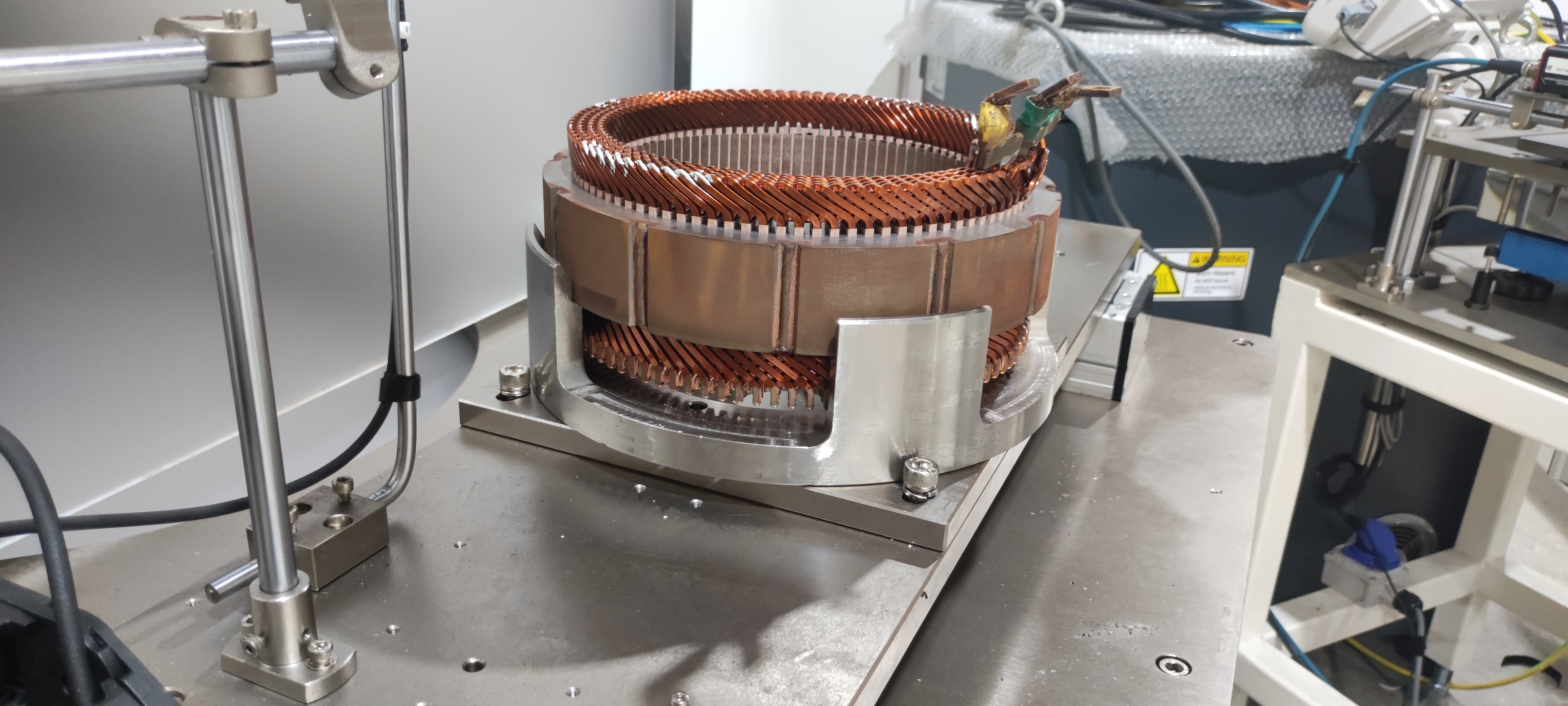
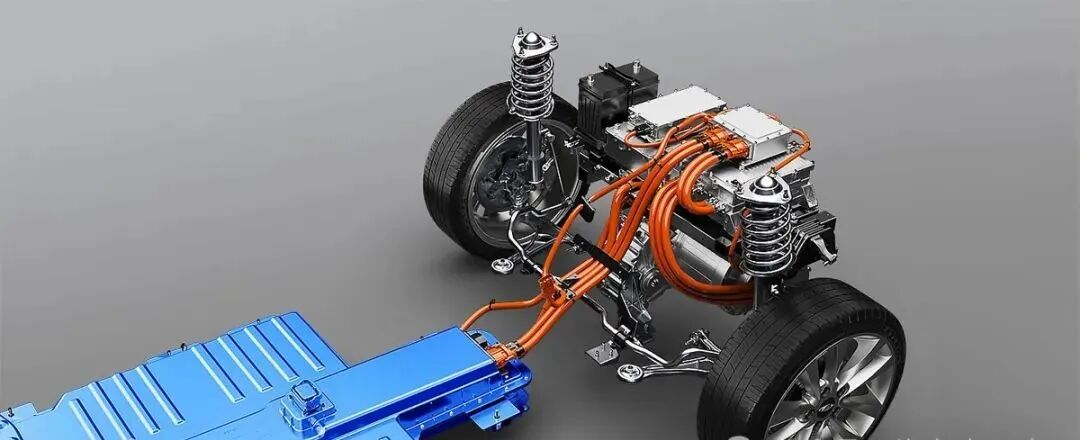
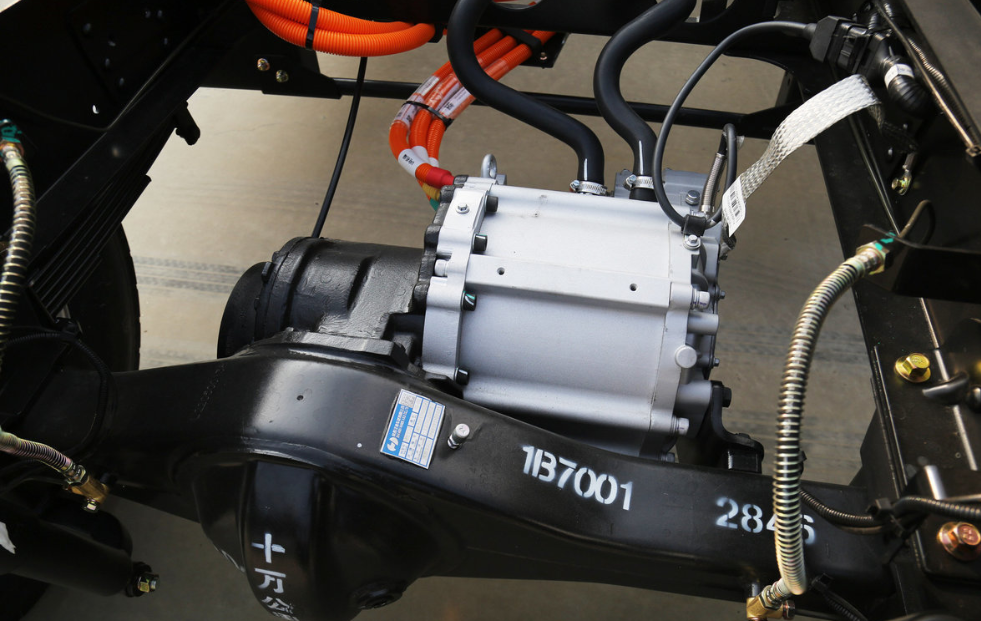
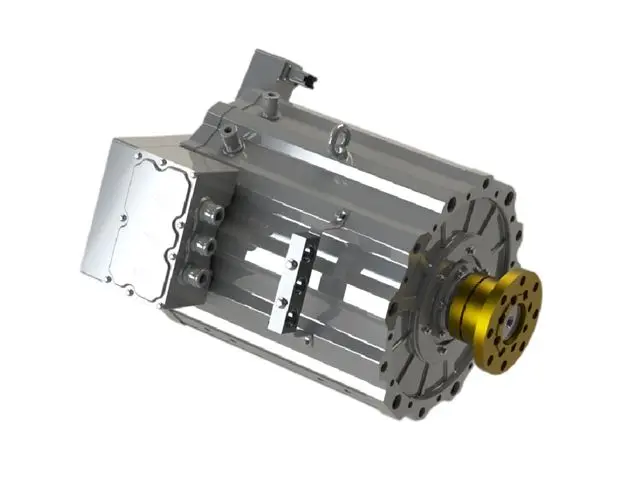
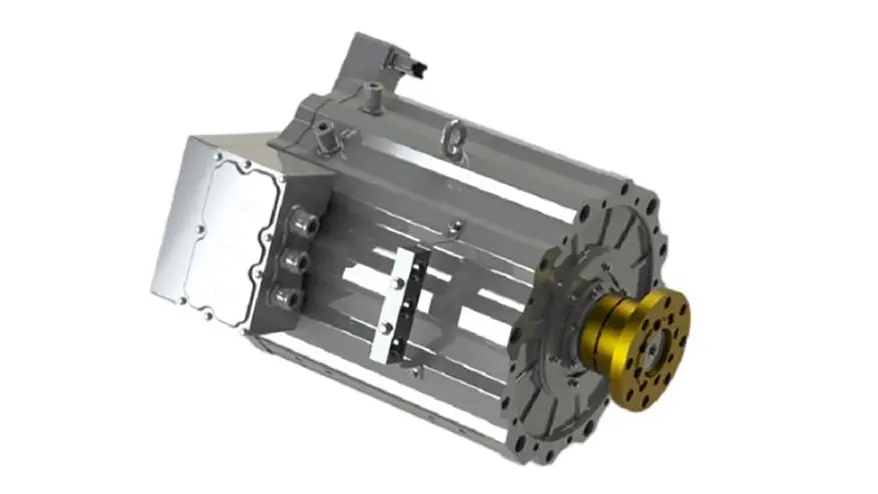
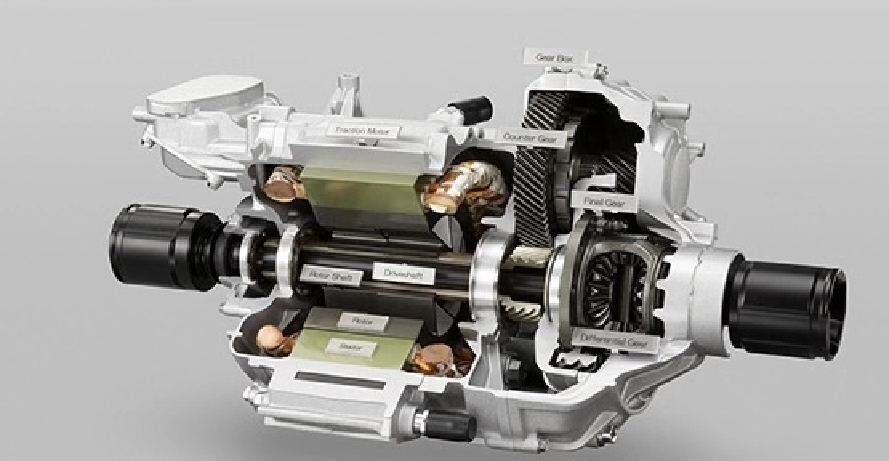
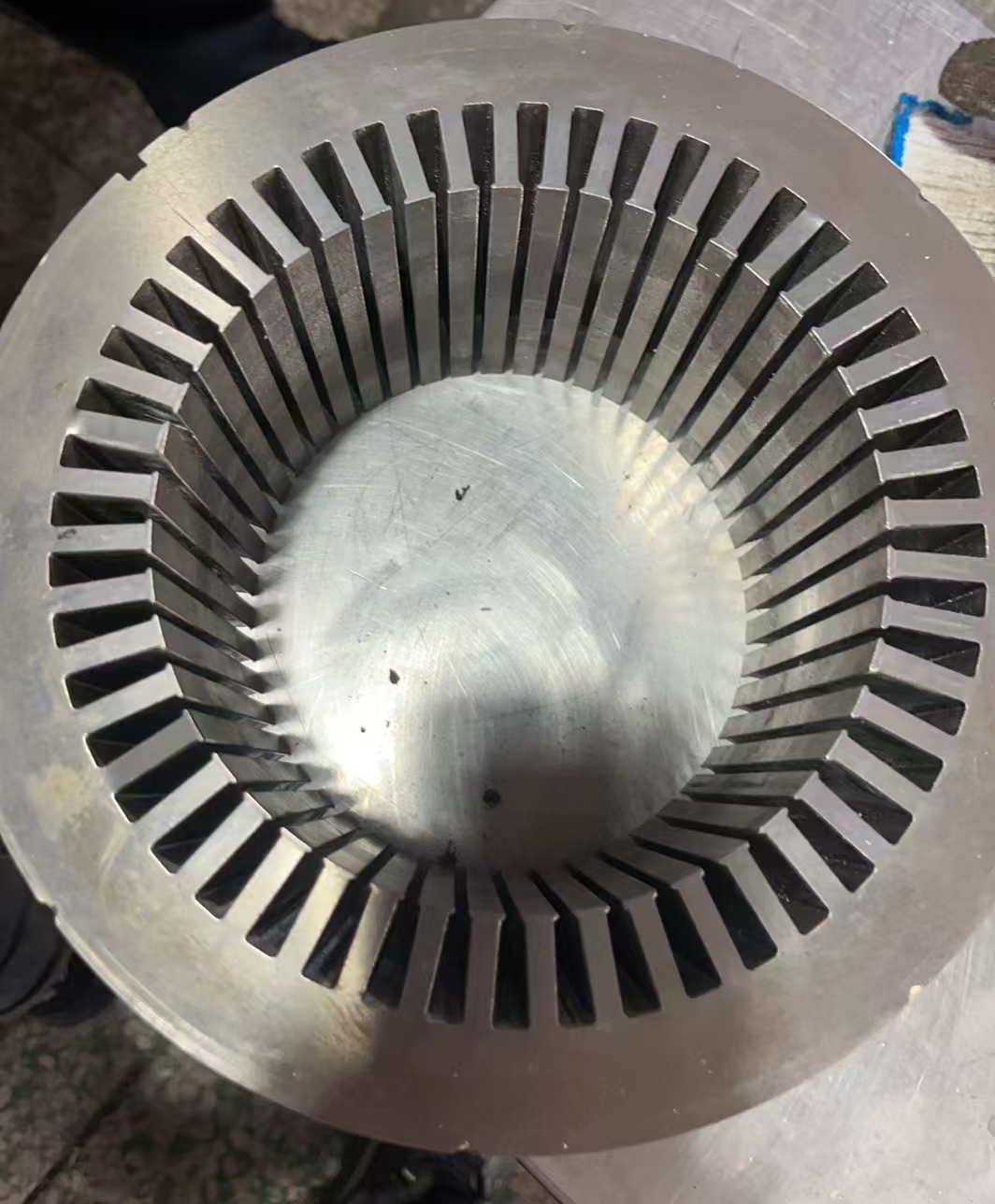
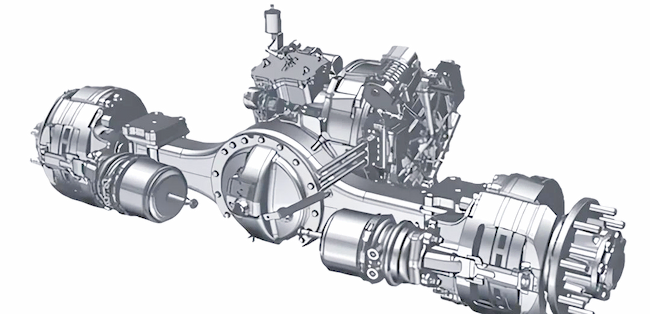
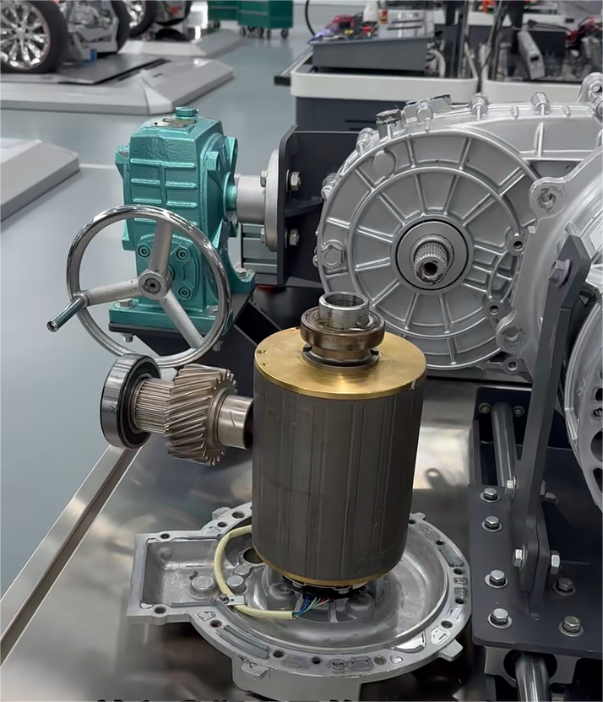
3. Direct Drive Electric Motor vs. Conventional Drive Systems
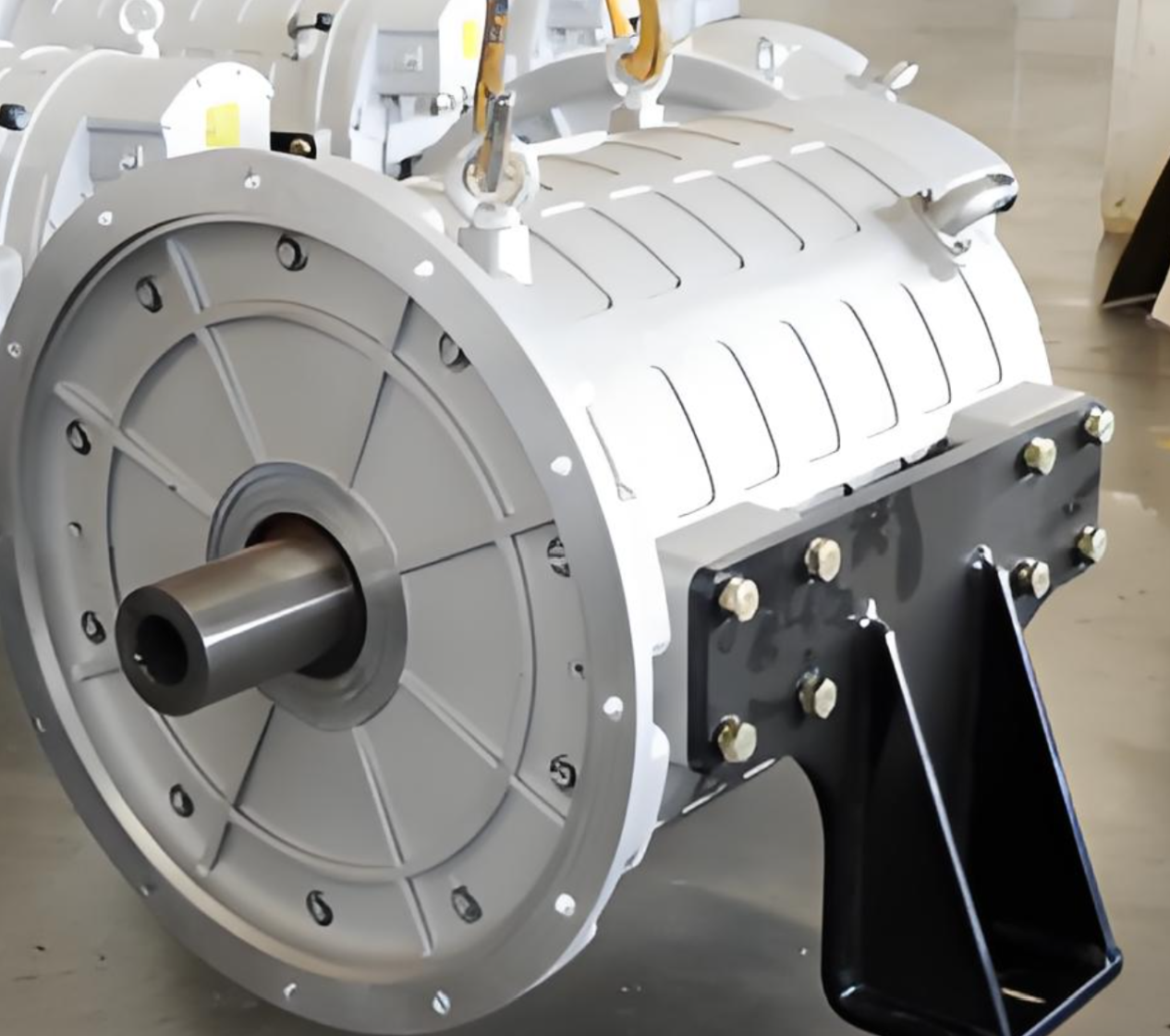
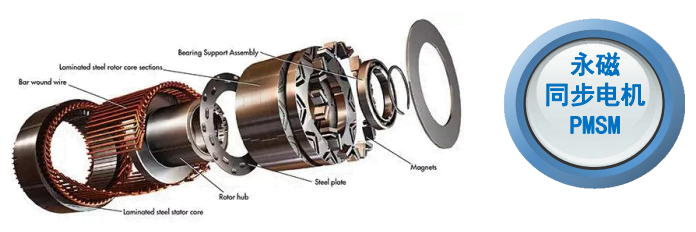
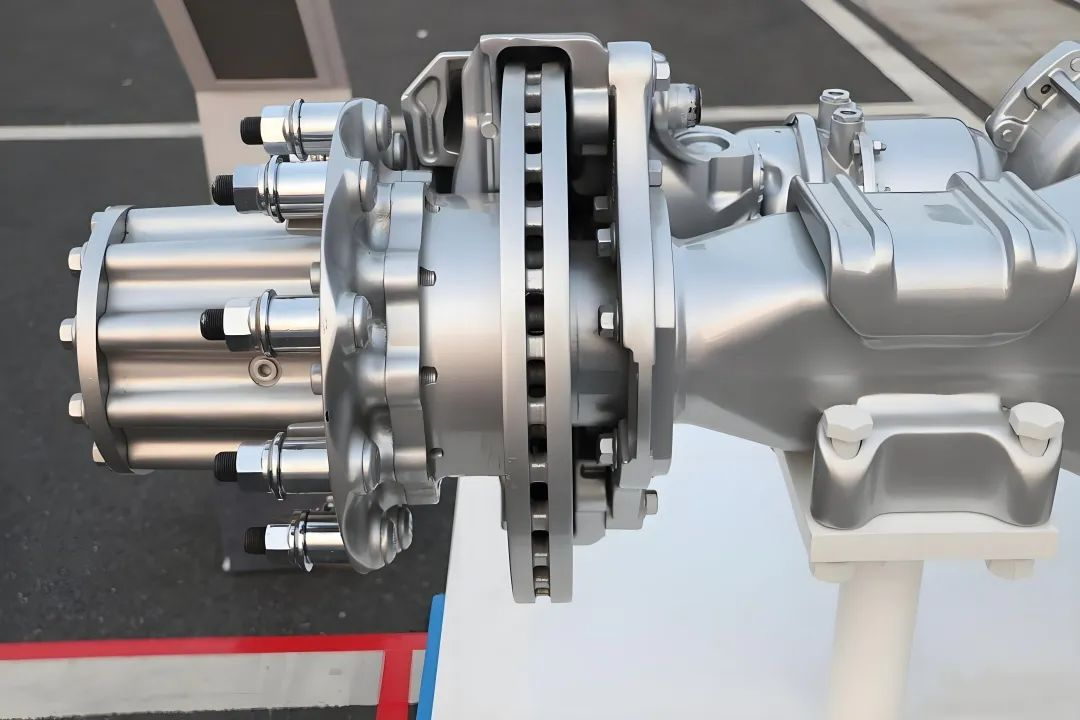
Direct drive electric motors connect the motor shaft directly to the wheel hub, axle, or propeller, eliminating multi-stage gearboxes, driveshafts, and differential assemblies. This architecture is increasingly favored across commercial platforms.
Key advantages over traditional multi-gear transmissions:
- Minimal mechanical components, reducing service requirements dramatically
- Instant, high starting torque, ideal for high-load applications such as buses, refuse trucks, and port tractors
- Lower mechanical losses, translating into better energy utilization and longer range
- Improved NVH performance, enhancing driver comfort and reducing cabin vibration
- Weight reduction, enabling increased payload for freight vehicles
By removing complex mechanical interfaces, direct-drive systems improve reliability and reduce long-term TCO, which is critical in high-utilization commercial fleets.
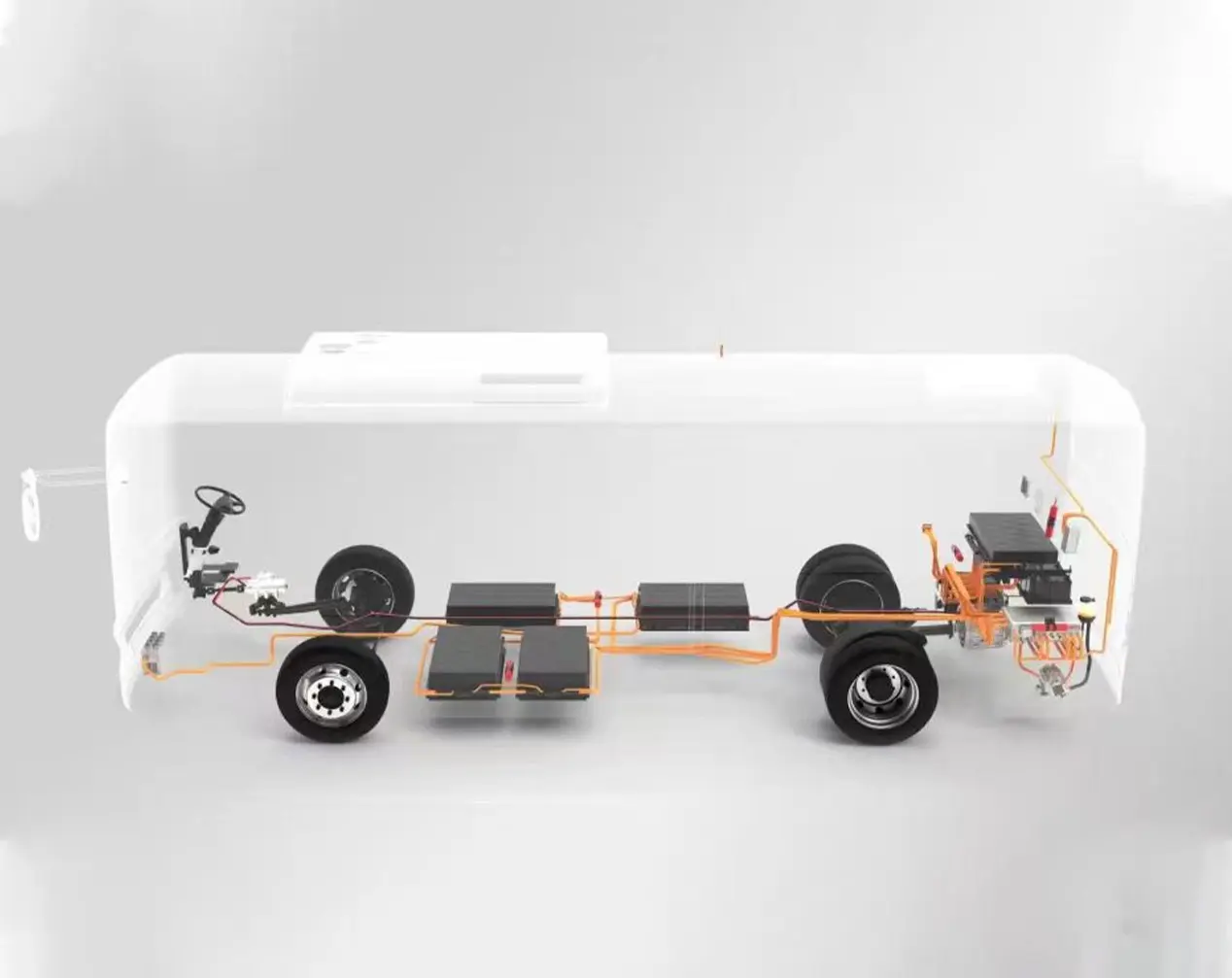
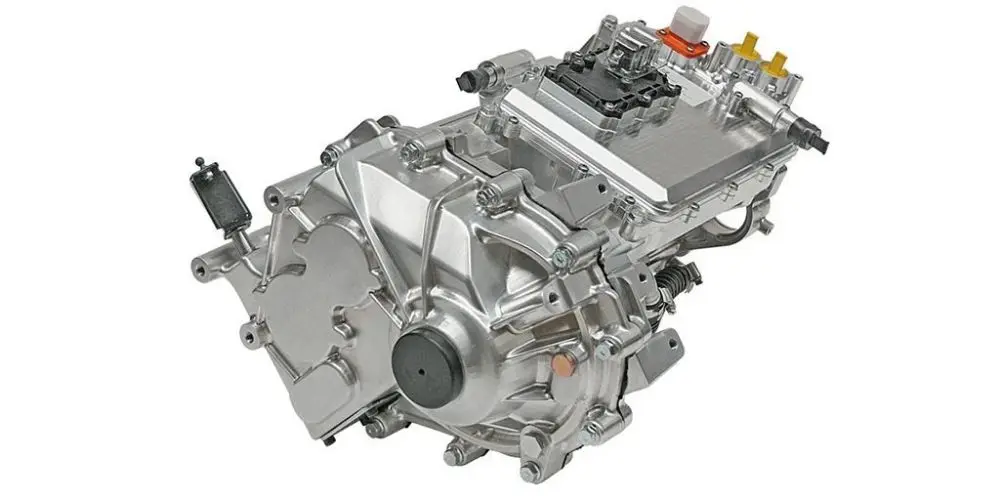
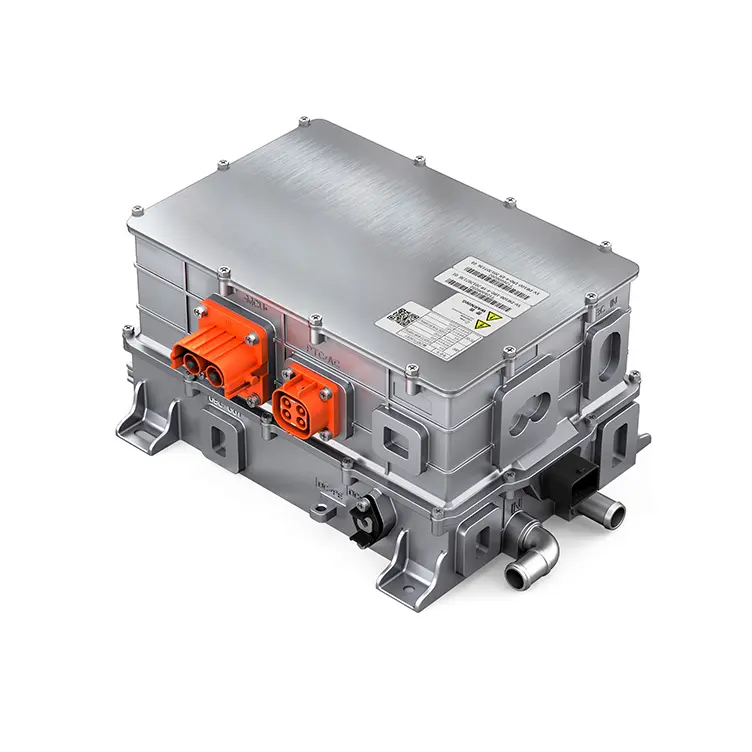
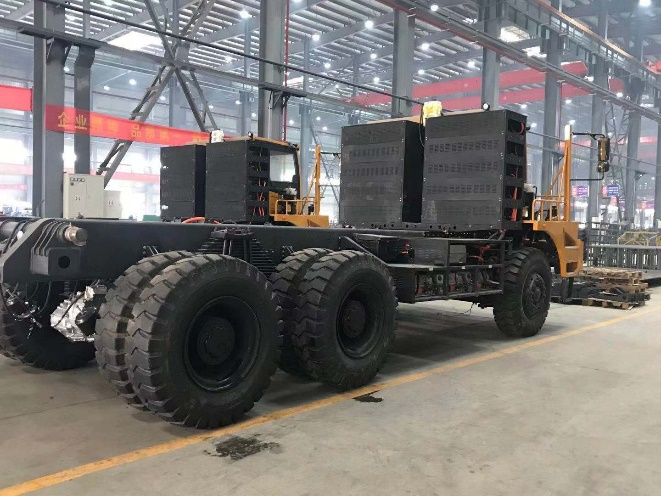
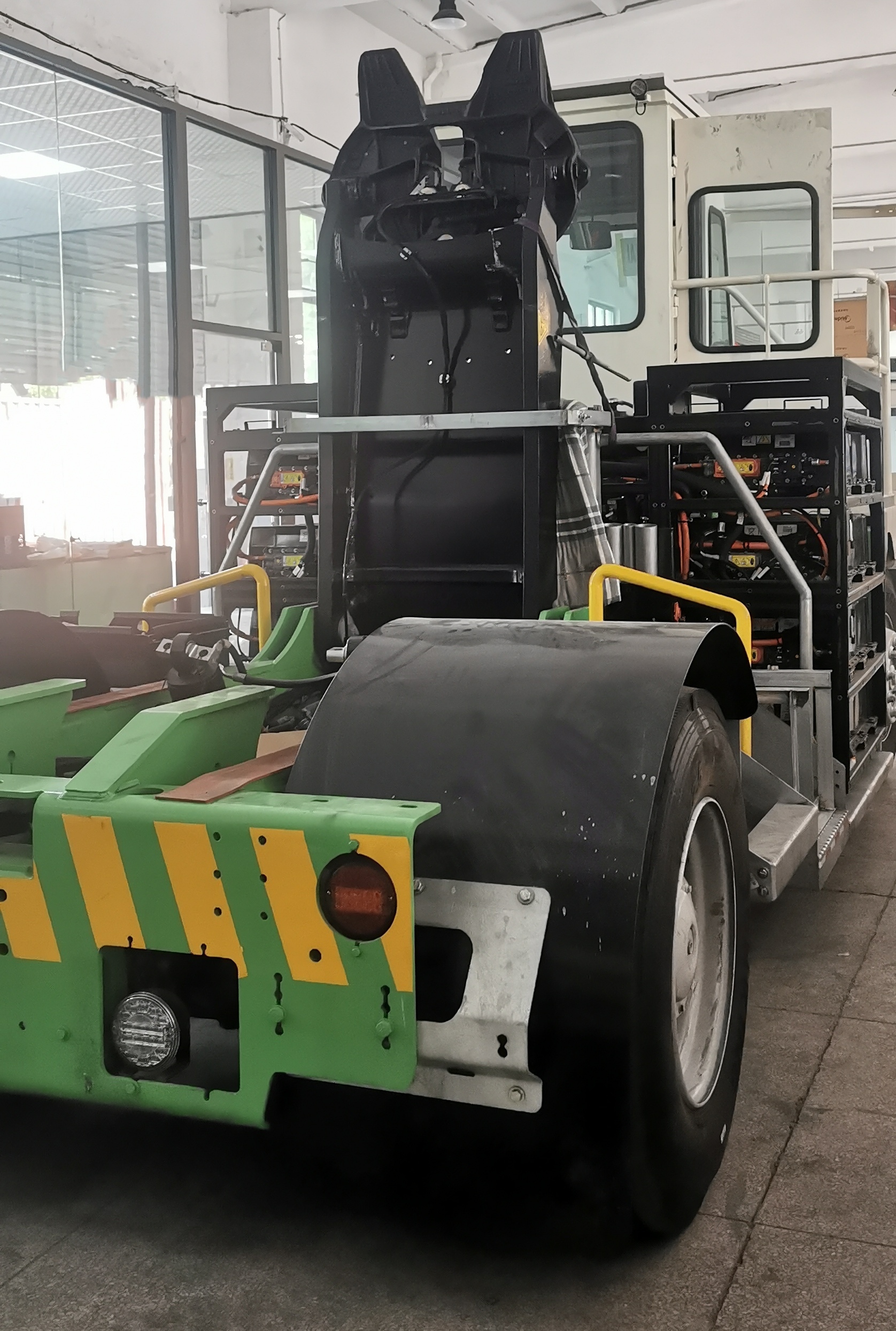
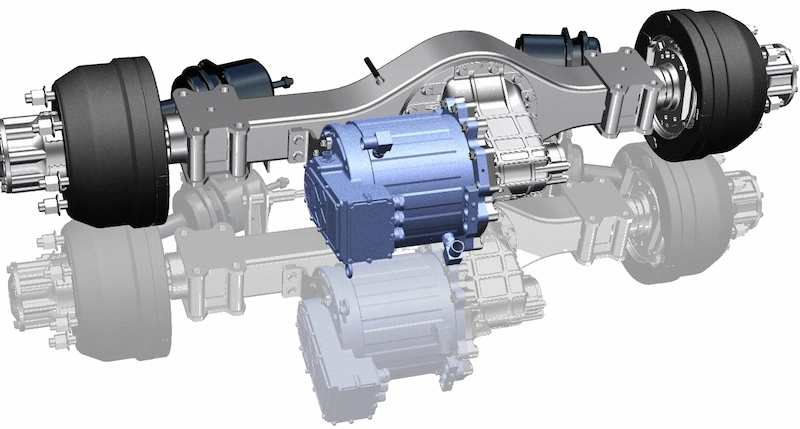
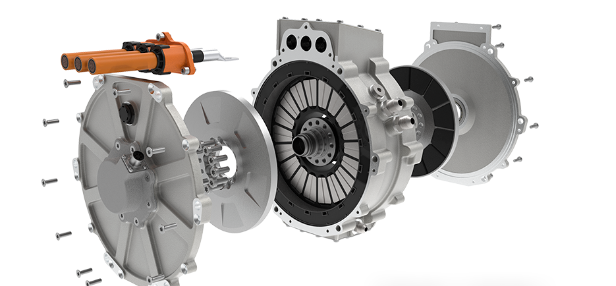
4. Power Architecture in High-Output EV Systems (Without Battery Dependency)
High-output commercial EVs demand propulsion systems that remain robust regardless of battery chemistry or energy supply configuration. Modern architectures integrate high-voltage inverters, bidirectional charging systems, DC–DC converters and liquid-cooled thermal management into a unified platform centered around the motor controller. This integration enhances reliability, system compactness and OEM installation efficiency. The modular approach supports battery-electric, hybrid-electric, fuel-cell electric and generator-assisted electric configurations, allowing manufacturers to use a single propulsion platform across multiple vehicle models and energy strategies, significantly reducing development time and platform complexity.

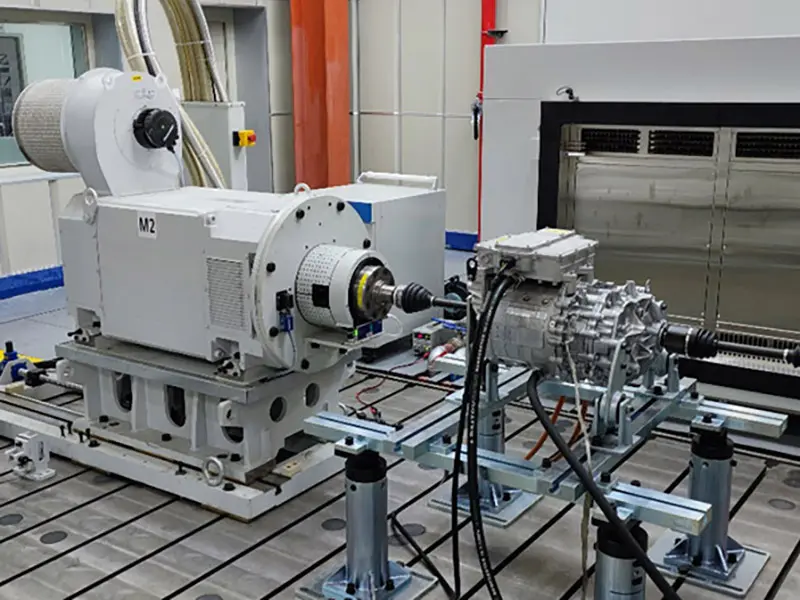
5. Real-World Duty Cycles: How Powertrain Design Changes Performance in Heavy Vehicles
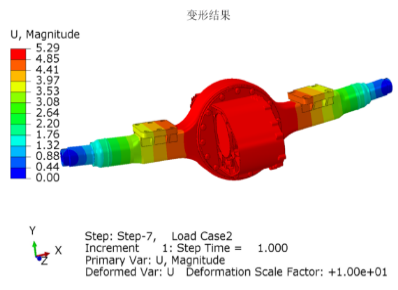
Commercial vehicles face far more demanding operating conditions compared to passenger cars. Heavy-duty trucks, transit buses and industrial vehicles must routinely manage high starting torque, frequent acceleration and braking, long operating hours under thermal stress and constant low-speed maneuvering under heavy load. Direct drive motors excel in these environments due to their ability to deliver strong torque at low speeds with minimal mechanical complexity. Meanwhile, variable speed motor controllers continuously adapt power output, manage thermal loads and optimize regenerative braking to maintain efficiency and durability. This intelligent alignment between electric motor characteristics and real-world duty cycles allows commercial EVs to outperform traditional diesel vehicles in both energy efficiency and operational stability.
6. Decision Guide: How OEMs and Fleet Operators Choose the Right Motor & Controller Platform
When designing or selecting propulsion systems, OEMs and operators typically consider:
- Rated and peak torque matched to vehicle load and gradeability
- Thermal endurance under continuous heavy-duty operation
- Efficiency maps across different speeds and duty cycles
- Power electronics integration (charger, DC–DC, inverter)
- Mechanical architecture: direct drive vs. gearbox-based drives
- Redundancy, functional safety, and diagnostic capability
- Lifecycle TCO, including energy cost, maintenance, and service intervals
For heavy-duty EVs, direct drive motors often provide superior reliability, while advanced controllers deliver the adaptability needed for diverse real-world environments.
7. Cost, Reliability, and Lifecycle Advantages of Integrated Propulsion Systems
Integrating a variable speed motor and controller with a direct drive electric motor into a unified propulsion platform greatly reduces system complexity and long-term maintenance demands. With fewer mechanical components and optimized power control, energy consumption decreases while operational uptime increases—critical benefits for logistics fleets and public transportation. Reduced wear, longer service intervals and simplified maintenance workflows translate into lower total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifecycle. When deployed across large commercial fleets, these advantages compound to deliver substantial long-term financial and operational value.
8. Industry Applications Beyond Road Vehicles
The same propulsion technologies that power modern commercial EVs are now extending into broader heavy-duty and industrial sectors. Electric vessels and ferries benefit from the high torque and corrosion-resistant direct drive configurations. Airport and port ground support equipment rely on zero-emission, low-noise operation, making integrated electric propulsion an ideal solution. Agricultural machinery, construction equipment and industrial automation systems also adopt smart motor control technology to achieve higher operational precision, lower energy consumption and significantly improved durability.
9. Strategic Outlook: Building Future-Ready Commercial EV Platforms
The next generation of commercial EV platforms will prioritize high power density electric motors, intelligent motor controllers, durable direct drive architectures and deeply integrated power electronics. Modular propulsion designs will allow OEMs to cover an entire range of commercial vehicles from trucks and buses to specialized machinery and marine vessels when using the same scalable core technology. With software-defined torque management, intelligent power control and adaptable system architecture becoming industry standards, integrated electric propulsion systems are set to define the competitive foundation of future commercial mobility. As global industries accelerate toward electrification, propulsion systems built on these principles will lead the development of efficient, reliable and future-ready commercial EV ecosystems.