Which Motor is Used in Electric Buses? An In-Depth Analysis of Mainstream Technologies and Cutting-Edge Trends
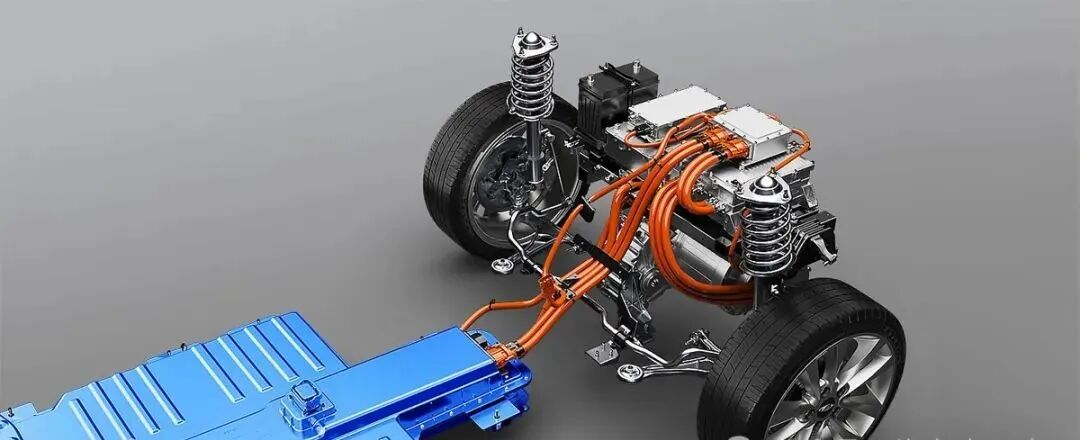
In the global wave of transition towards zero-emission urban public transport, the core component determining the performance of electric buses—the drive motor—directly impacts vehicle efficiency, range, and reliability. Currently, industry solutions are competing around higher efficiency, greater integration, and smarter control. Advanced drive systems, such as Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) series with power ratings covering 60kW to 350kW, are meeting the stringent demands of various vehicles from mini-vans to heavy-duty buses through highly integrated designs. This article provides an in-depth analysis of mainstream motor technologies, key technical challenges, and future trends incorporating cutting-edge solutions in the electric bus sector.
i. Comprehensive Comparison and In-Depth Analysis of Mainstream Motor Technologies
1. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM): The Mainstream Choice for High-Performance Buses
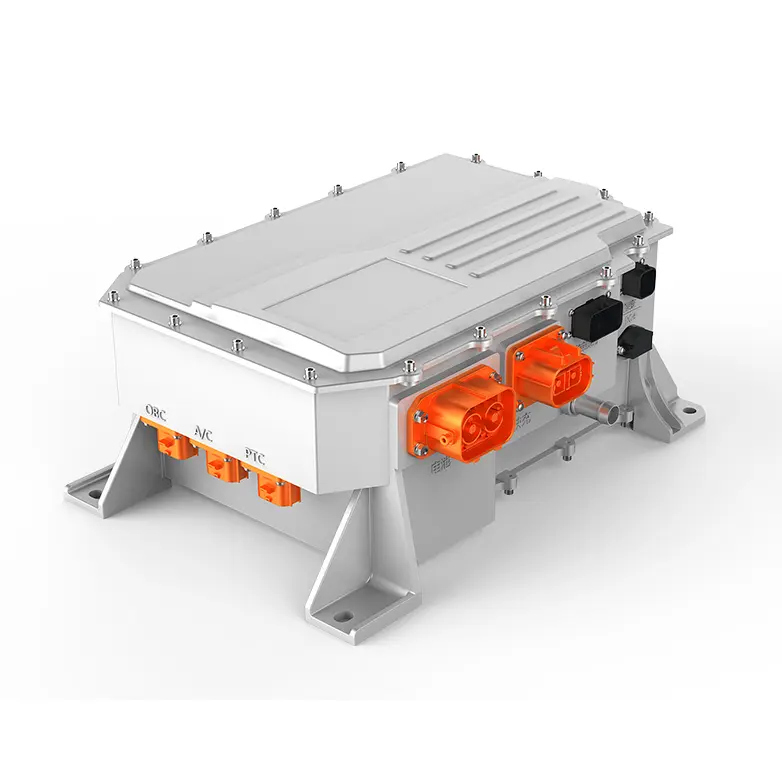
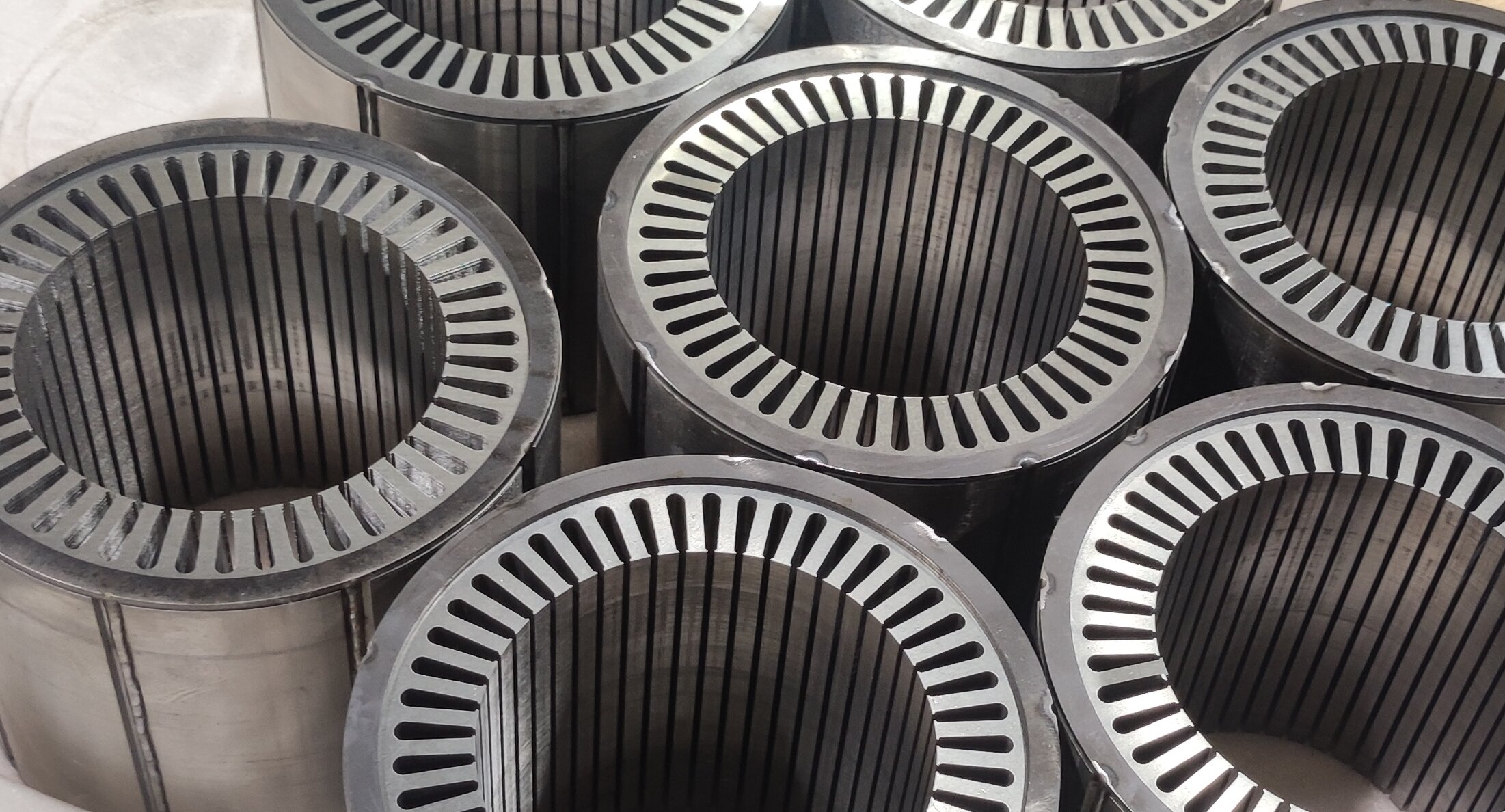
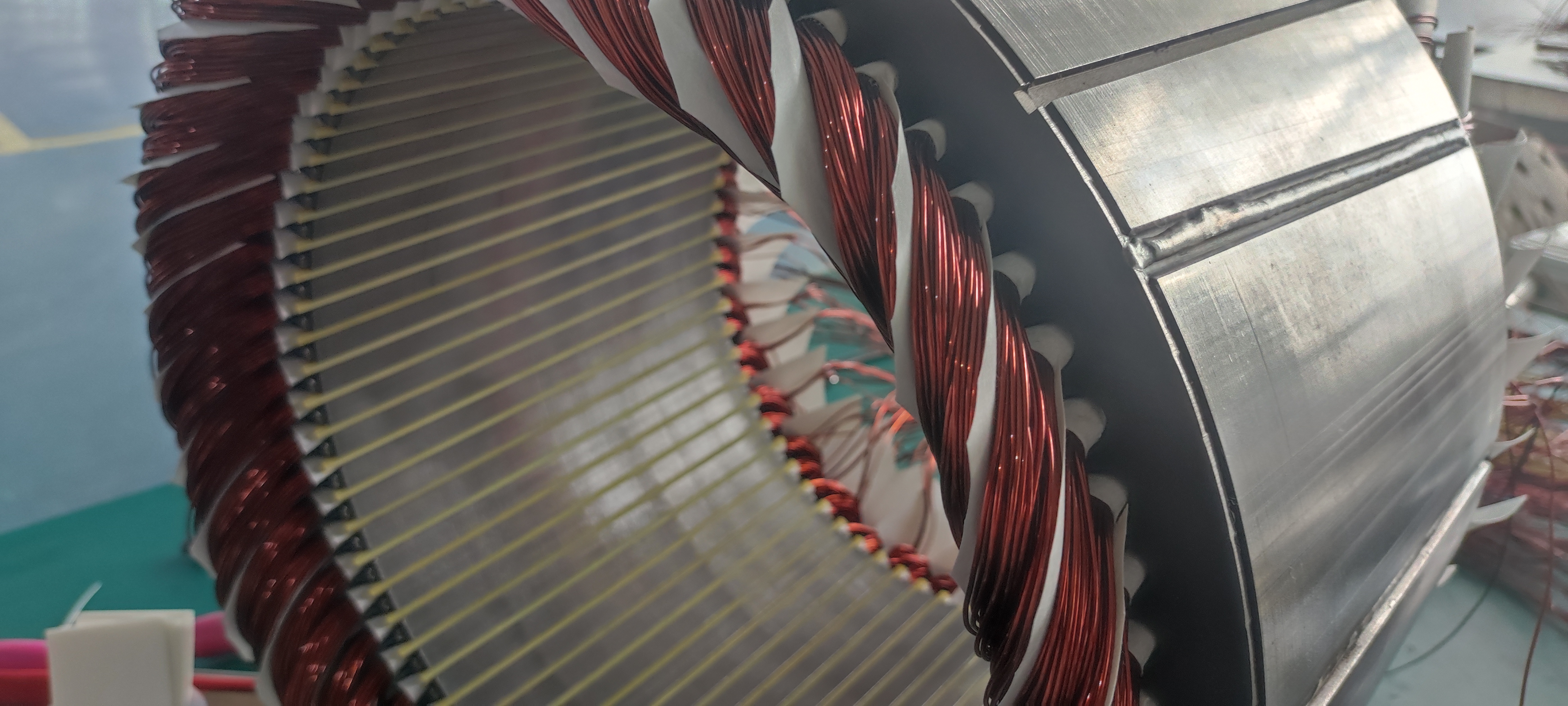
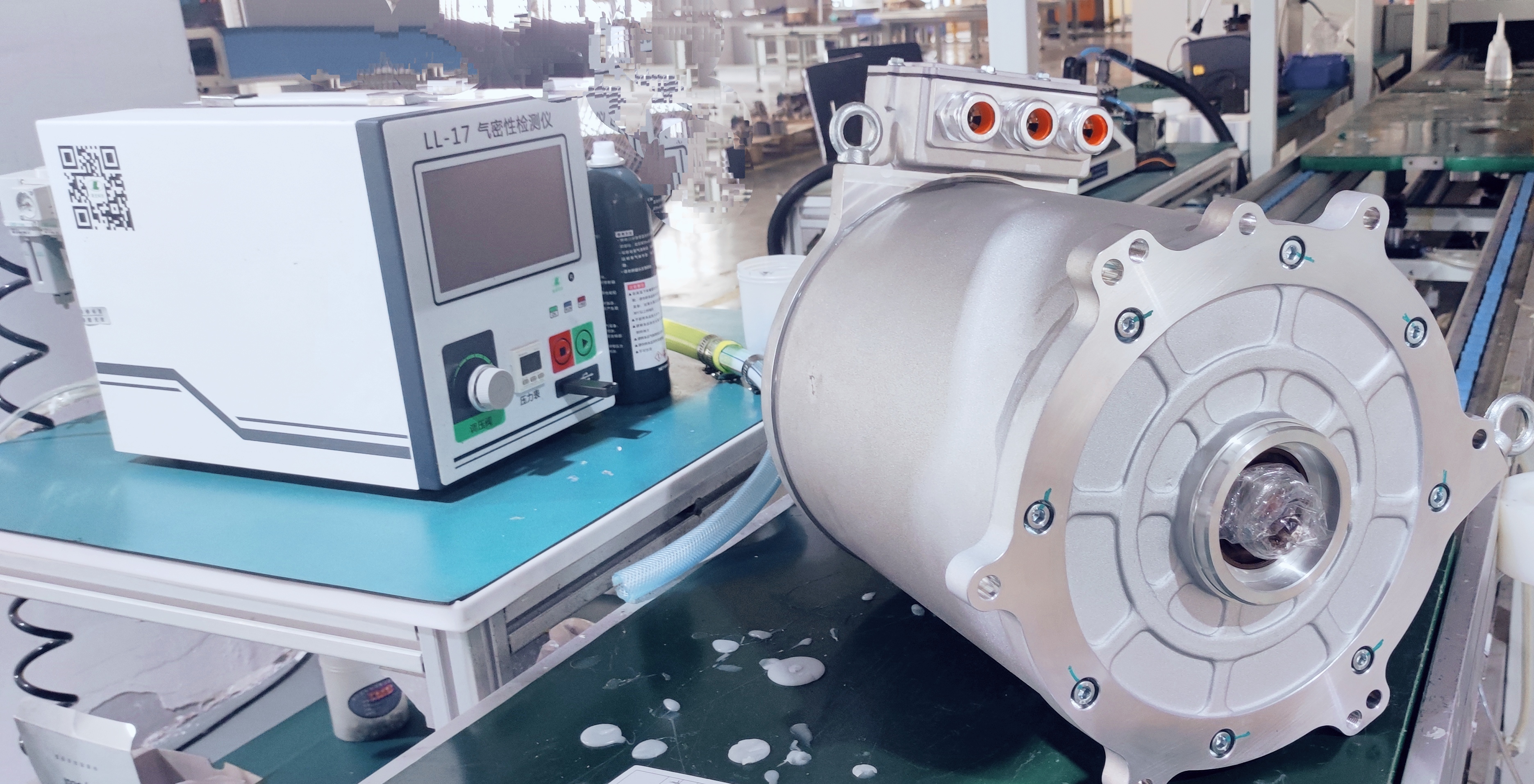
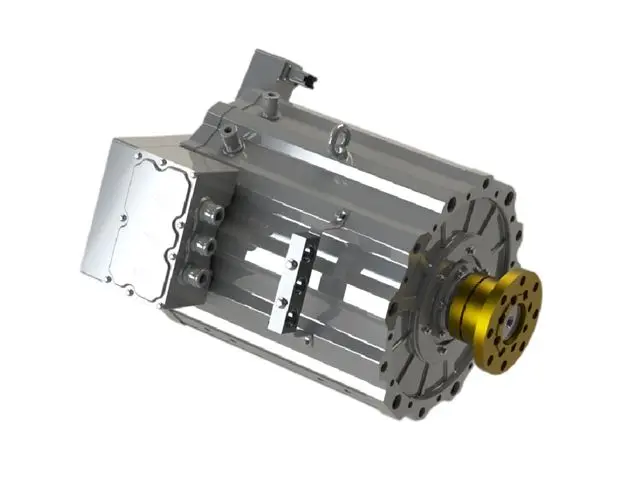
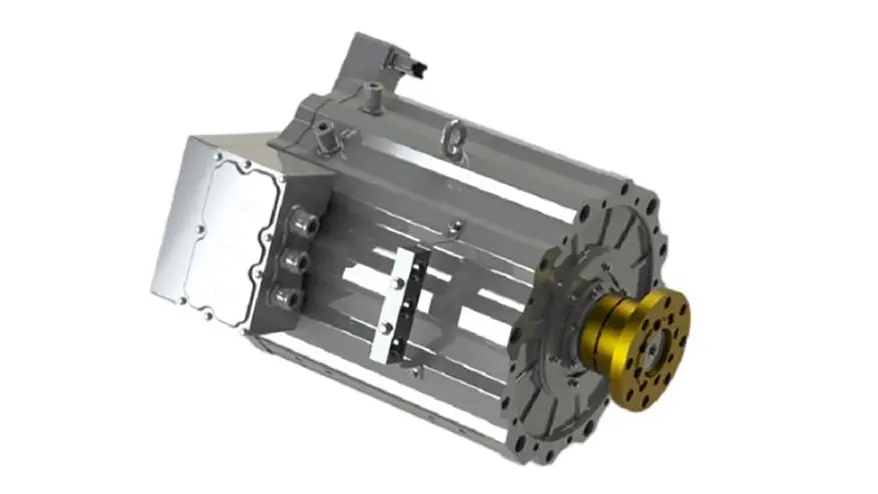
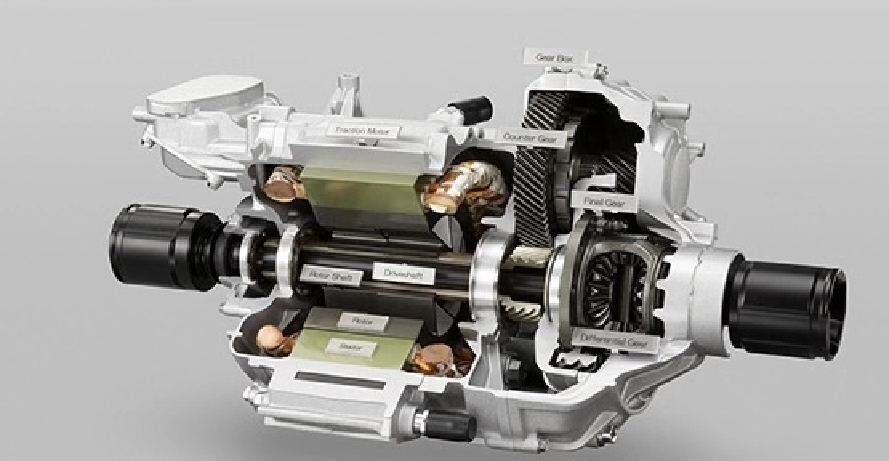
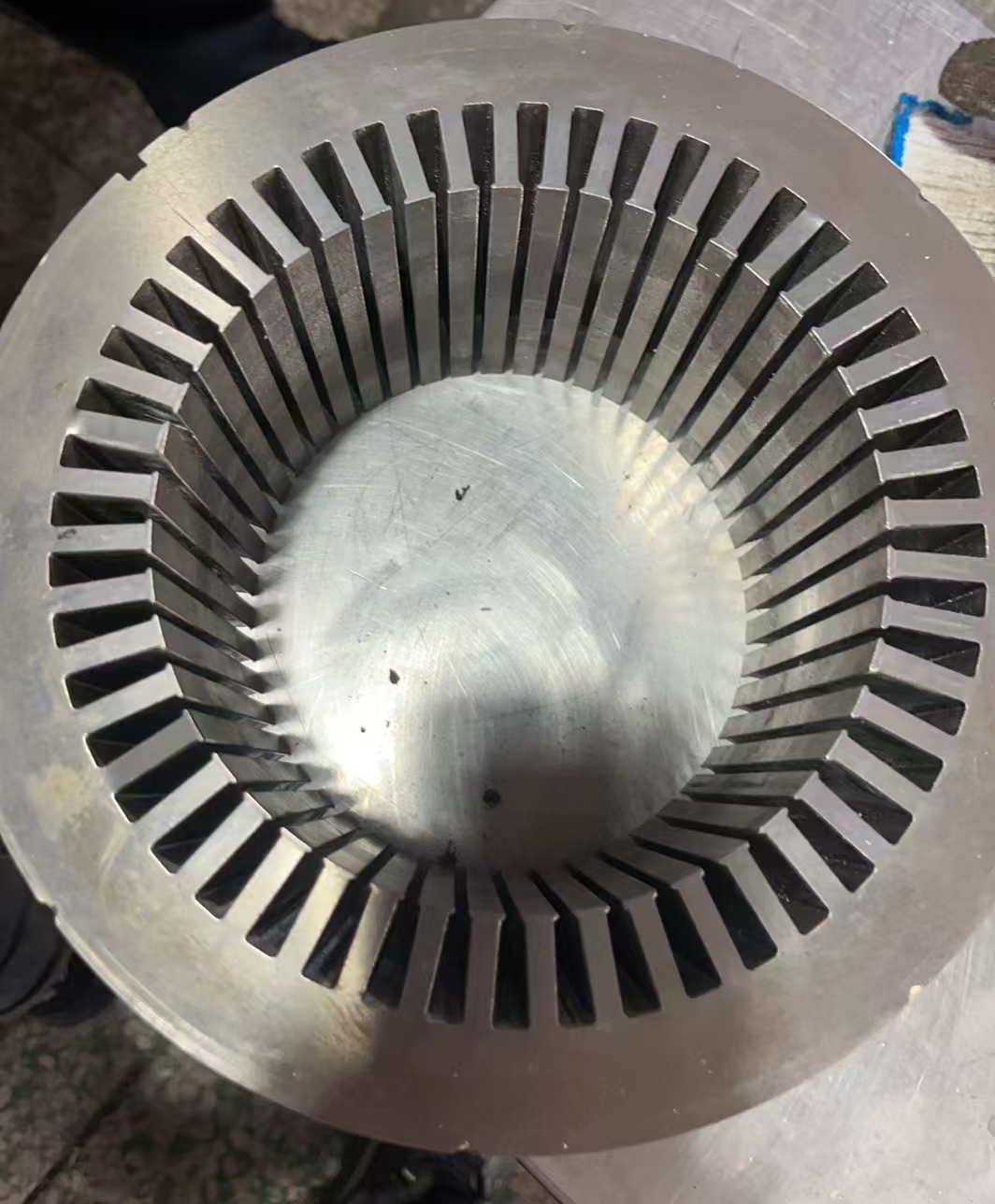
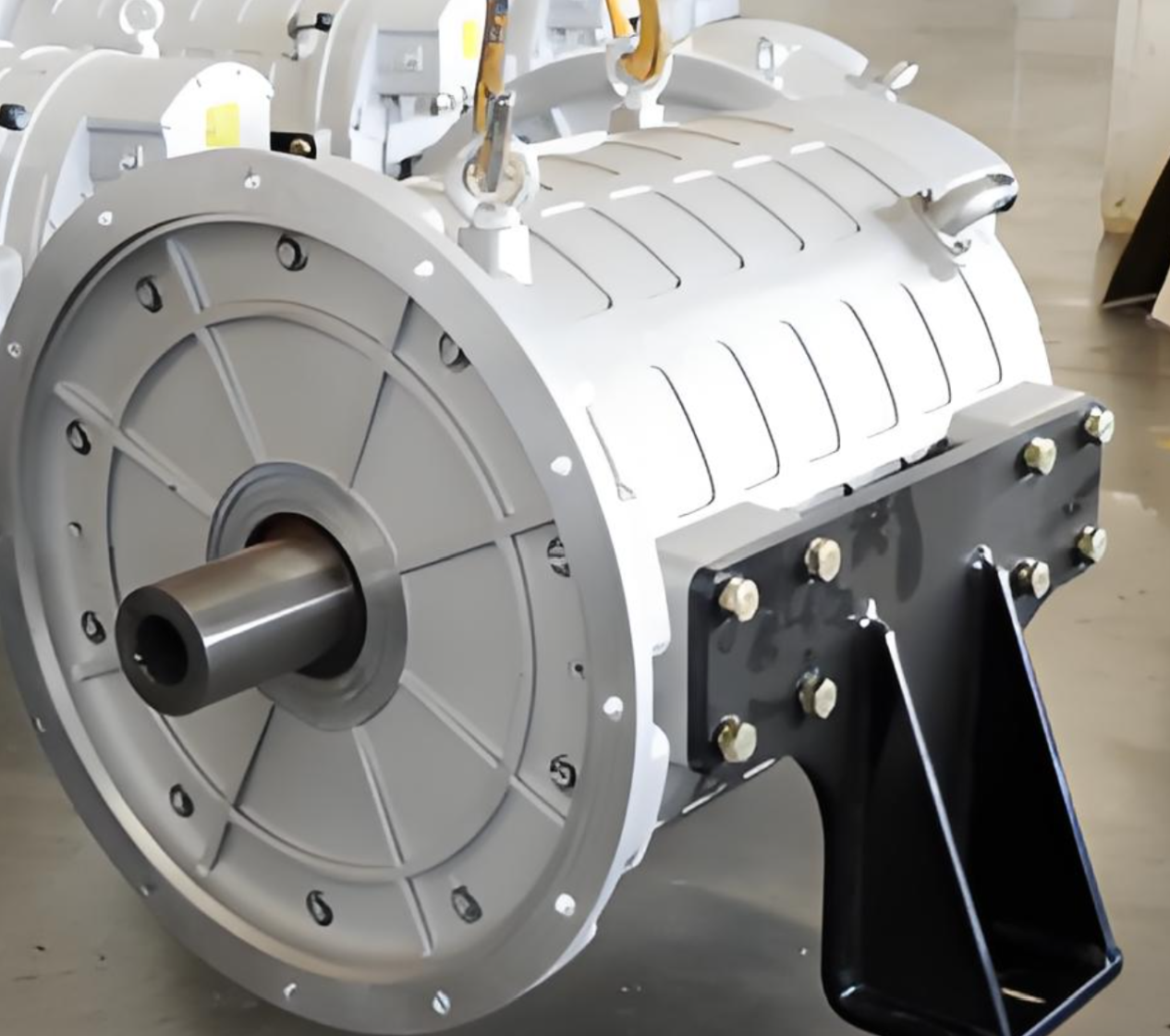
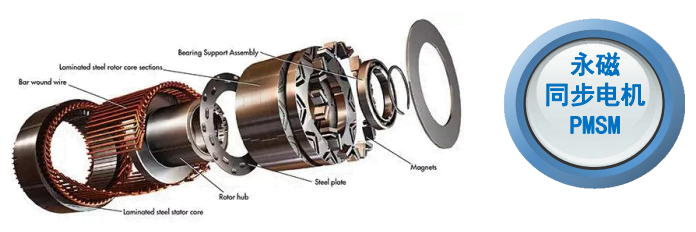
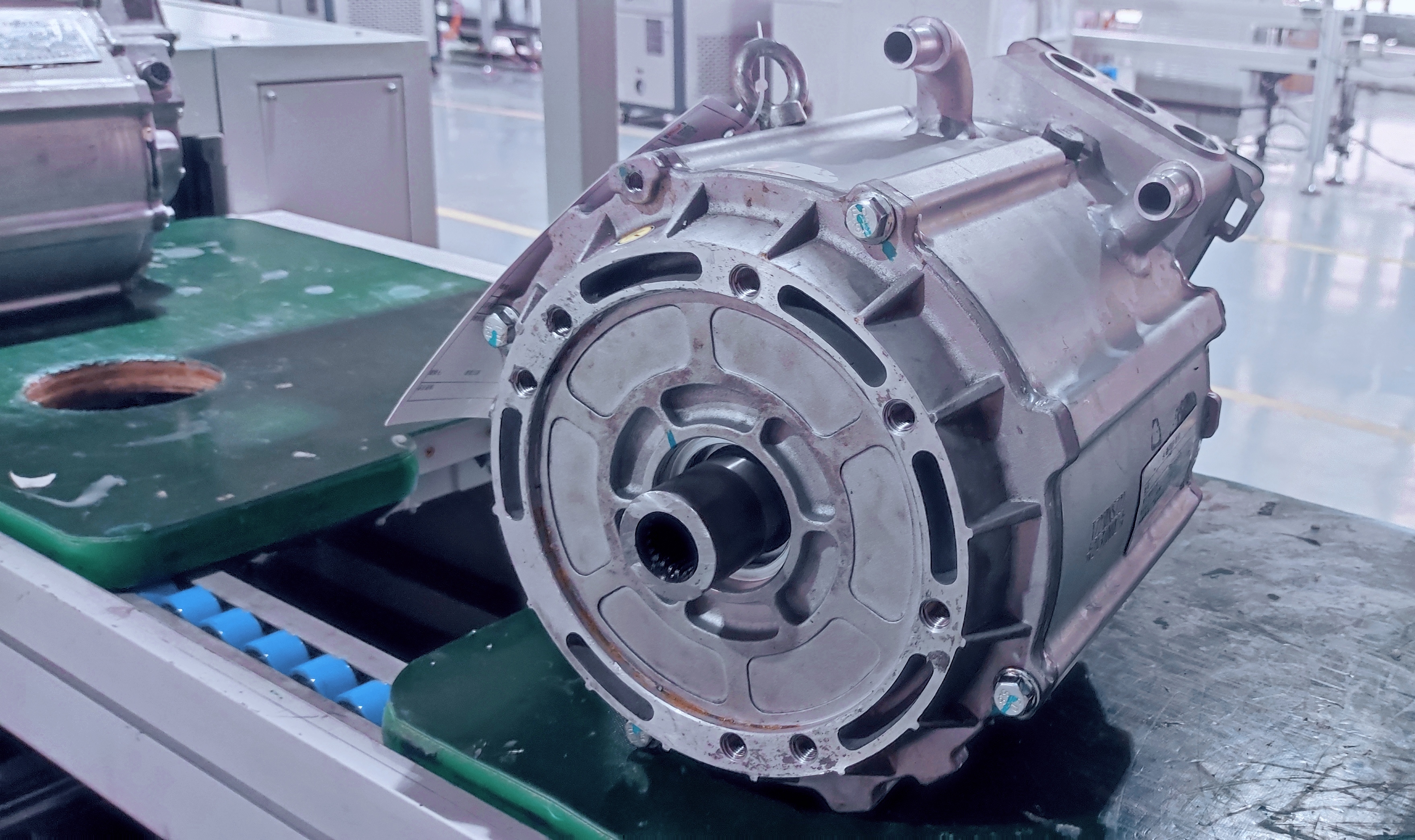
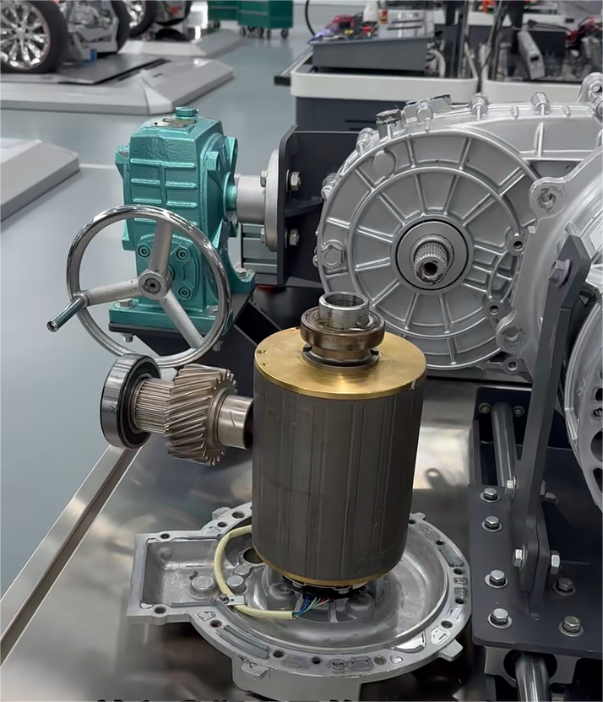
PMSM motors have become the absolute mainstream for mid-to-high-end electric buses due to their exceptional power density and efficiency. Their technical core lies in using high-performance rare-earth permanent magnet materials (like Neodymium magnets) to create the rotor magnetic field.
Current advanced technical features include:
-
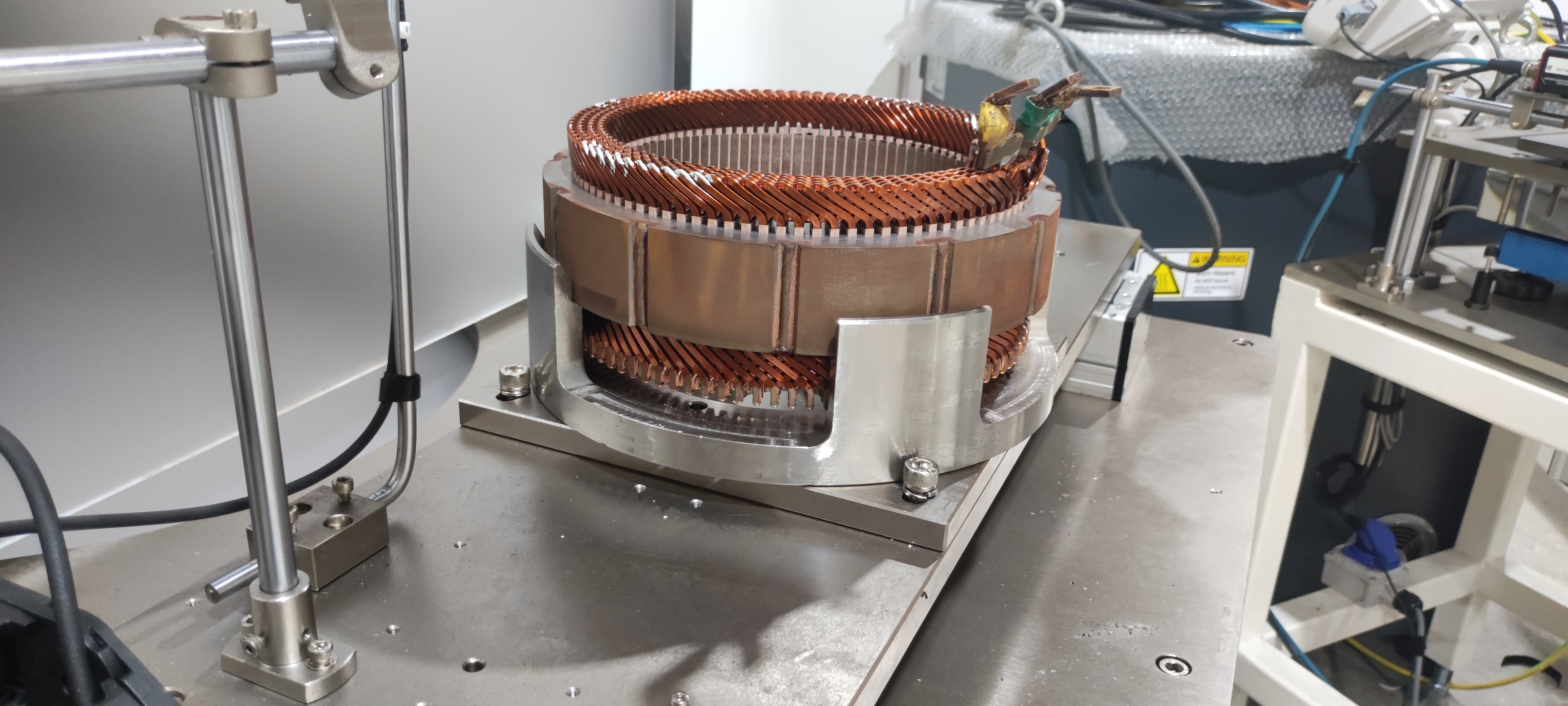
High Power Density & Compact Structure: Through optimized magnetic circuit design, new-generation motors achieve significant power increases while maintaining a compact structure. For instance, certain advanced PMSM models utilize interior permanent magnet (IPM) rotors and optimized stator slot designs, achieving high torque density and a wide constant power speed range, enabling the placement of high-power drive units within limited chassis space.
-
-
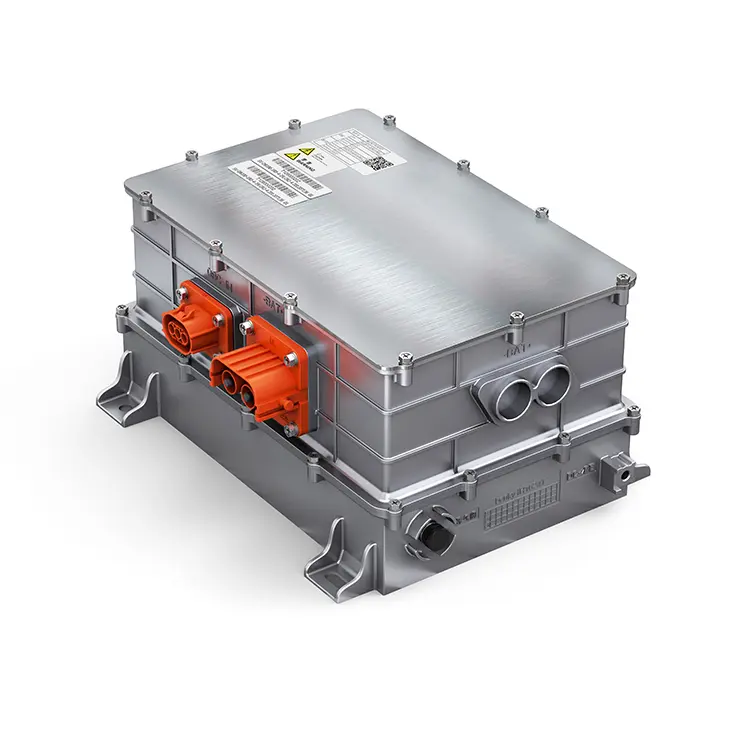
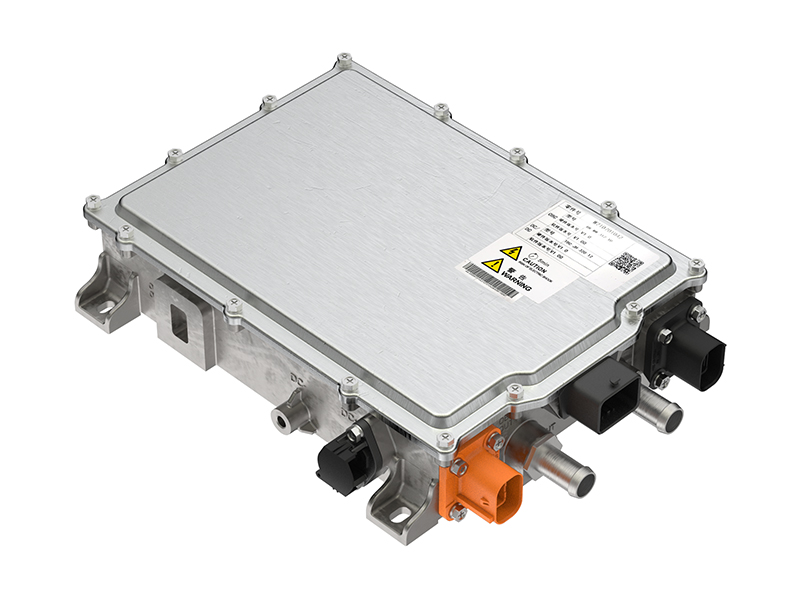
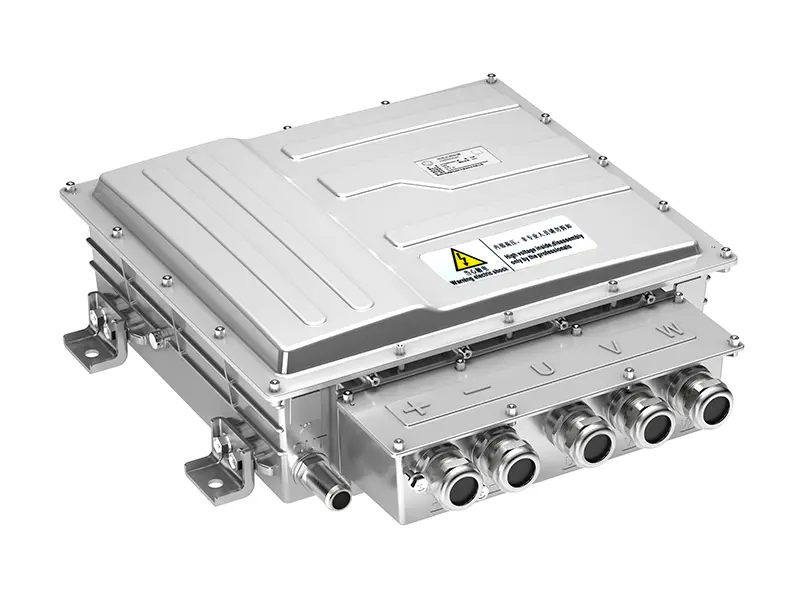
Full-Range Efficient Control & Advanced Controllers: With advanced Field-Oriented Control (FOC) algorithms, the motor maintains high efficiency across a wide speed range. The matching advanced Motor Controller Unit (MCU) often utilizes double-sided water cooling technology and supports SVPWM modulation strategies, ensuring stable high-power output and low harmonic distortion under high-frequency operating conditions.
-
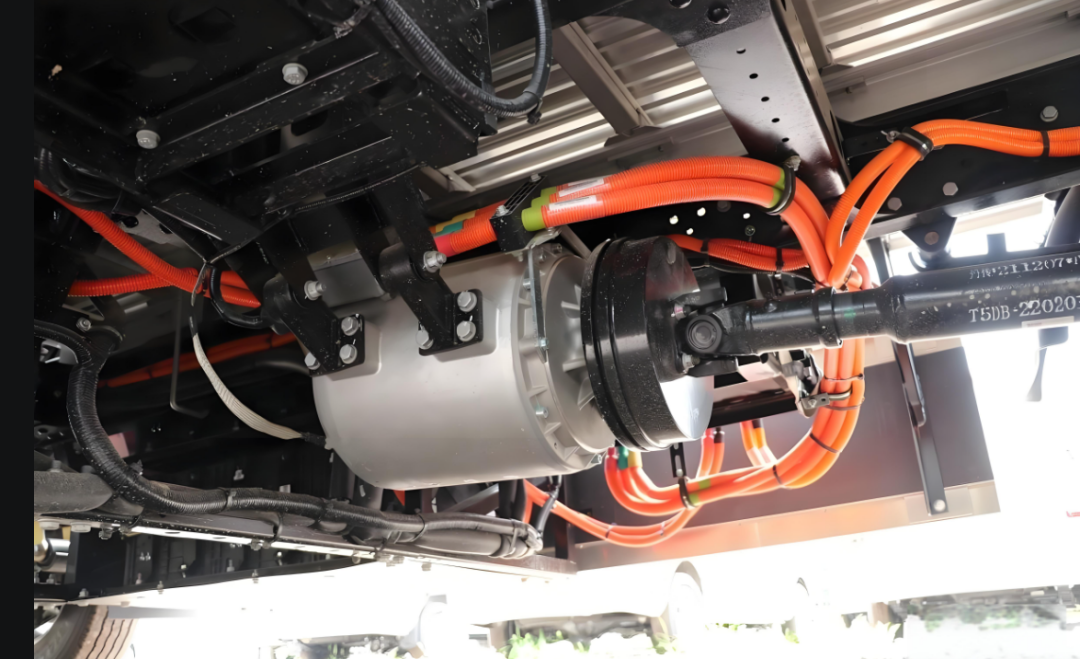
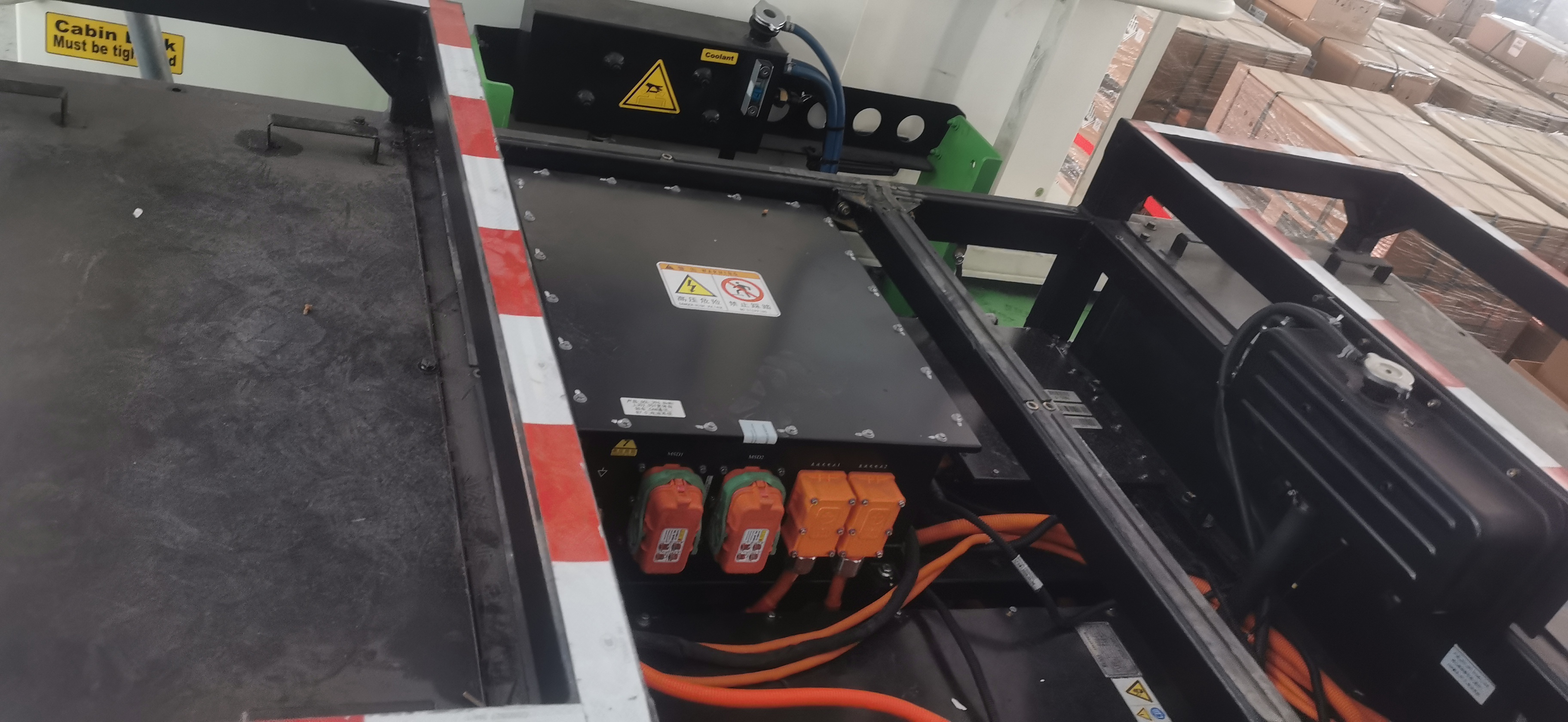
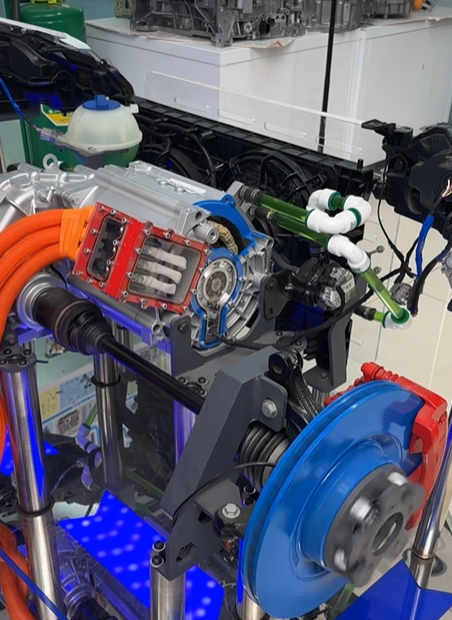
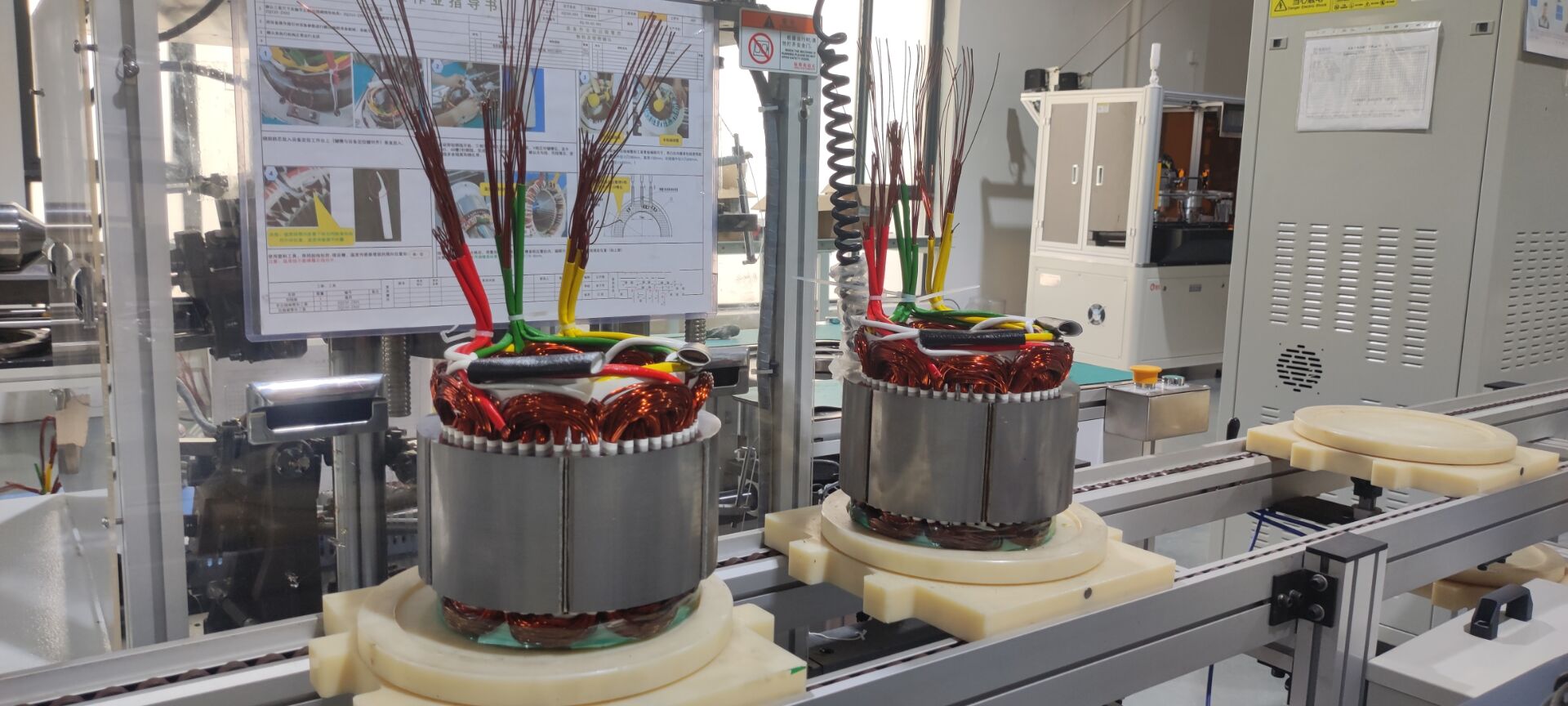
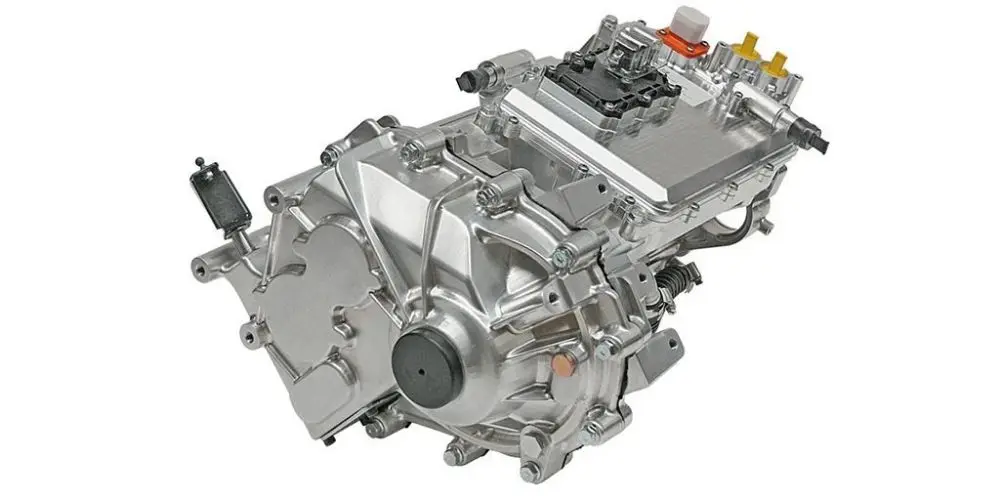
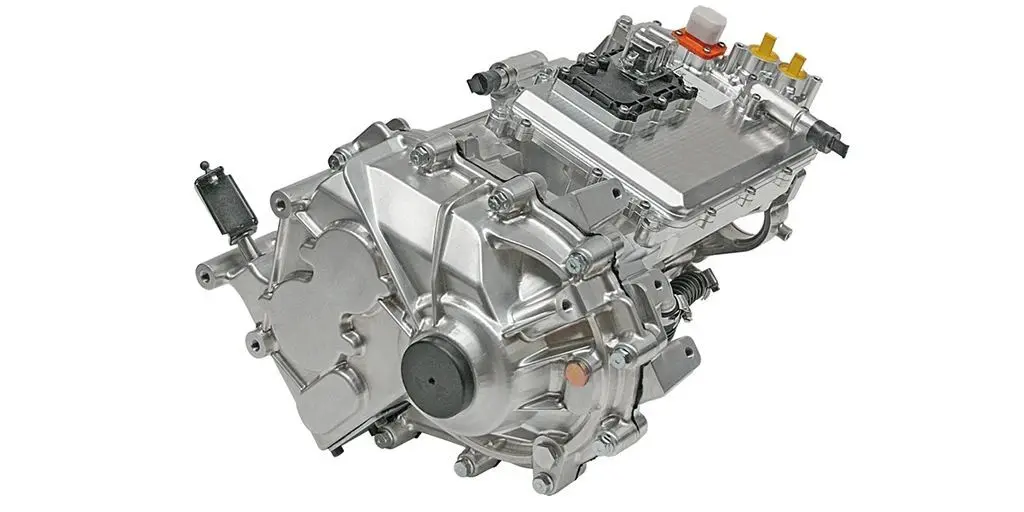
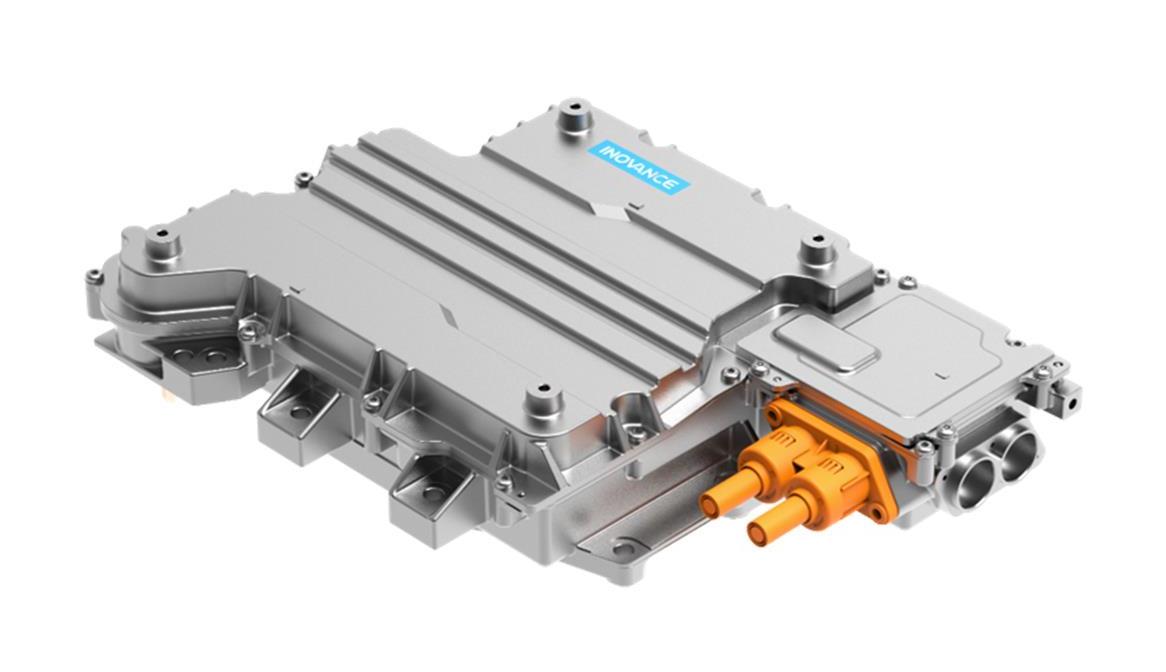
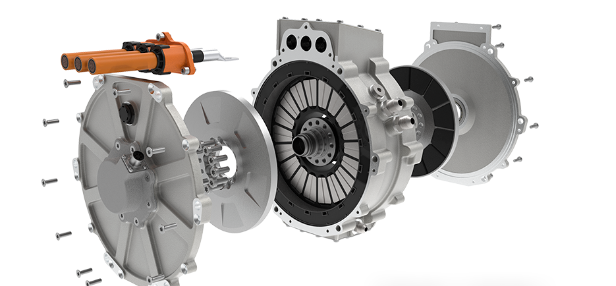
Integration and Lightweighting: Highly integrated design of the motor, controller, and gearbox has become a trend. This "multi-in-one" e-drive axle not only reduces connection components but also reduces system weight. Leading integrated solutions in the industry involve the holistic design of the motor, gearbox, and controller, effectively reducing part count, volume, and weight.
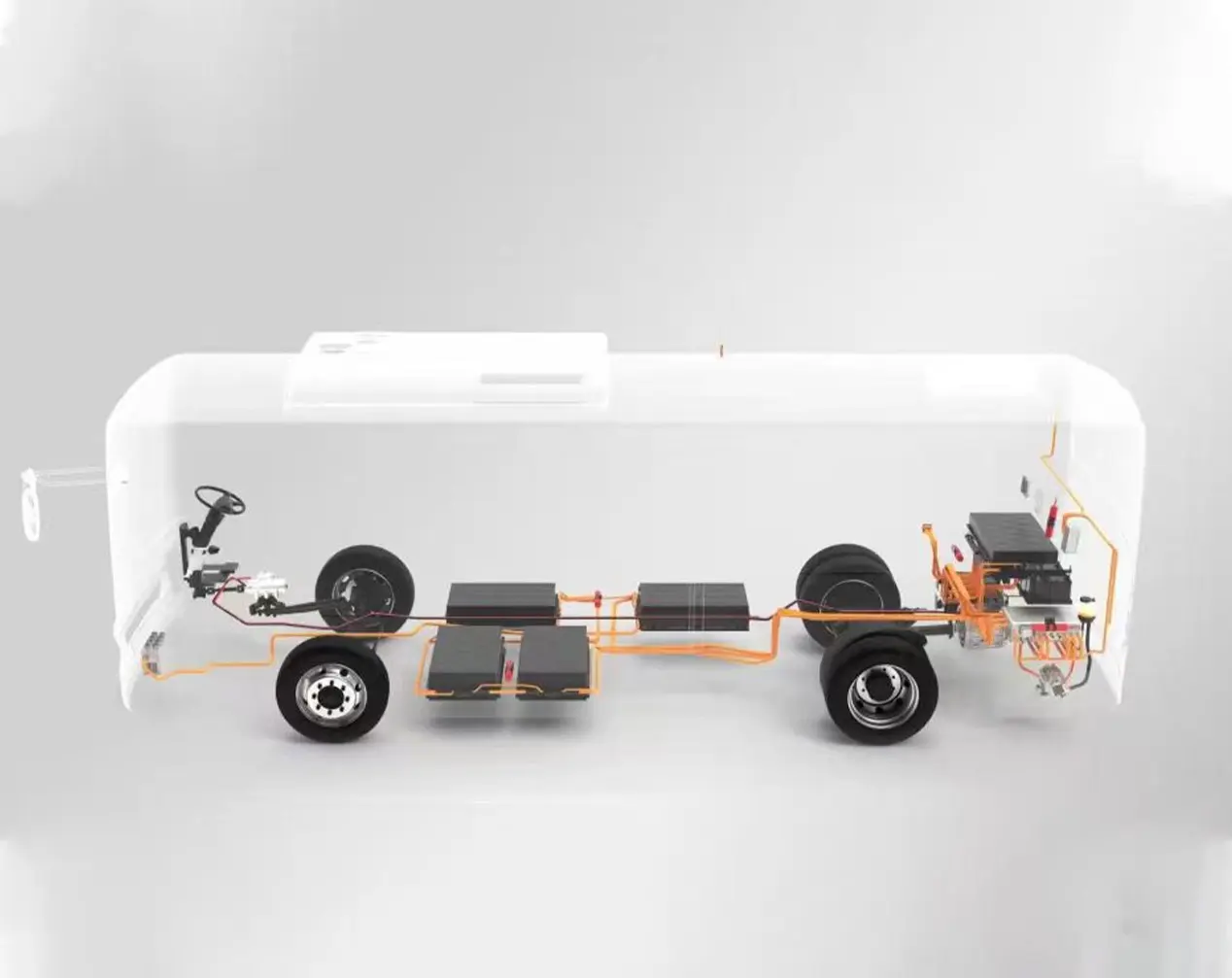
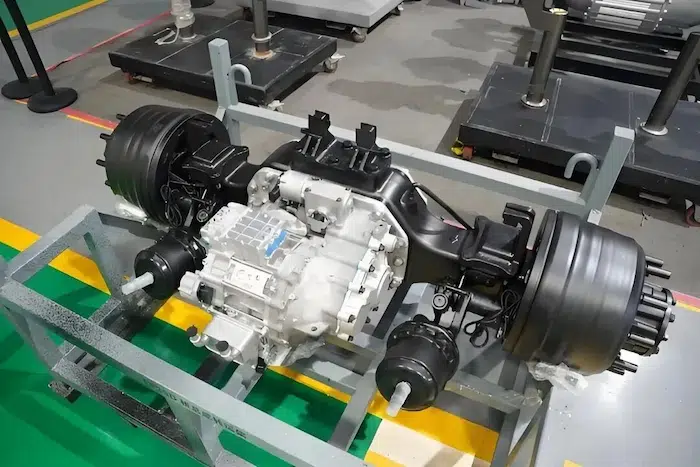
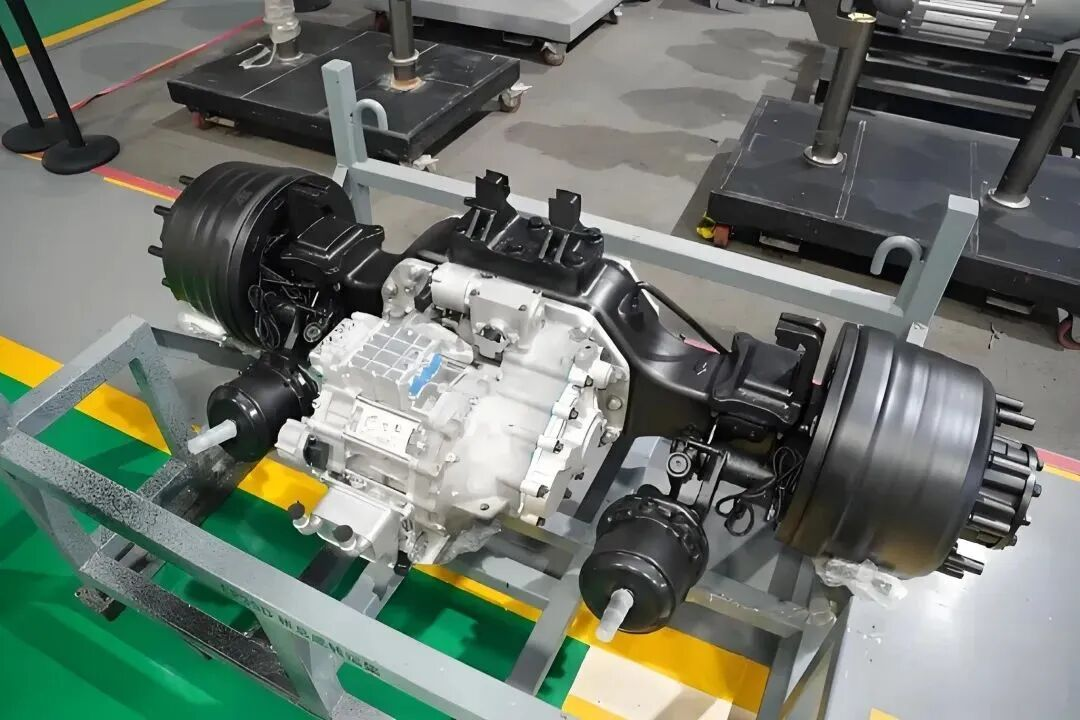
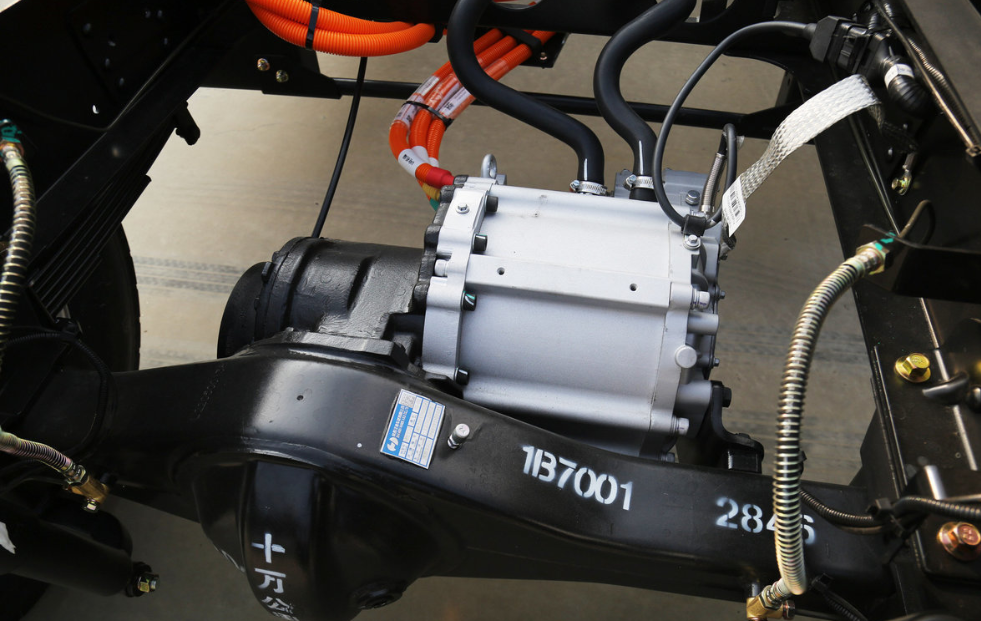
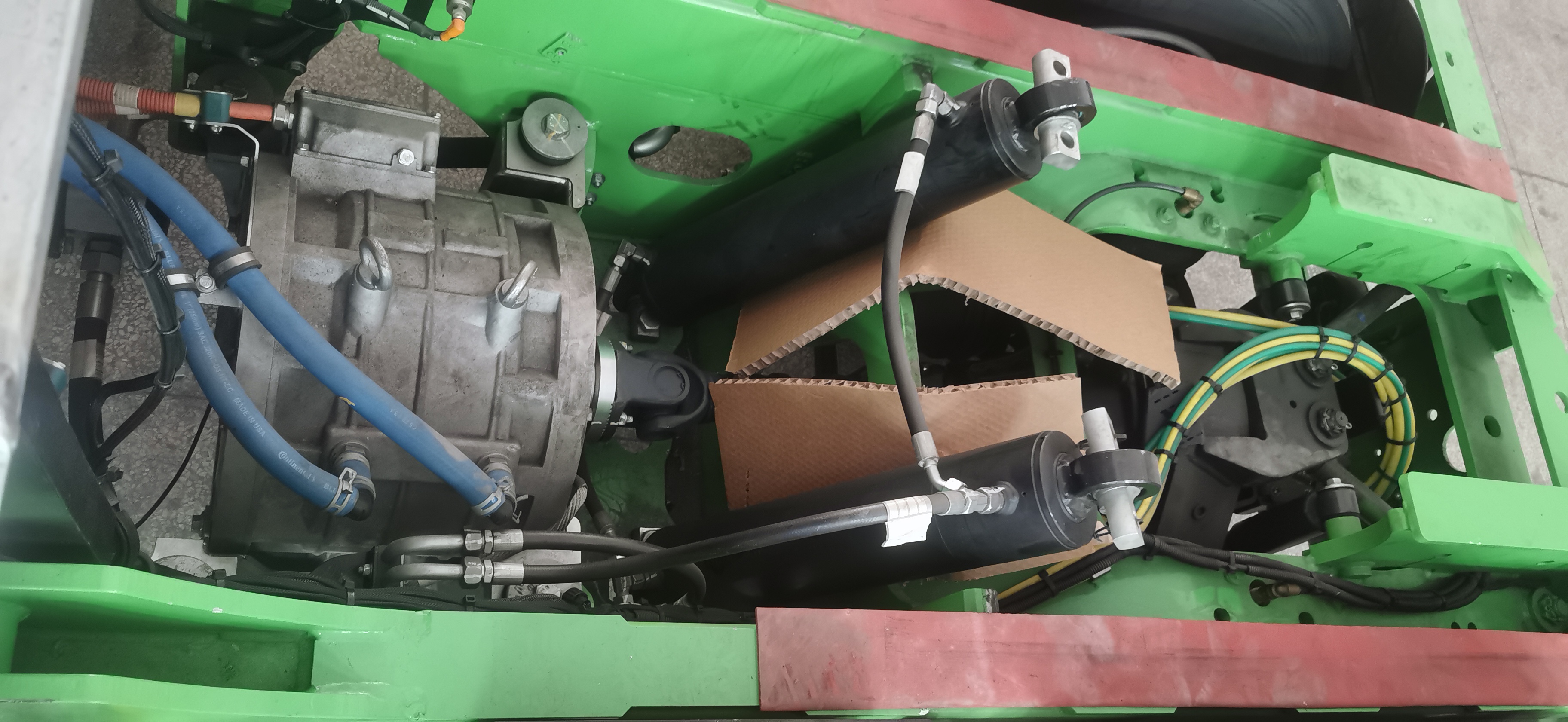
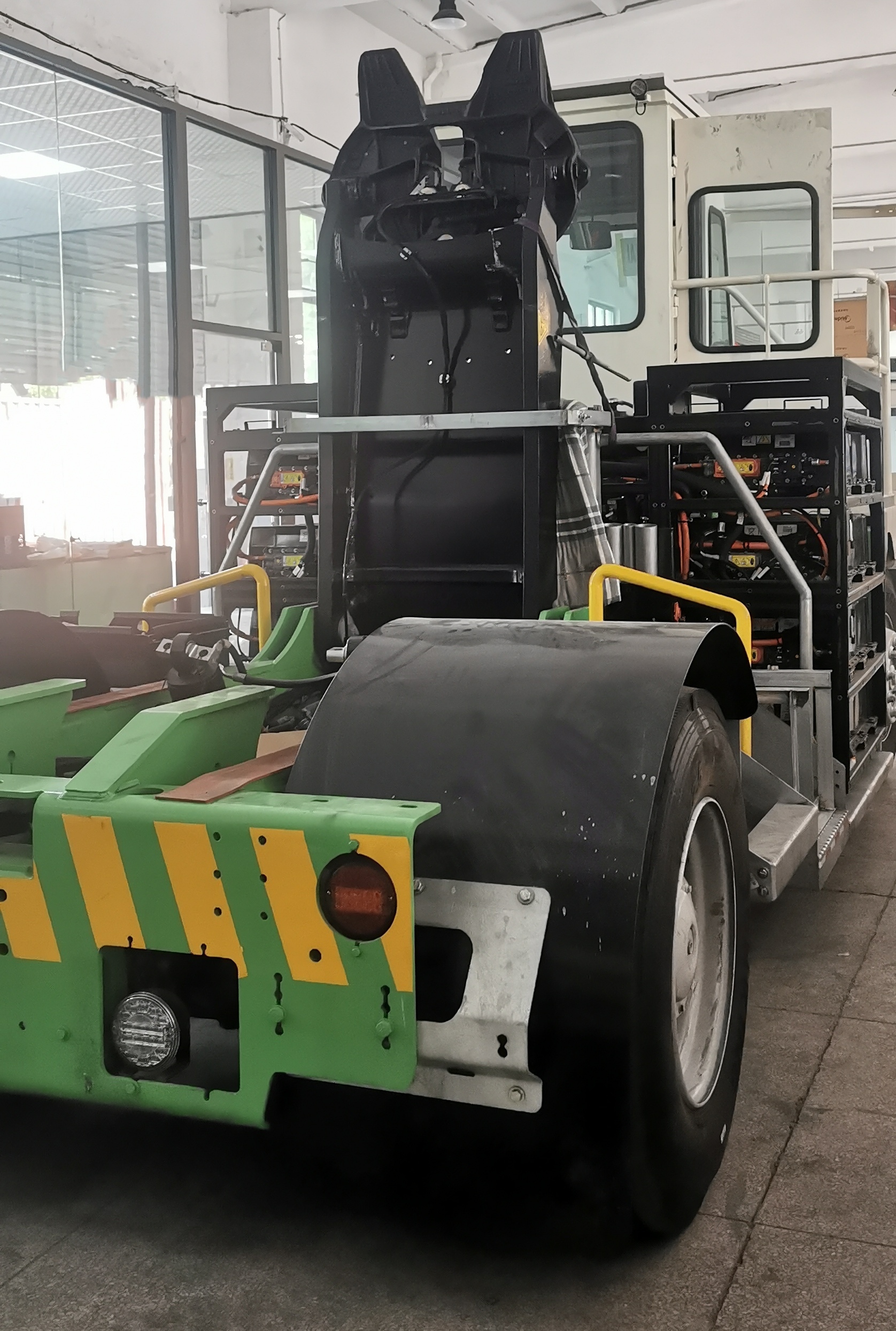
2. Integrated E-Axles: An Innovative Path for Centralized Drive
The Central Drive E-Axle is another important technological pathway. It highly integrates the motor, gearbox, and differential into a compact powertrain.
Its core advantages and technological progress are reflected in:
-
High Integration & Convenient Packaging: E-Axles designed for buses and trucks feature a high degree of integration, freeing up more space for chassis layout, facilitating the placement of battery packs and other systems.
-
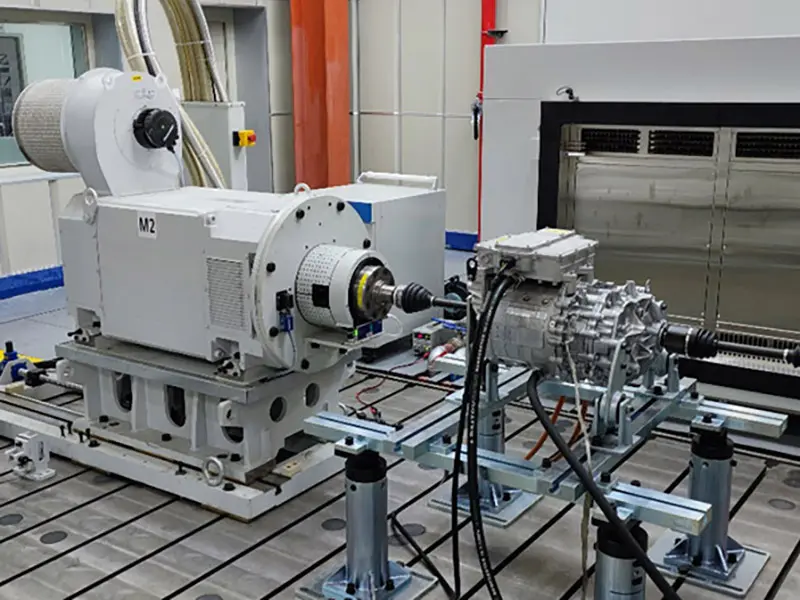
Excellent Efficiency and Reliability: Utilizing optimized gear design and efficient lubrication systems results in high transmission efficiency. Rigorous bench and road testing ensure product reliability and durability. This approach balances the high efficiency of traditional central drives with packaging flexibility.
ii. Key Technical Challenges and Innovative Solutions for Electric Bus Motors
1. The Ultimate Pursuit of Thermal Management: From Basic Cooling to Intelligent Temperature Control
Efficient and stable motor operation heavily relies on excellent thermal management. Cutting-edge solutions have evolved into sophisticated multi-path collaborative cooling systems:
-
-
Stator Winding Direct Oil Cooling: Coolant oil flows directly inside channels within the hairpin windings, offering extremely high heat removal efficiency. Advanced thermal management systems employ strategies to independently monitor temperatures at multiple key points inside the motor, ensuring the system always operates within the optimal temperature window.
-
-
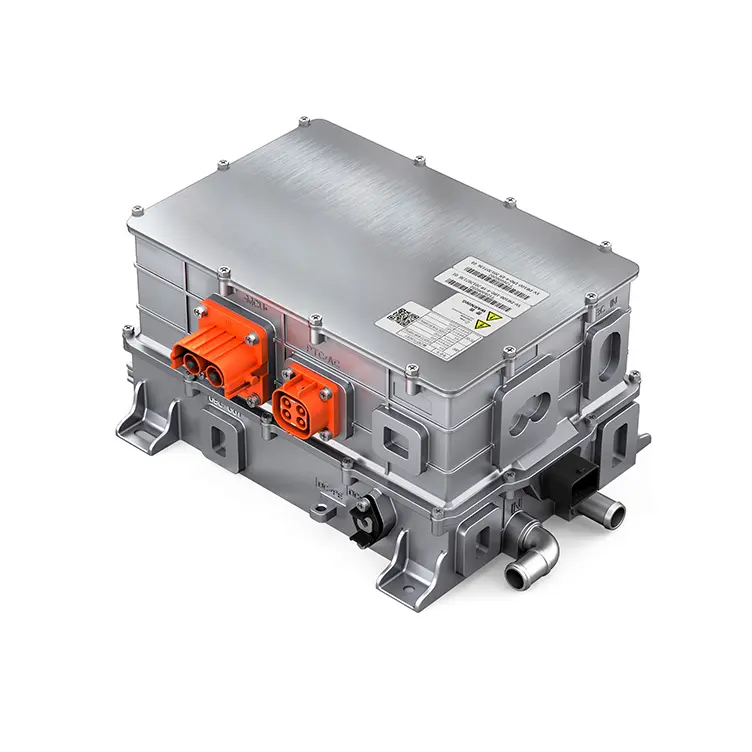
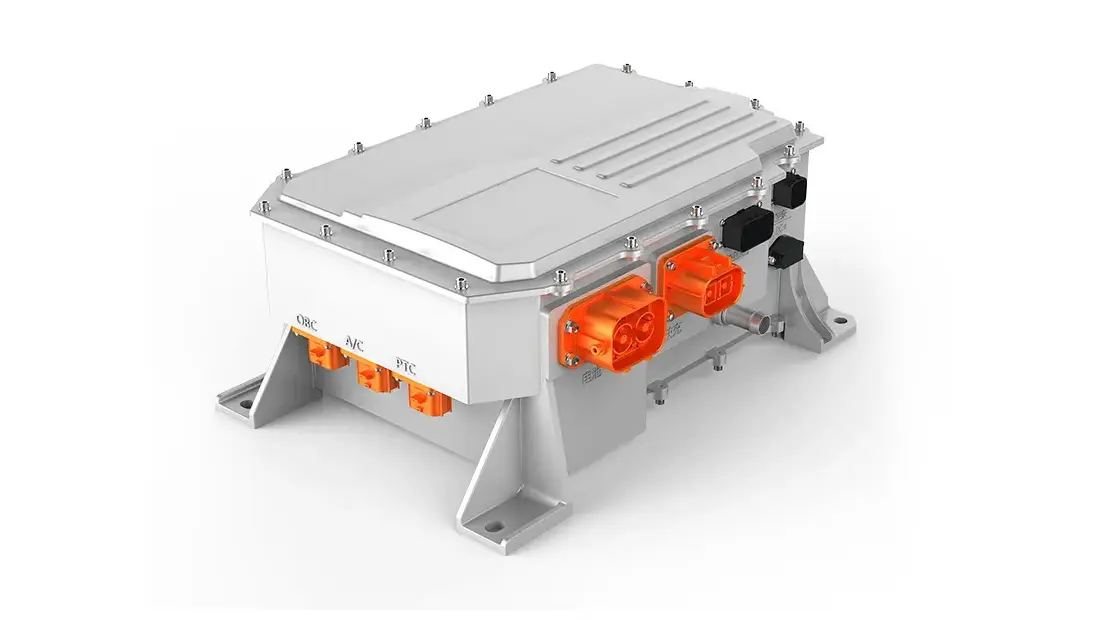
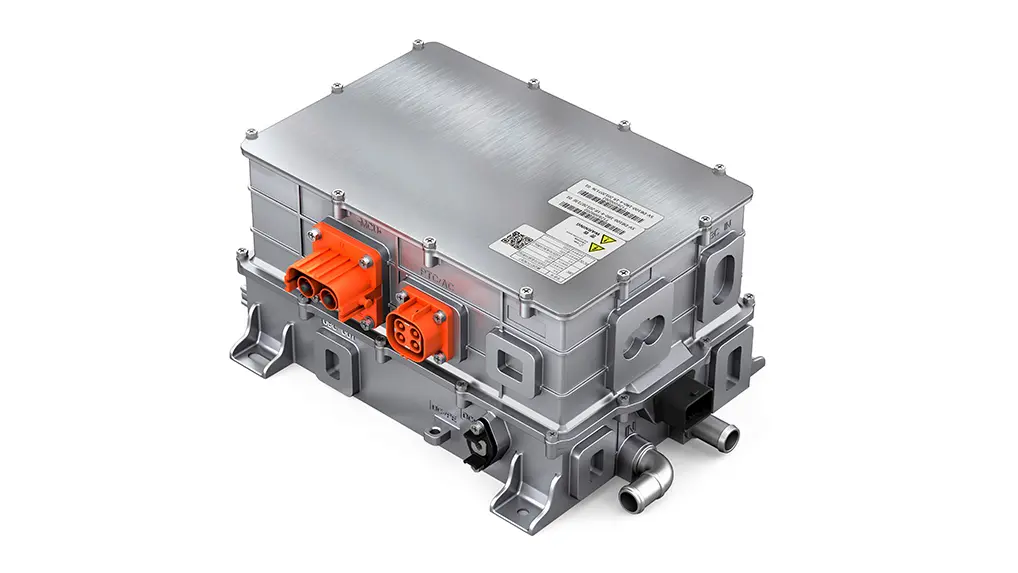
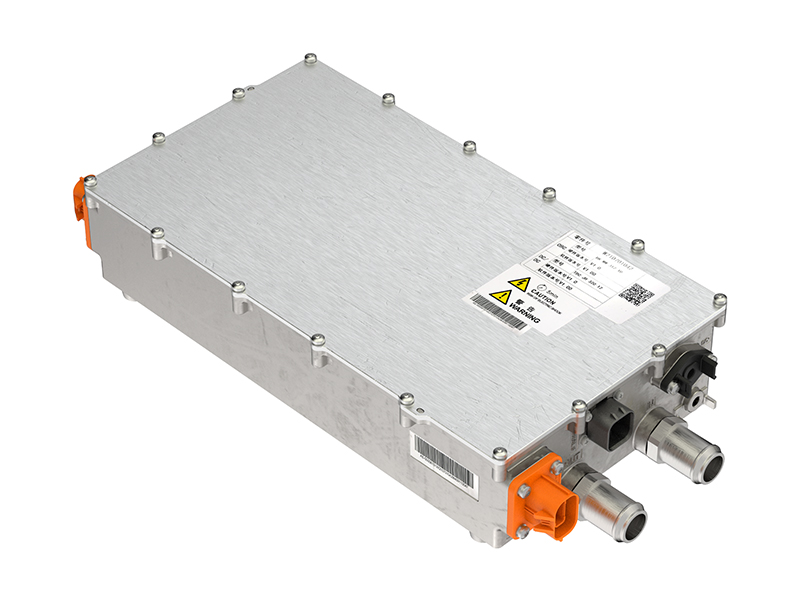
Intelligent Thermal Control Strategies: Based on real-time temperature feedback and predictive models, coolant flow and motor load are dynamically regulated. Some advanced integrated power supply units (CDU), which combine OBC, DCDC, and PDU functions, provide a stable energy distribution foundation for the vehicle's thermal management, including the e-drive system.
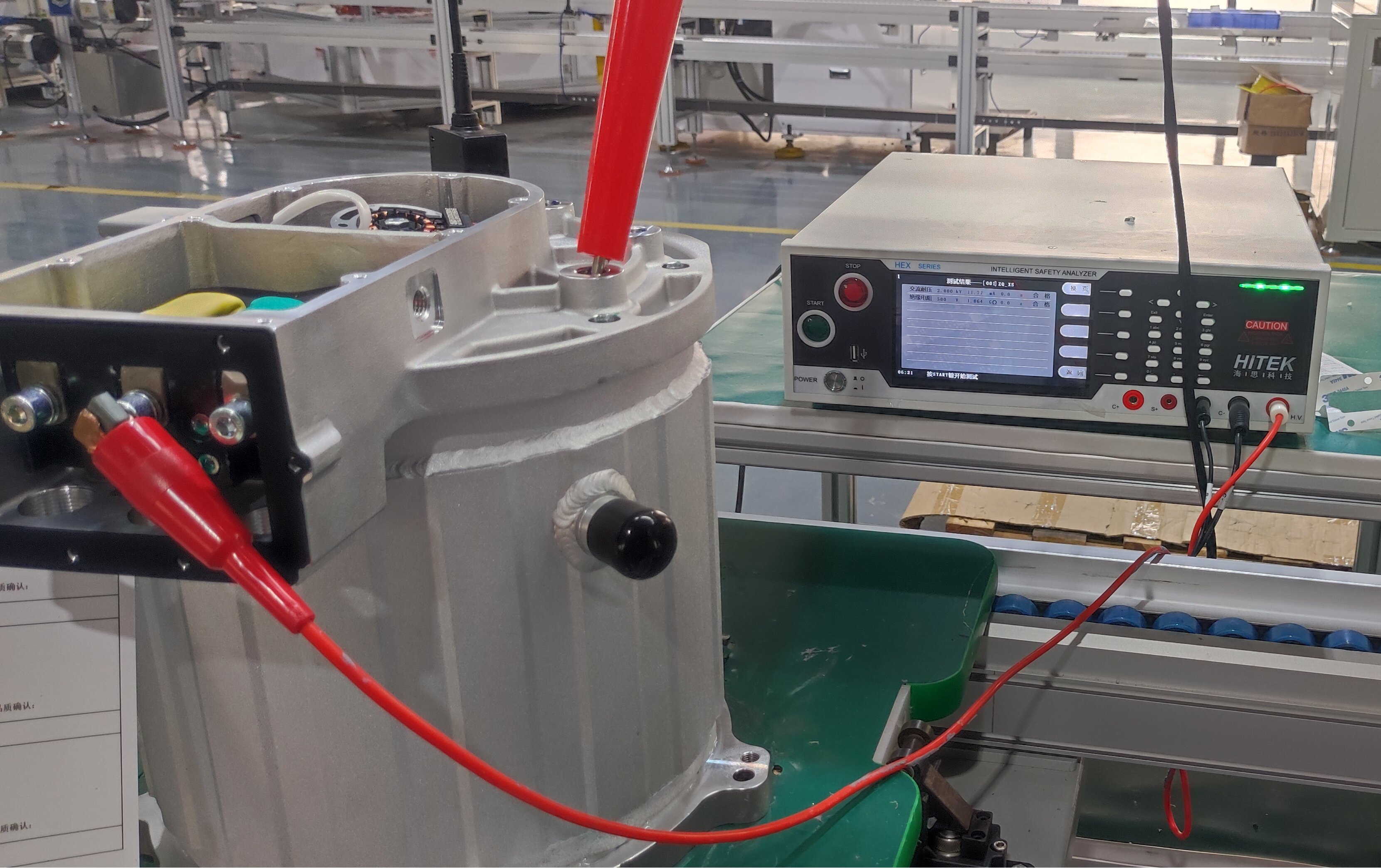
2. Ensuring System Reliability and Durability: From Design to Monitoring
Facing the daily high-intensity operation of buses, reliability is paramount. This relies on:
-
Key Material and Process Upgrades: Such as using high-temperature, high-coercivity rare-earth permanent magnets; in terms of process, automated winding technology and vacuum impregnation ensure consistency and reliability of insulation treatment.
-
Whole-Vehicle Matching and Control Strategies: Successful e-drive systems rely on deep whole-vehicle matching expertise and advanced control strategies. For example, motor controllers designed specifically for commercial vehicles feature optimized control logic for precise torque control and a smooth ride experience. Their energy conversion efficiency is significantly improved compared to industry averages.
iii. Integration and Synergy: System-Level Development Trends
The future competitiveness of electric buses will increasingly depend on the deep integration and intelligent synergy of the drive system with other vehicle parts.
1. Deeply Integrated E-Drive Platforms and Electric Chassis
Next-generation drive systems are moving towards integrating the motor, controller, gearbox, onboard charger, etc., into a single platform. A platform-based design philosophy allows the same e-drive platform to be adapted for different vehicle models and power requirements. Going a step further, complete electric chassis solutions are emerging. These integrate high-power PMSMs (sometimes featuring six-phase design for enhanced redundancy safety), large-capacity battery packs, dedicated front and rear axles, and suspension systems, providing a ready-to-use platform for vehicle manufacturers, greatly improving development efficiency and supply chain resilience.
2. Intelligent Linkage with Whole-Vehicle Energy Management
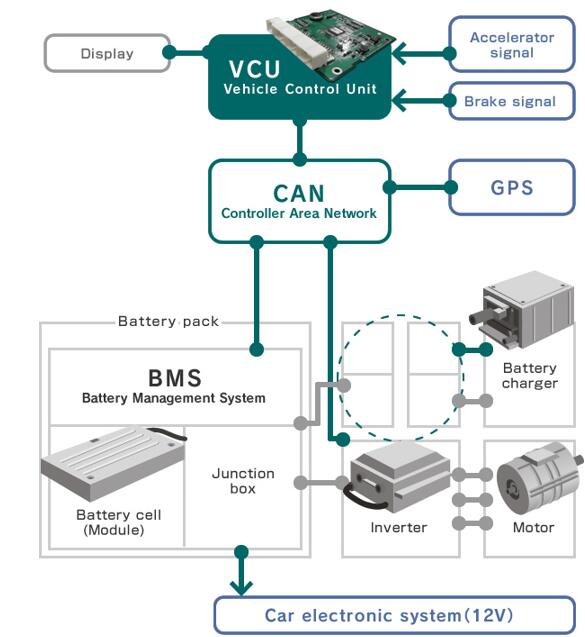
The motor becomes a core participant in the vehicle's energy flow management. Through real-time communication with the Battery Management System (BMS), Thermal Management System (TMS), and cloud platforms, predictive energy management is achieved. The Vehicle Control Unit (VCU), acting as the "brain" of the electric vehicle, coordinates the MCU, BMS, and other auxiliaries. Based on vehicle status and driver intent, it formulates optimal energy management strategies, thereby comprehensively improving energy efficiency.
iiii. Future Outlook: New Materials and Concepts Driving Technological Change
Technological evolution is endless. Some cutting-edge explorations are shaping the blueprint for the next generation of electric bus motors:
-
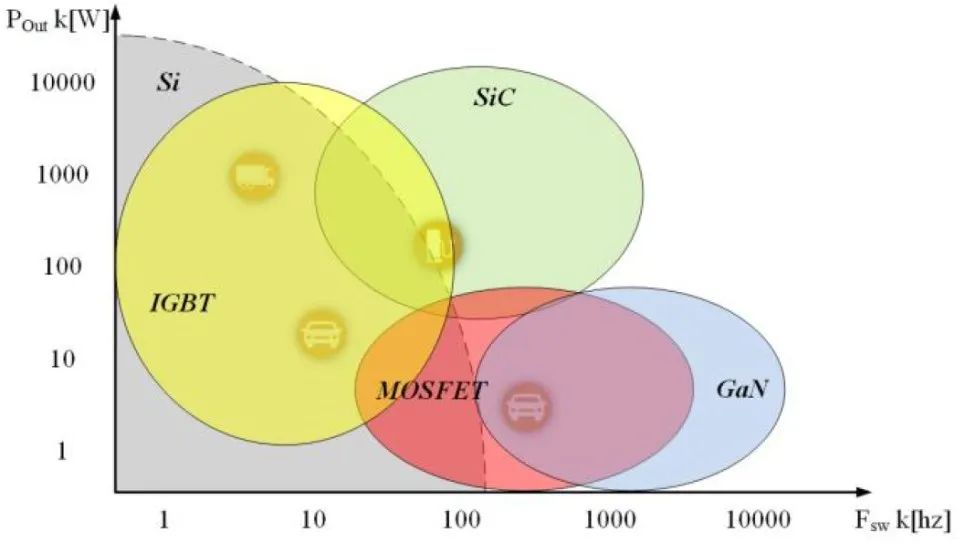
Application of New Materials: Using wide-bandgap semiconductors like Silicon Carbide (SiC) in controllers can significantly reduce switching losses. Research into low-heavy-rare-earth or even non-rare-earth permanent magnet materials is an important direction for addressing resource challenges.
-
Diversified Application Scenarios: Advancements in e-drive technology are expanding its application range to sectors like mining/port machinery and electric vessels. This places higher demands on environmental adaptability, power, and torque, consequently promoting diversified technological development.
Conclusion
From highly efficient and reliable Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors to highly integrated E-Axles and future-oriented electric chassis, electric bus drive technology is rapidly evolving towards integration, intelligence, and platformization. Solutions incorporating high-power density motors, intelligent thermal management, advanced control strategies, and predictive health monitoring are continuously pushing performance boundaries, providing stronger, smarter core power for green urban mobility globally. The choice of technology path increasingly focuses on lifecycle cost and benefits, aiming for a sustainable transition to public transport electrification.
This article is based on analysis of publicly available industry technical materials and development trends, aiming to provide objective technical interpretation. Specific technical parameters and applications should be verified with official manufacturer information.