The development trend of electric drive systems in 2026
The global electric vehicle (EV) industry is stepping into a new stage of high-quality development, and the electric drive system, as the "power core" of EVs, is undergoing a comprehensive upgrade driven by technological innovation. Among them, the electric vehicle control unit (VCU) has evolved from a traditional functional controller to the core command center of the electric drive system, becoming the key fulcrum shaping the development trend of electric drive systems in 2026.
This blog will deeply explore how the vehicle control unit in EV drives the innovation of electric drive systems, interpret the core development trends of electric drive systems in 2026, analyze the technical upgrade direction of VCU, and discuss its practical application effects and future evolution paths, helping readers fully grasp the technological frontier of the EV industry.
I. Introduction: The Core Upgrade Point of Electric Drive Systems - Electric Vehicle Control Unit
Looking back at the development of electric drive systems, the evolution from scattered electronic control units (ECUs) to integrated domain controllers has been centered on improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing performance. By 2026, this evolution has entered a critical stage dominated by the electric vehicle control unit.
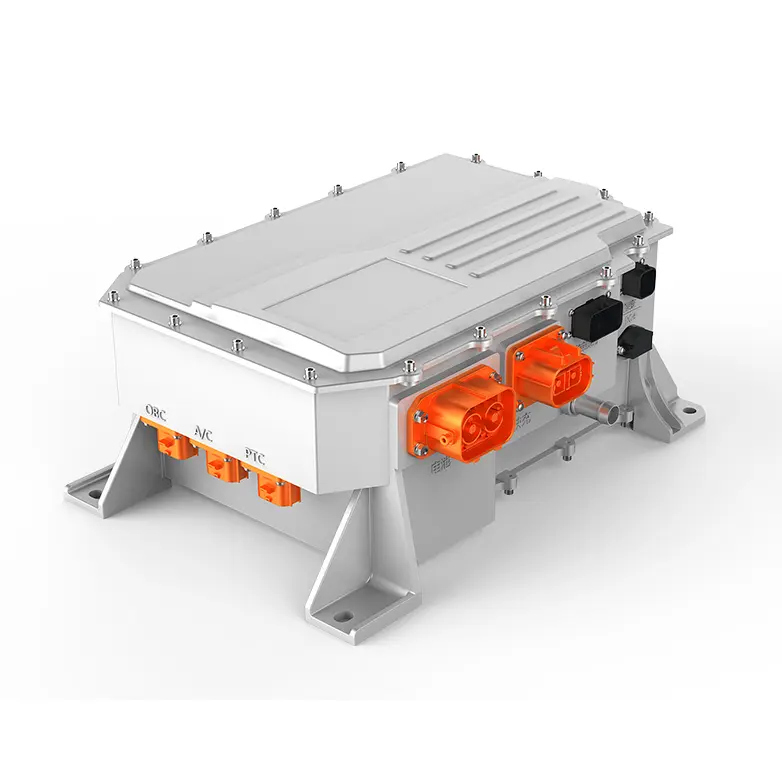
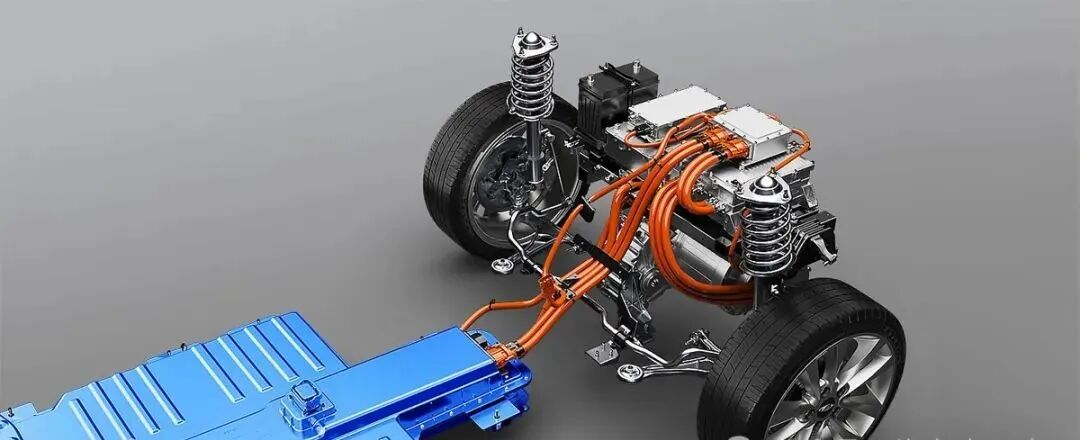
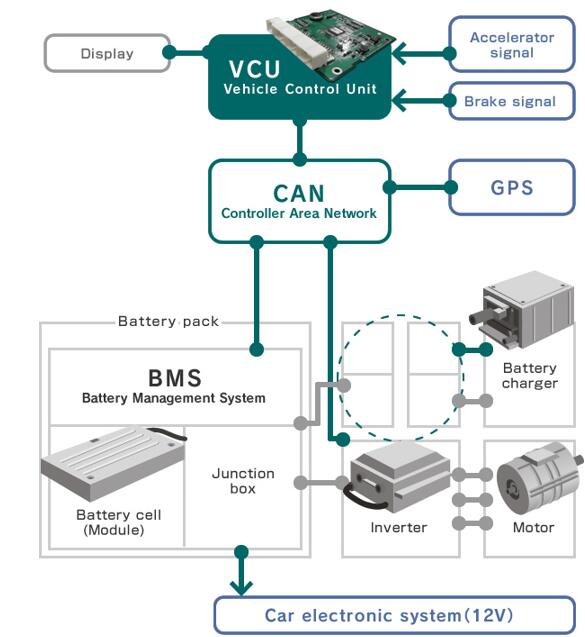
As the "brain" of the electric drive system, the vehicle control unit in EV is responsible for coordinating and managing core components such as drive motors, motor controllers, and electromechanical coupling assemblies. It directly determines the overall efficiency, safety, and intelligence of the electric drive system. Based on the technical foundation of 2025—such as the international advanced level of Si-based motor controllers and the industrialization of wide-bandgap power device controllers—the VCU in 2026 will further integrate intelligent algorithms and cross-domain control capabilities, promoting the electric drive system to leap from "functional realization" to "performance optimization".
II. Core Component Technology Trends of 2026 Electric Drive Systems (Driven by VCU)
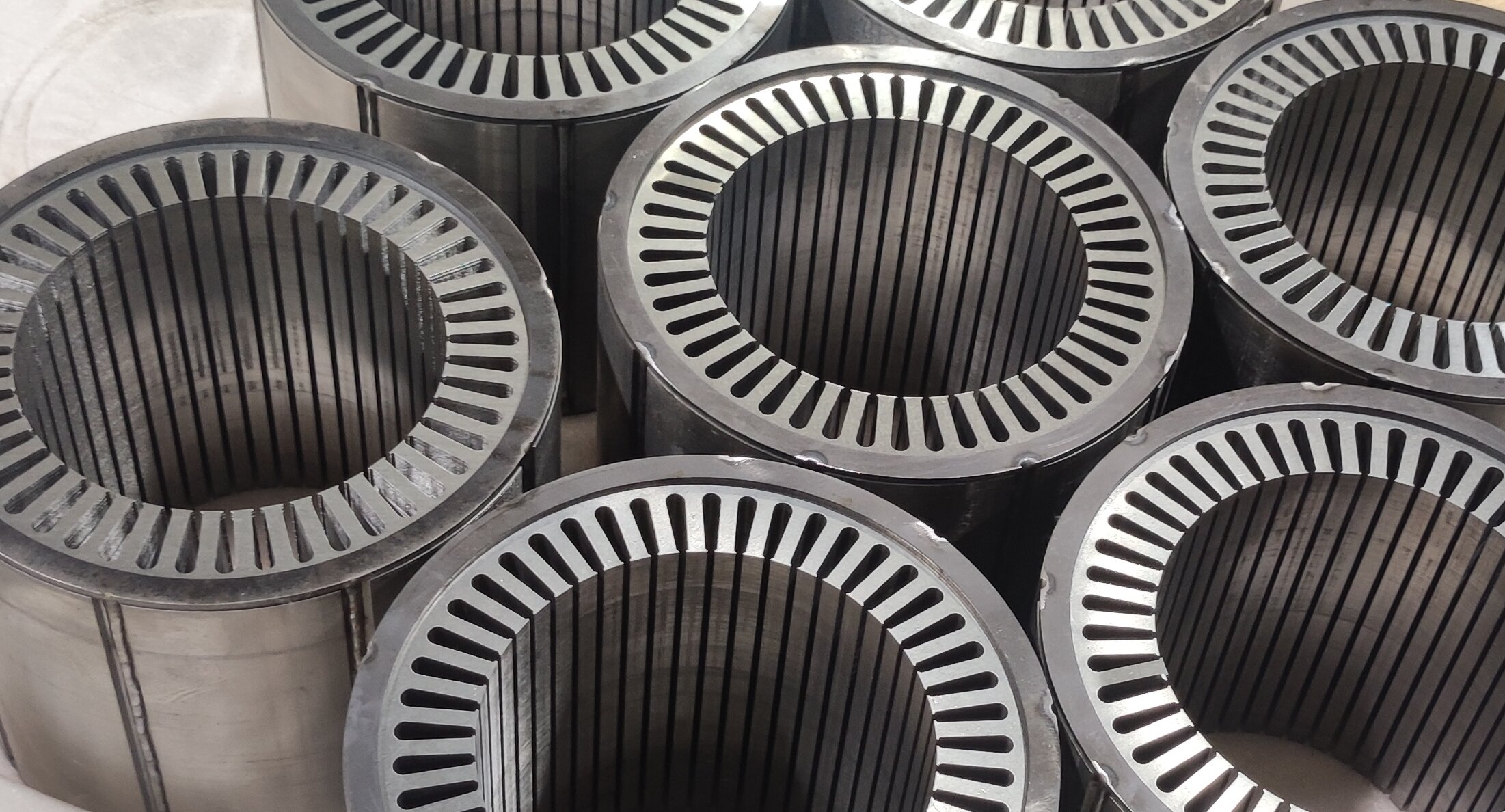
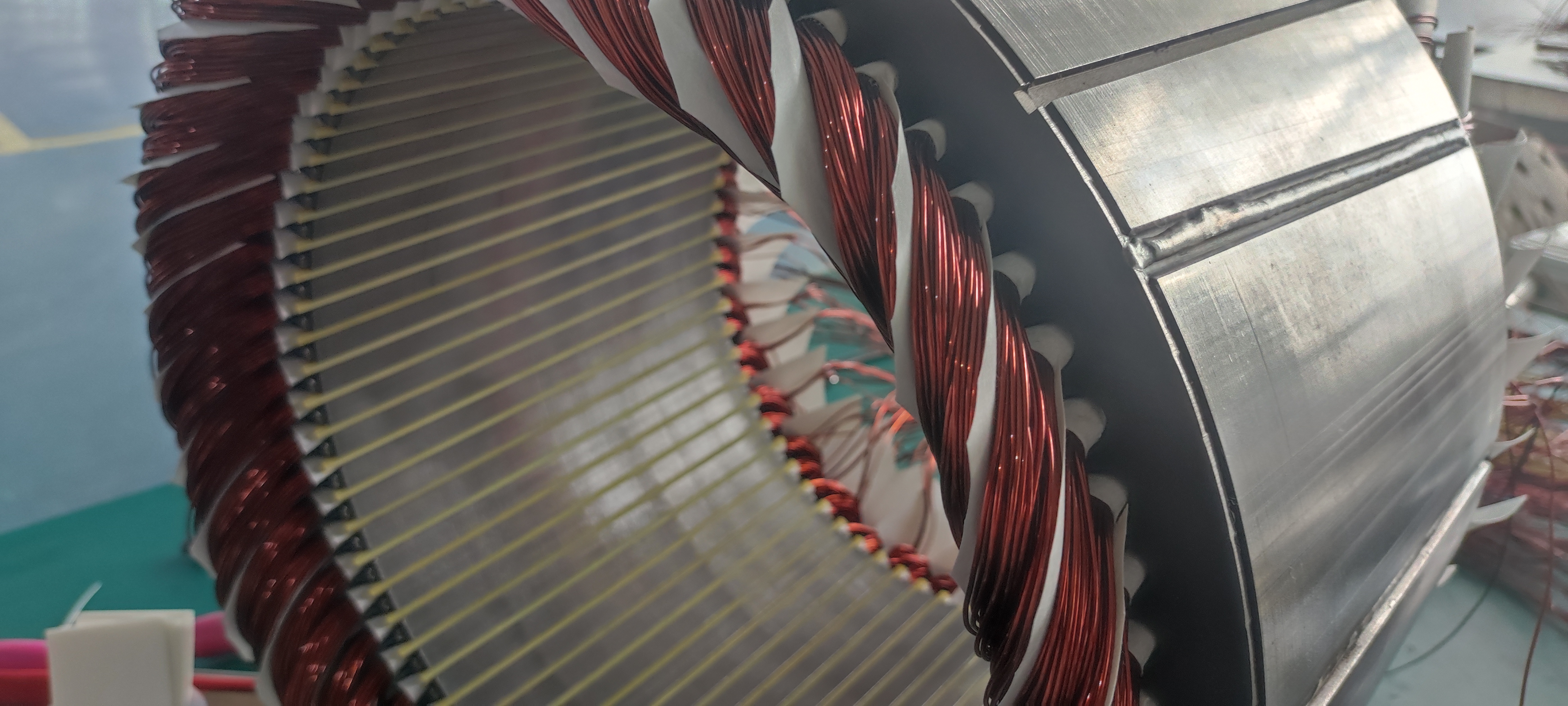
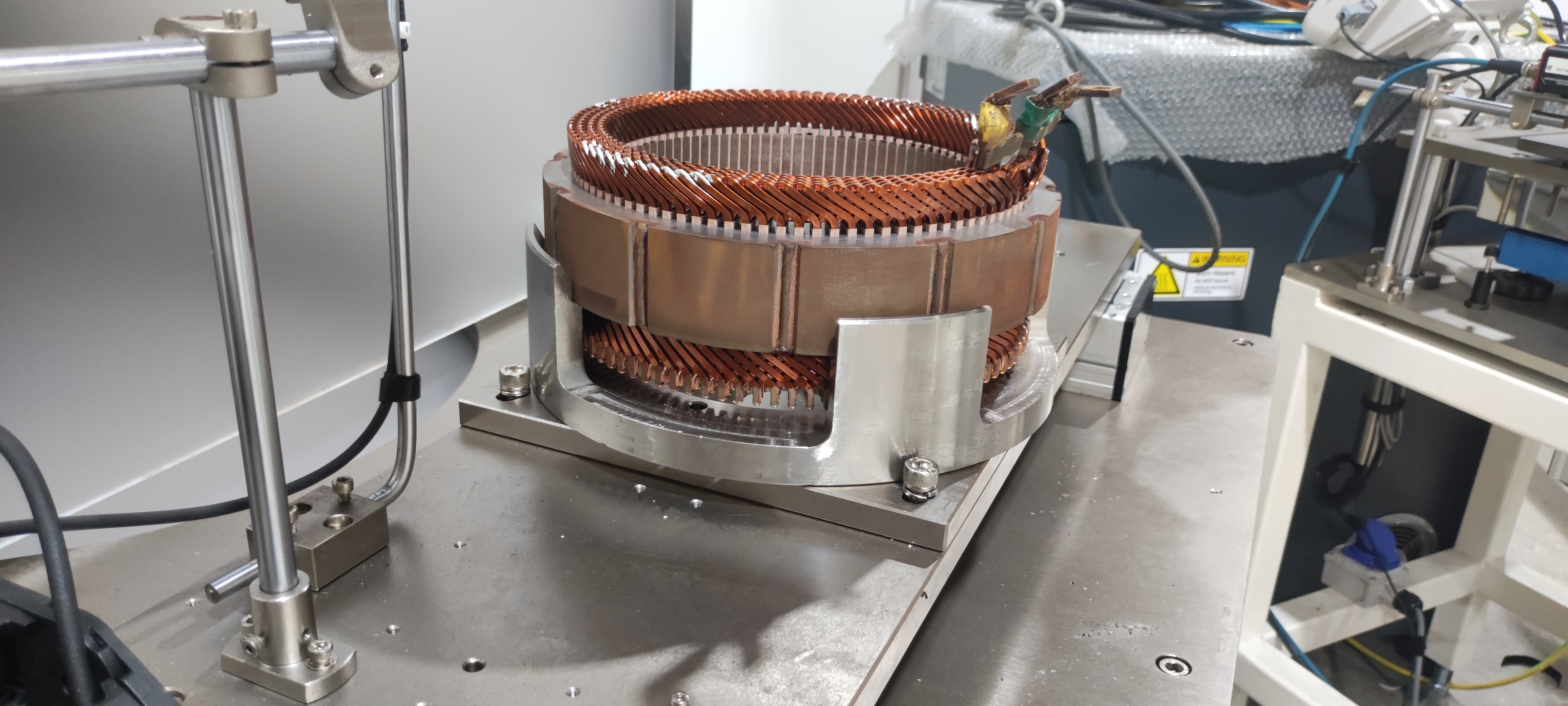
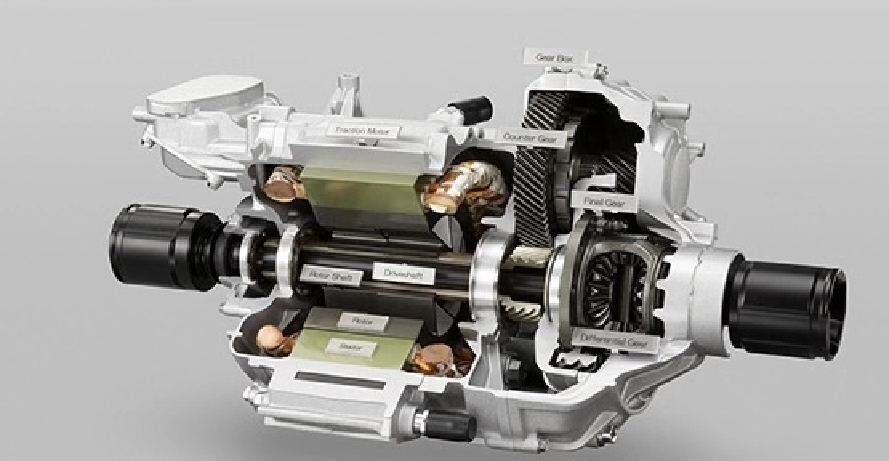
2.1 Drive Motor: High-Voltage, High-Efficiency Upgrade & VCU Synergy
In 2026, the key performance of drive motors has reached an international advanced level, moving towards high-voltage and high-speed directions, and advanced manufacturing processes have been widely applied, with some key manufacturing equipment realizing localization. For popular passenger cars, motor products have achieved high reliability, long life, and maintenance-free features. The electric vehicle control unit (VCU) plays a key synergistic role in this process.
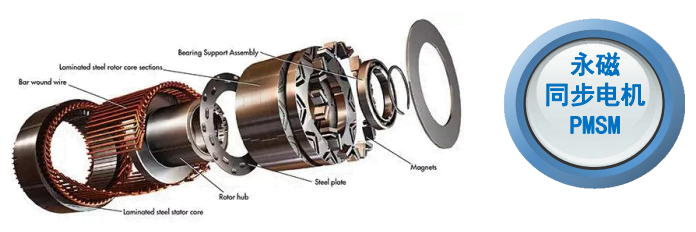
The VCU optimizes the matching strategy between the motor and the power system in real time. For example, aiming at the high-voltage flat wire stator technology of the motor, the vehicle control unit in ev precisely controls the current output to avoid insulation risks caused by PDIV (Partial Discharge Inception Voltage) problems; for new motor topologies such as axial flux motors and light rare earth synchronous motors, the VCU customizes adaptive control algorithms to maximize the motor's efficiency potential.
In addition, the VCU cooperates with the motor's efficient cooling system (including oil cooling technology) to realize dynamic thermal management. According to the motor's real-time load and temperature data, the VCU adjusts the cooling power, ensuring the motor operates stably under full working conditions while reducing energy waste, which responds to the industry's key research direction of ultra-efficient cooling technology in 2025.
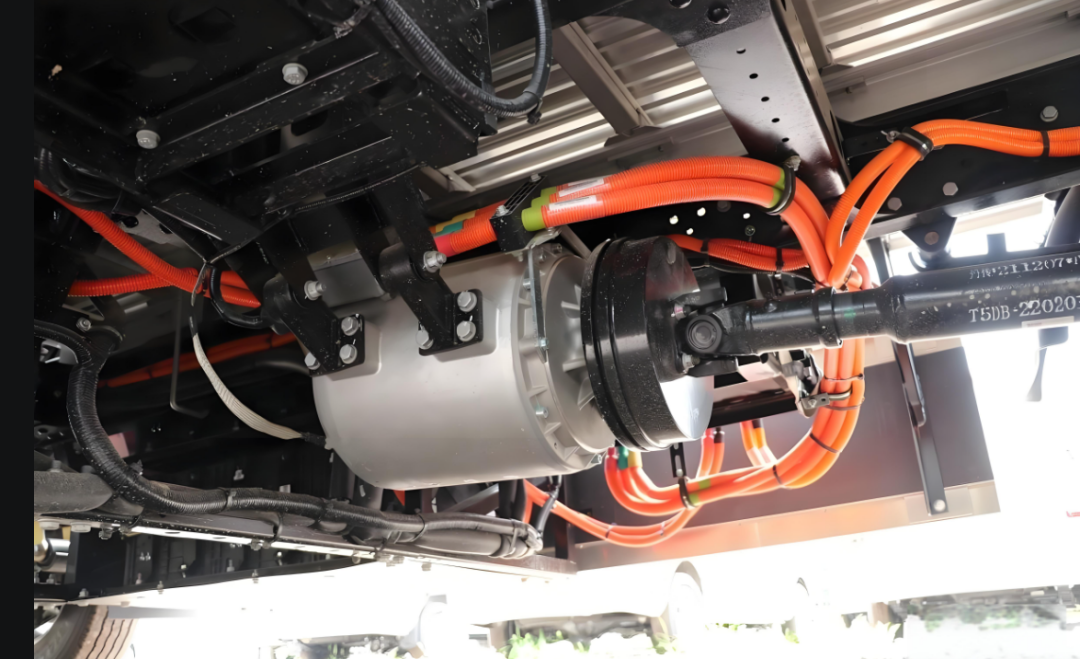
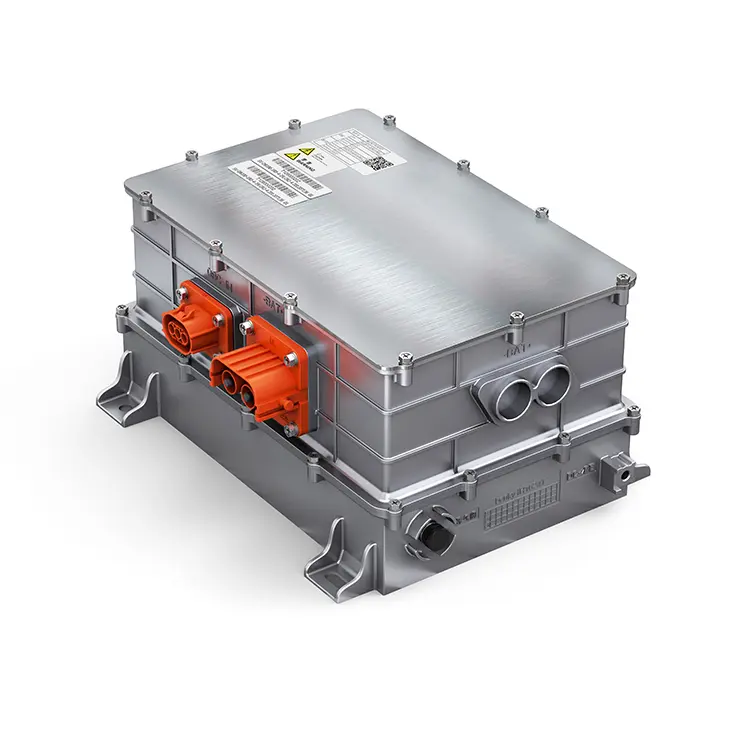
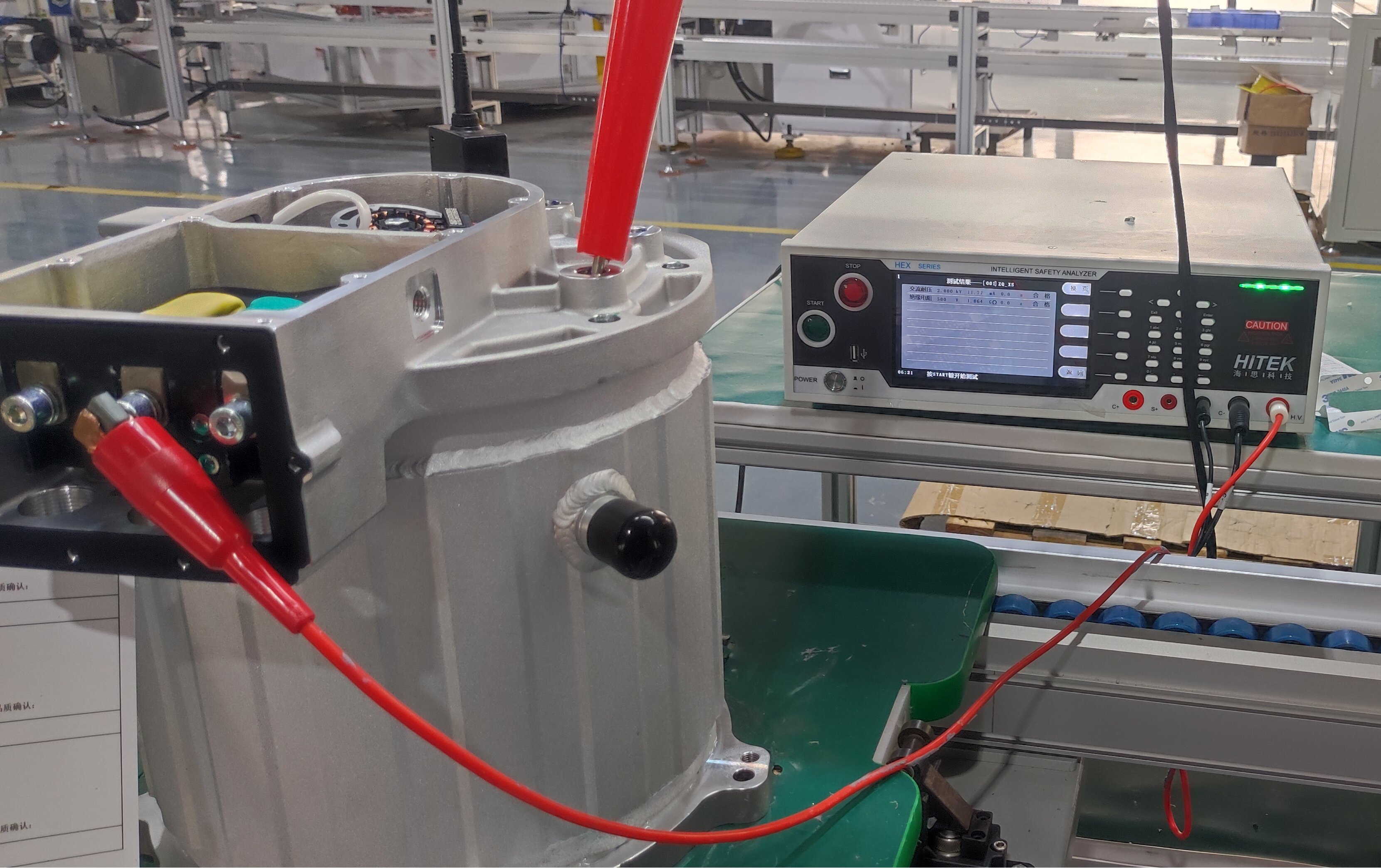
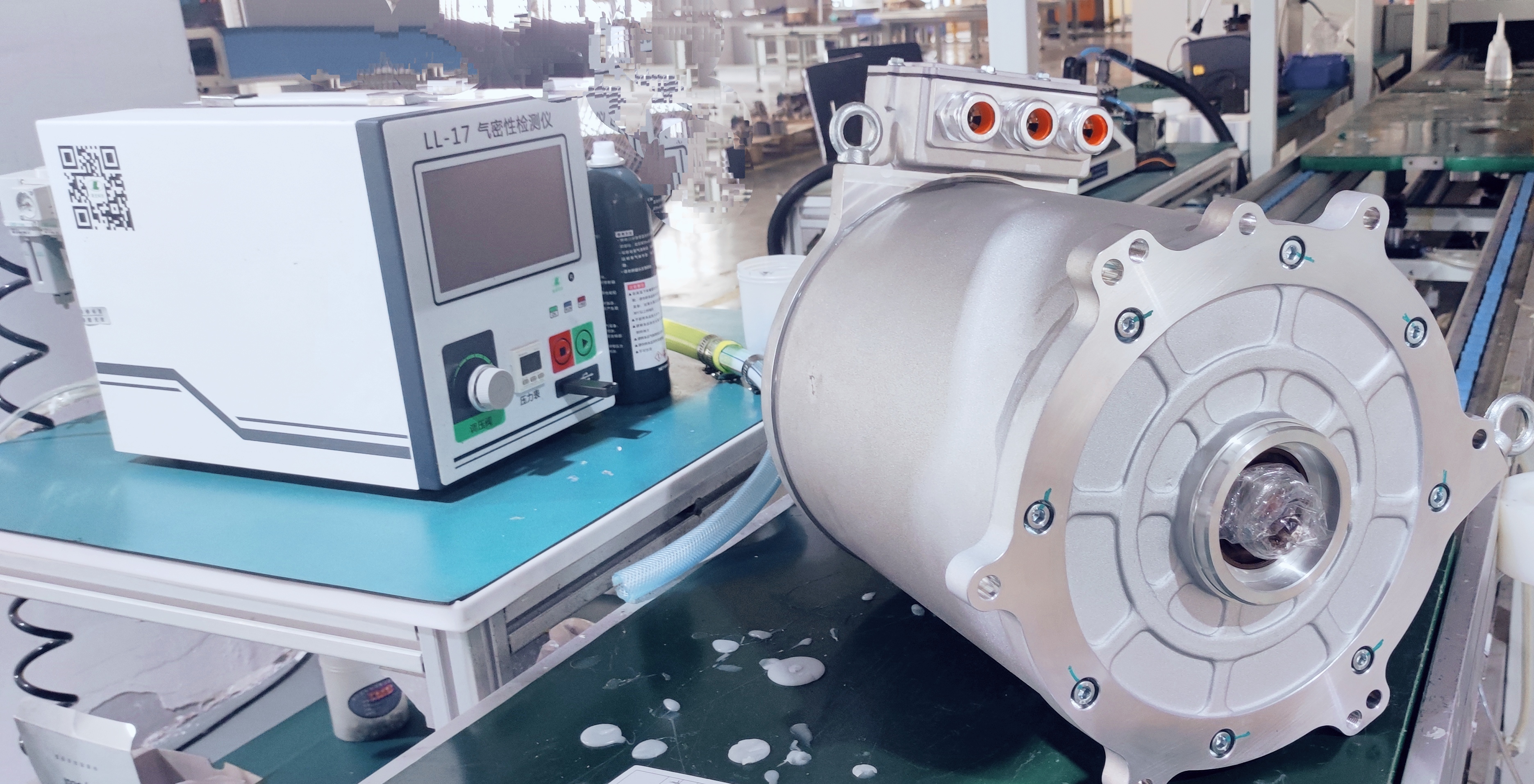
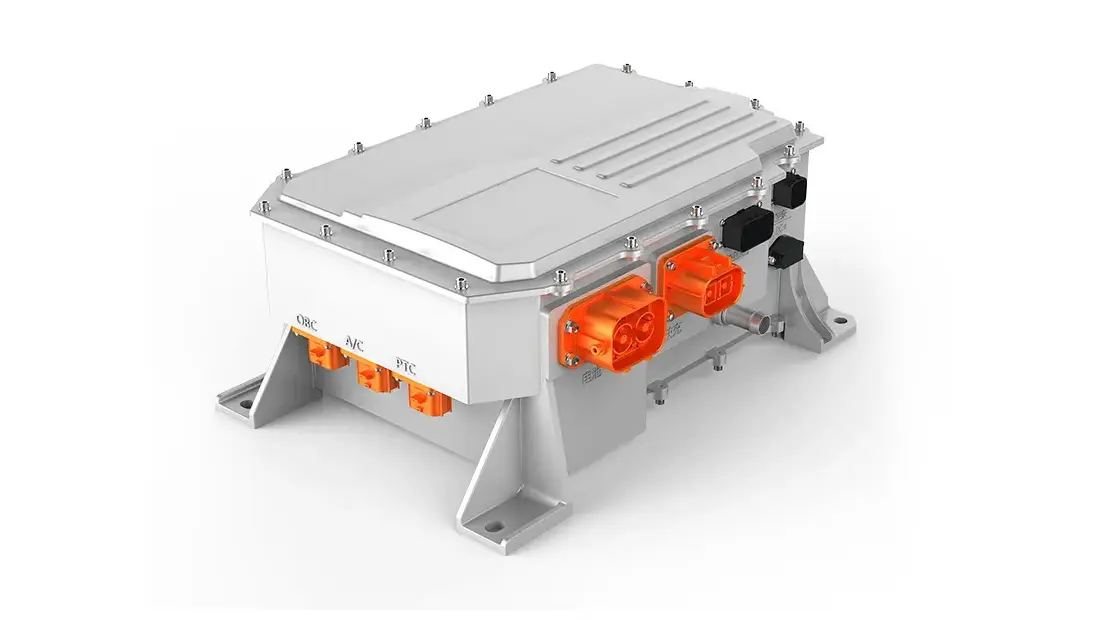
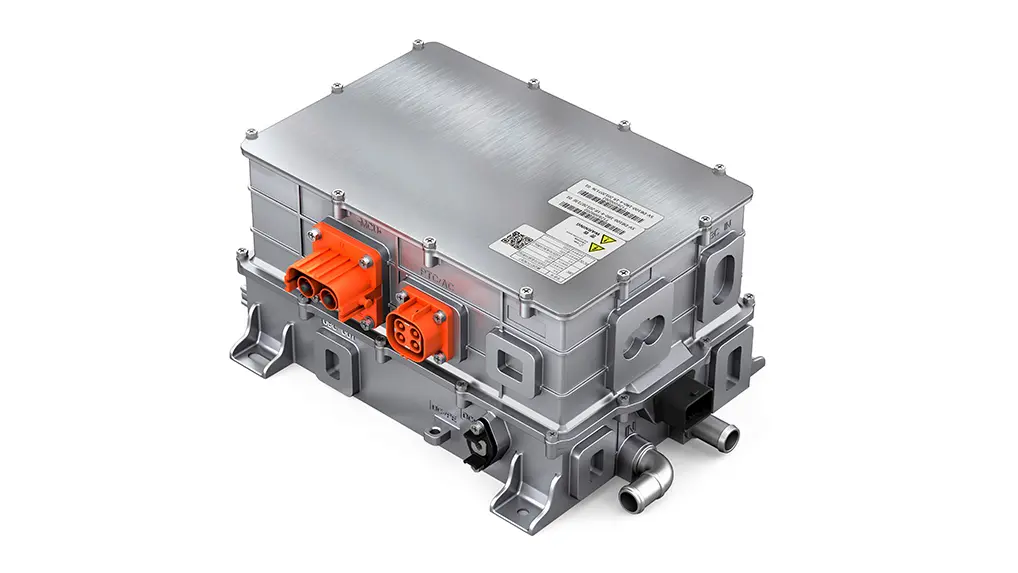
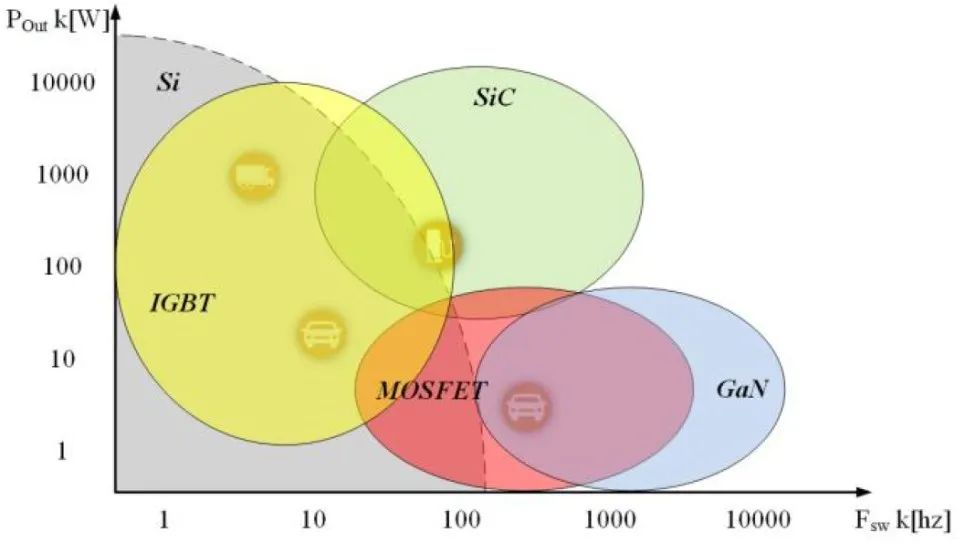
2.2 Motor Controller: Wide-Bandgap Upgrade & VCU Integration
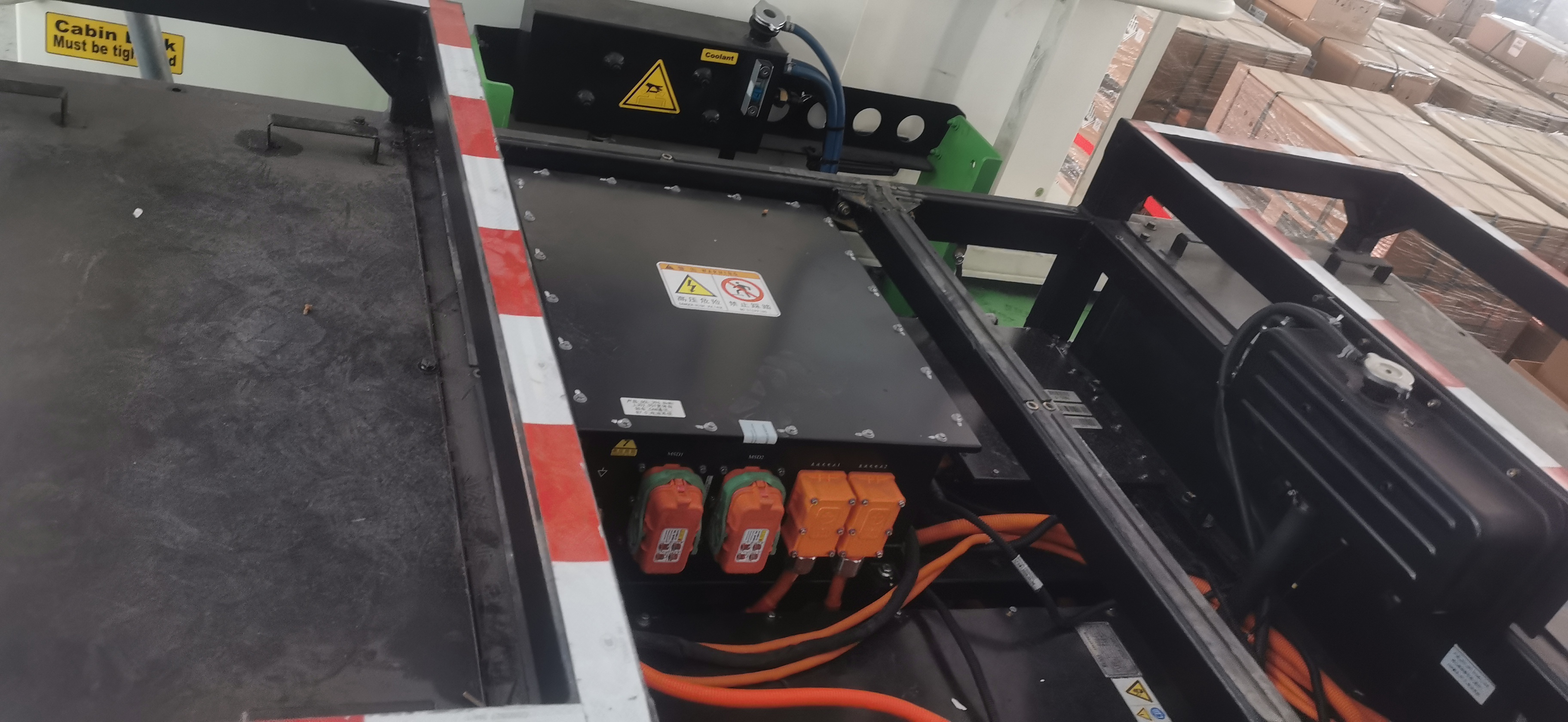
In 2026, the key performance indicators of Si-based motor controllers have reached the international advanced level, and high-voltage and advanced processes have been maturely applied. More importantly, motor controllers based on wide-bandgap power devices (such as SiC chips) have realized industrialization, and the electric vehicle control unit has promoted the deep integration of motor controllers with the entire electric drive system.
The vehicle control unit in EV is closely linked with the motor controller to build an intelligent monitoring architecture for the operation status of the electric drive system. The VCU collects real-time data such as the operating status of power devices and the efficiency of the controller, optimizes PWM modulation strategies and current control algorithms through AI technology, and effectively improves the electromagnetic compatibility of the system. This solves the industry's demand for improving electromagnetic compatibility through the algorithm optimization proposed in 2025.
At the same time, the VCU promotes the integrated design of motor controllers. It integrates functions such as DCDC, OBC, and boost converters into the motor controller, and realizes the electromechanical-thermal integrated design of high-density power components through unified control of the VCU, reducing the volume and weight of the system while improving overall efficiency.
For commercial vehicles, motor controllers are mainly multi-in-one integrated, and power device-level integrated products have become an important technical direction. The VCU adapts to this trend, realizes centralized control of integrated controllers, and strengthens the stability of the commercial vehicle power system supply chain.
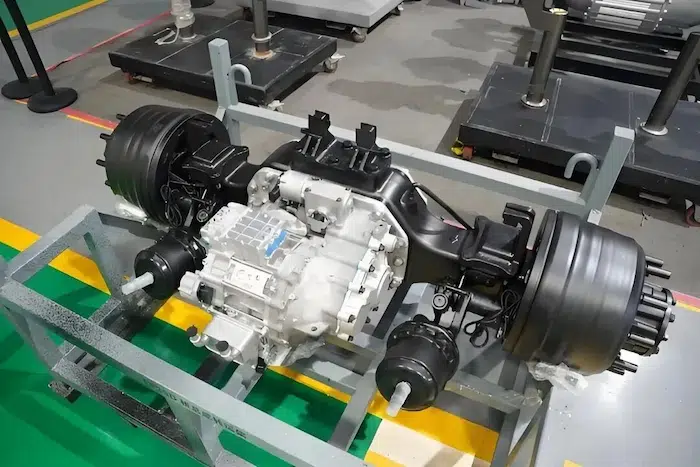
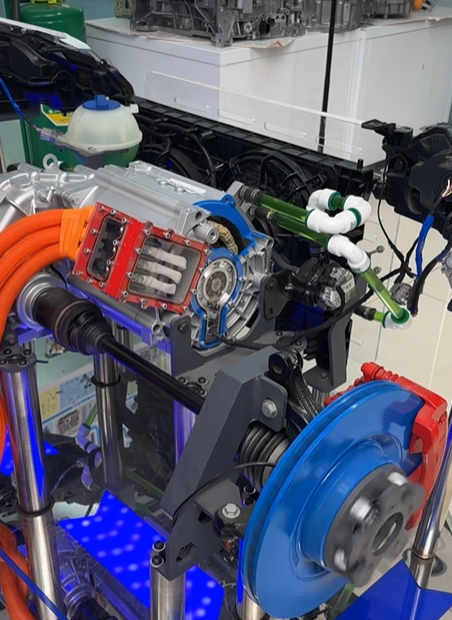
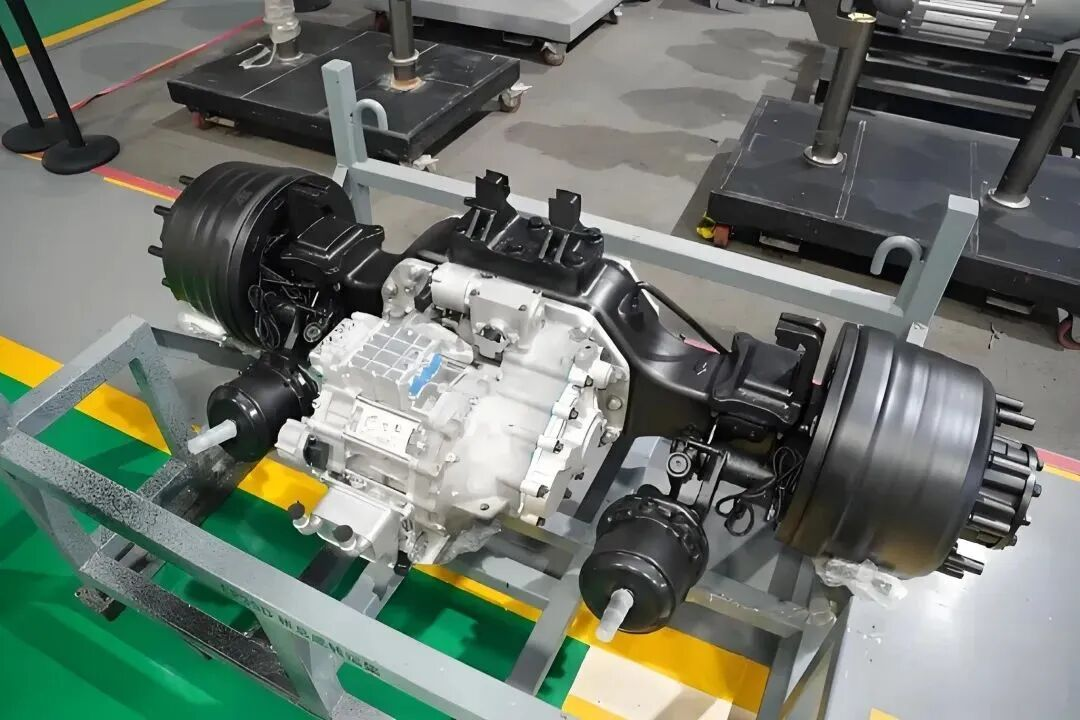
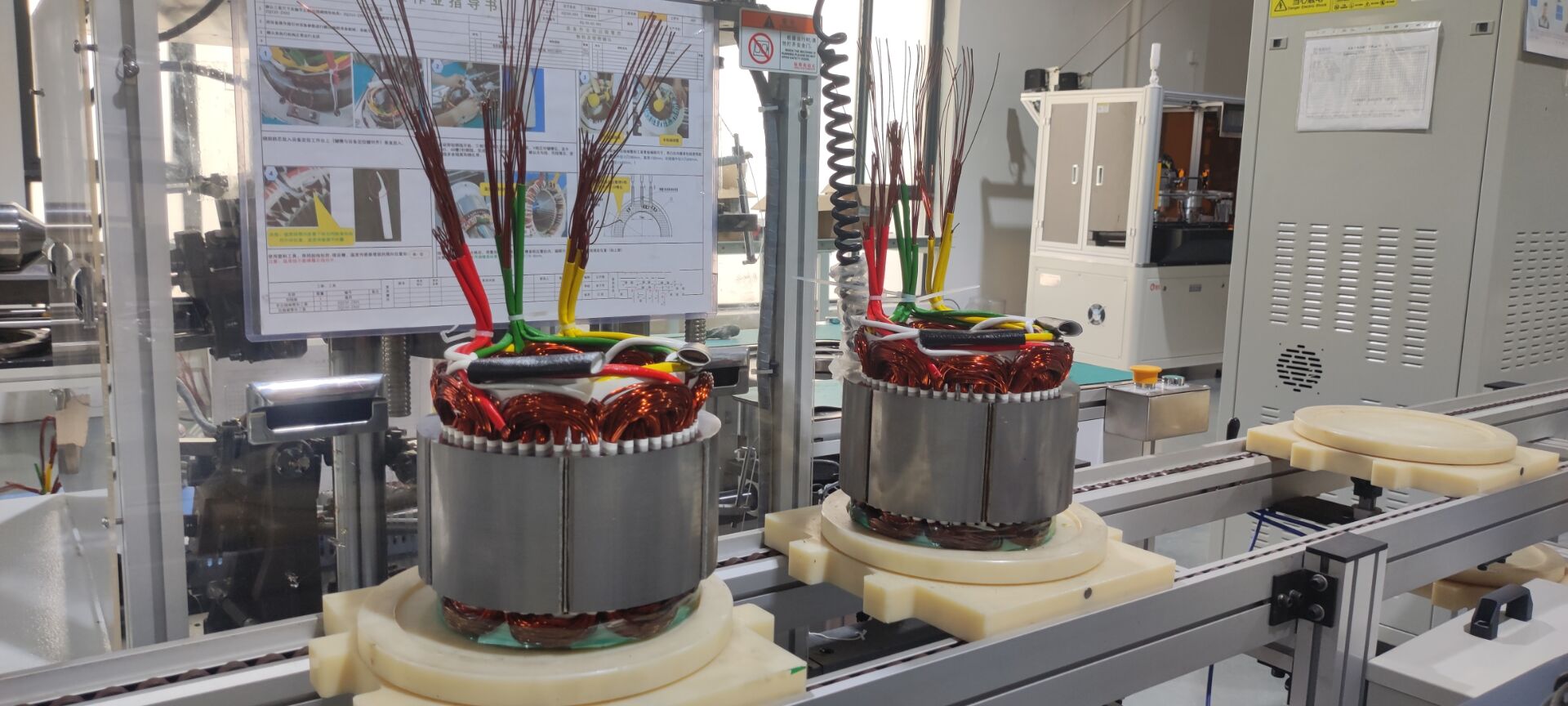
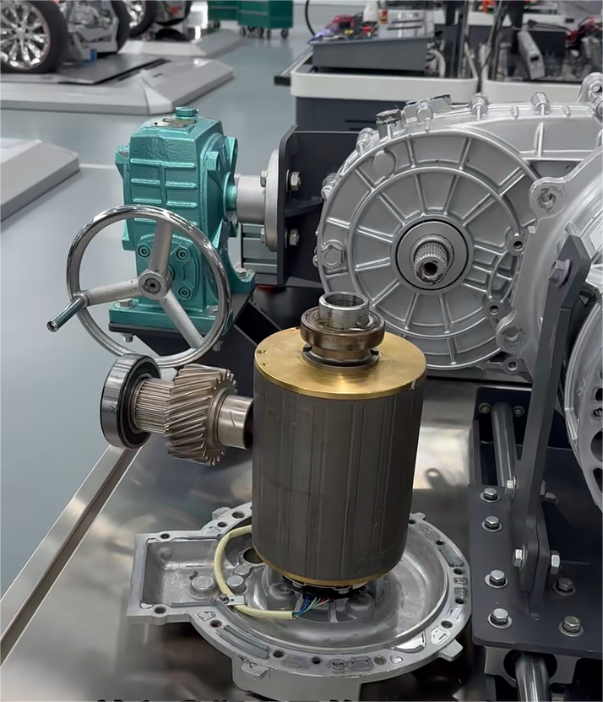
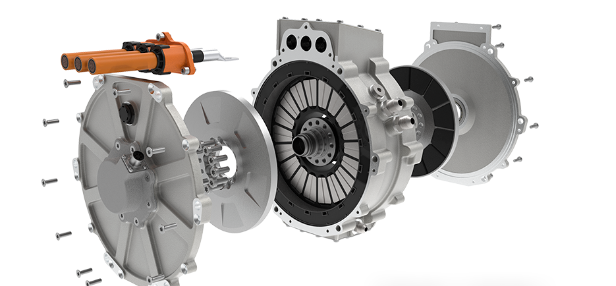
2.3 Electric Drive Assembly: High Integration & VCU Coordination Control
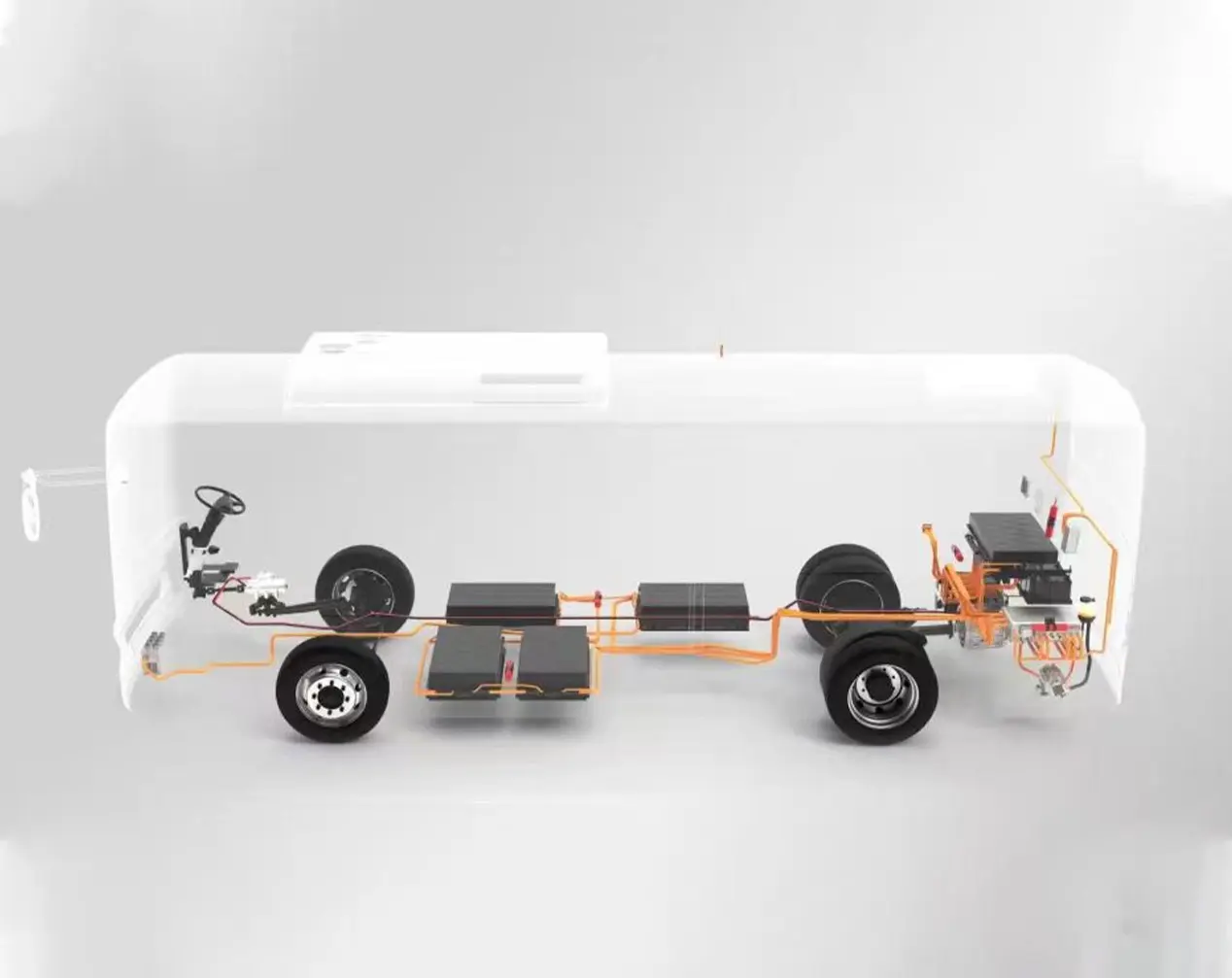
In 2026, the performance of plug-in electromechanical coupling assemblies has reached the international advanced level, and the integration degree of electromechanical coupling electric drive assemblies has been continuously improved. The comprehensive competitiveness of China's independent electric drive industry has reached an international advanced level, with significantly enhanced sustainable development capacity, and the domestic self-sufficiency rate of core components has exceeded 50% in terms of commodity value. The electric vehicle control unit is the core of the coordinated control of the electric drive assembly.
For passenger car pure electric drive assemblies, the VCU promotes in-depth integration of power electronics, cross-domain function integration, and application of lightweight materials, reducing the weight, volume, and cost of the electric drive system. It focuses on coordinating the work of high-speed reducers, multi-speed transmissions, and high-performance brakes and optimizes the control strategy of the entire assembly based on real-time road conditions. For example, the VCU adjusts the gear shifting logic of the multi-speed transmission to ensure smooth power output and improve energy utilization efficiency.
For plug-in hybrid assemblies, the VCU focuses on multi-power coordinated control. It integrates functions such as in-depth integration, efficient heat exchange, and domain control, and promotes the research and application of functional safety and cybersecurity technologies. In the commercial vehicle field, the VCU optimizes the performance of the power assembly for different application scenarios, further improving the integration degree and efficiency of the power assembly device.
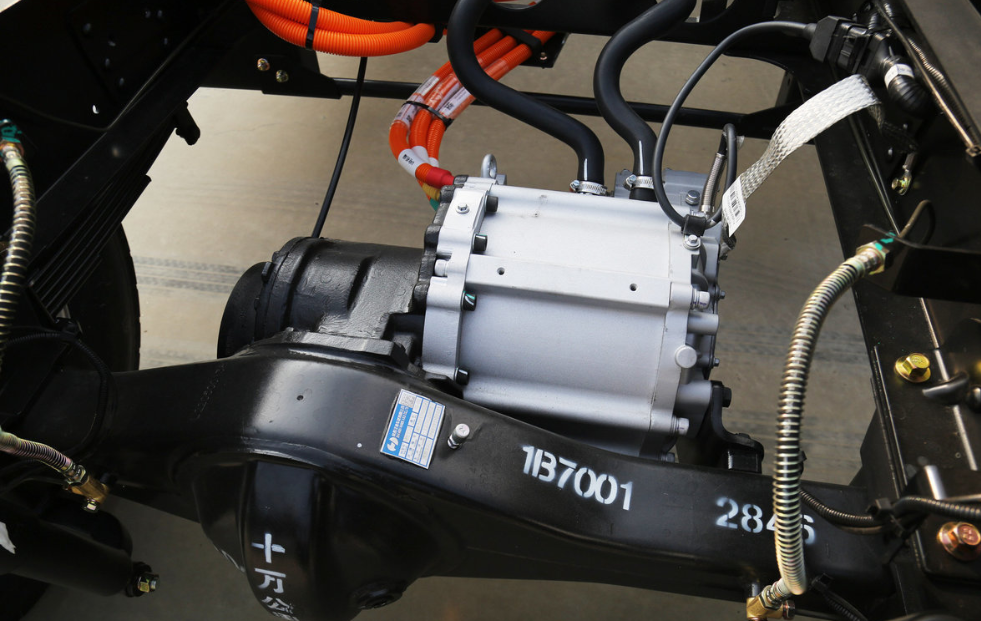
For hub and wheel-side motor assemblies, which are in small-batch demonstration operation in 2026, the vehicle control unit in EV solves the core problems of poor coordination and low efficiency. It coordinates the output of multiple hub motors to realize functions such as in-situ steering and promotes the localization of key components and cost control. At the same time, the VCU participates in the whole-chain engineering application verification of hub electric wheels, including weight reduction, key components and materials, and manufacturing processes.
2.4 VCU's Core Support for Multi-Motor Layout & Angle Module
The popularization of multi-motor layouts (dual-motor, four-motor) and the maturity of angle module technology in 2026 cannot be separated from the strong control capability of the electric vehicle control unit. For example, BMW's small-batch mass-produced dual-rotor motors rely on the VCU to provide real-time and accurate control signals to realize precise control of torque output and speed adjustment, ensuring the stability and power performance of the vehicle.
The VCU accurately calculates the optimal output angle of the motor through advanced algorithms, making the motor operate in the high-efficiency range under all working conditions. This not only improves the overall energy utilization rate of the electric drive system but also reduces the noise of the motor under all working conditions, which is consistent with the 2025 technical research direction.
For distributed electric drive systems, the VCU coordinates the output of multiple motors in real time, realizing four-wheel independent drive and improving the vehicle's passability and handling performance. The angle module technology, under the control of the VCU, adjusts the motor's output angle in real time according to the driving conditions, further tapping the potential of the electric drive system's efficiency.
III. Key Challenges Facing 2026 Electric Drive Systems (VCU-Oriented Solutions)
While the 2026 electric drive system is developing rapidly, it still faces many core challenges. The electric vehicle control unit (VCU) is the key to solving these challenges, and the industry needs to focus on the following directions to break through:
3.1 Technical Challenges of Core Components
In terms of drive motors, it is necessary to strengthen the research on ultra-efficient cooling (including oil cooling) technology, high-voltage flat wire stator PDIV insulation technology, all-condition low-noise technology, and new motor topologies (light rare earth/no rare earth synchronous motors, amorphous motors, etc.). The VCU needs to be compatible with these new technologies and develop adaptive control strategies to ensure the stable operation of the motor.
In terms of motor controllers, it is urgent to improve the electromechanical-thermal integration technology of high-density power components, power device integration and verification technology, and power battery pulse electric heating integration control technology. The vehicle control unit in EV needs to be deeply integrated with the motor controller to improve the design level and independent evaluation capability of products with high functional safety and cybersecurity levels.
3.2 Challenges of Electric Drive Assemblies
For passenger car pure electric drive assemblies, continuous investment is needed in power electronics, in-depth integration, cross-domain function integration, and lightweight material application to reduce the weight, volume, and cost of the system. The VCU needs to optimize the coordinated control strategy of the assembly to make up for the performance loss caused by cost control.
For plug-in hybrid assemblies, core technologies such as in-depth integration, efficient heat exchange, multi-power coordinated control, and domain controllers are key development directions, and the VCU is the core carrier of these technologies. In the commercial vehicle field, the supply chain of commercial vehicle-specific gearboxes needs to be strengthened, and the VCU should be oriented towards multi-integration, with power device-level integration as an important technical direction.
3.3 Green Manufacturing and Recycling Challenges
The electric drive system in 2026 faces the pressure of carbon reduction design, green manufacturing, and recycling. The industry needs to establish green manufacturing and smart factories, research recycling evaluation systems, and build recyclable production lines. The electric vehicle control unit, as a core electronic component, needs to realize green design from the material selection and manufacturing process.
The VCU can also participate in the full life cycle carbon emission management of the electric drive system. Through real-time monitoring of the operation status of the electric drive assembly, it optimizes the energy consumption strategy to reduce carbon emissions during the use stage. At the same time, the VCU's own recyclable design (such as modular structure) is also an important part of green manufacturing.
IV. 2026+ Electric Drive System Technology Framework & VCU's Core Position
4.1 Evolution of Electric Drive System Framework (From 2.0 to 3.0)
According to the "Energy-Saving and New Energy Vehicle Technology Roadmap 2.0", the drive motor system is the core component of the new energy vehicle power assembly and the key to realizing the conversion between electrical energy and mechanical energy. On this basis, the 2026 electric drive system 3.0 framework has been formed, which includes drive motors, motor controllers, electronic control integration systems, electric drive assemblies, testing and evaluation, and green manufacturing, covering the entire industrial chain of the electric drive system.
4.2 Core Position of VCU in the 3.0 Framework
The electric vehicle control unit (VCU) is the core of the electronic control integration system in the 3.0 framework, connecting all other modules. It realizes the centralized control of drive motors, motor controllers, and electric drive assemblies, and is an important part of testing and evaluation, and green manufacturing.
In the technical indicator system of the electric drive system, which covers 5 major sub-fields, the VCU's control accuracy, response speed, energy management efficiency, and other indicators are important components. The vehicle control unit in EV ensures that each core component of the electric drive system meets the technical indicators through real-time adjustment and optimization, promoting the overall performance upgrade of the system.
4.3 Key Research Directions of VCU in the Framework
Combined with the 3.0 framework, the key research directions of VCU mainly include three aspects: first, the integrated design of high-density power electronics, realizing the deep integration of VCU with motor controllers, power systems and other components; second, the research of intelligent algorithms, integrating AI and big data technology to improve the adaptive control and predictive maintenance capabilities of VCU; third, the research of functional safety and cyber security, improving the design level of VCU to meet the ASIL-D safety level requirements.
V. Future Outlook & Conclusion
5.1 Future Outlook (2026+)
Looking ahead to 2026+, the electric vehicle control unit (VCU) will lead the electric drive system toward smarter, more integrated, and greener development. It will deepen integration with autonomous driving for intelligent energy management, move toward vehicle-level integration to optimize overall performance, and adopt eco-friendly designs to reduce full-life-cycle carbon emissions. Additionally, the VCU will adapt to new energy technologies like solid-state batteries, fostering diversified development of electric drive systems.
5.2 Conclusion
In 2026, the electric vehicle control unit is the core driver of electric drive system innovation, boosting performance through cross-domain integration, AI empowerment, and multi-motor support. Despite challenges like technical difficulties and high costs, advancing VCU technology will clarify the future evolution of electric drive systems. Seizing VCU development opportunities enhances industry competitiveness, while bringing consumers safer, more efficient and intelligent driving experiences, accelerating EV popularization and the automotive industry’s green and intelligent transformation.