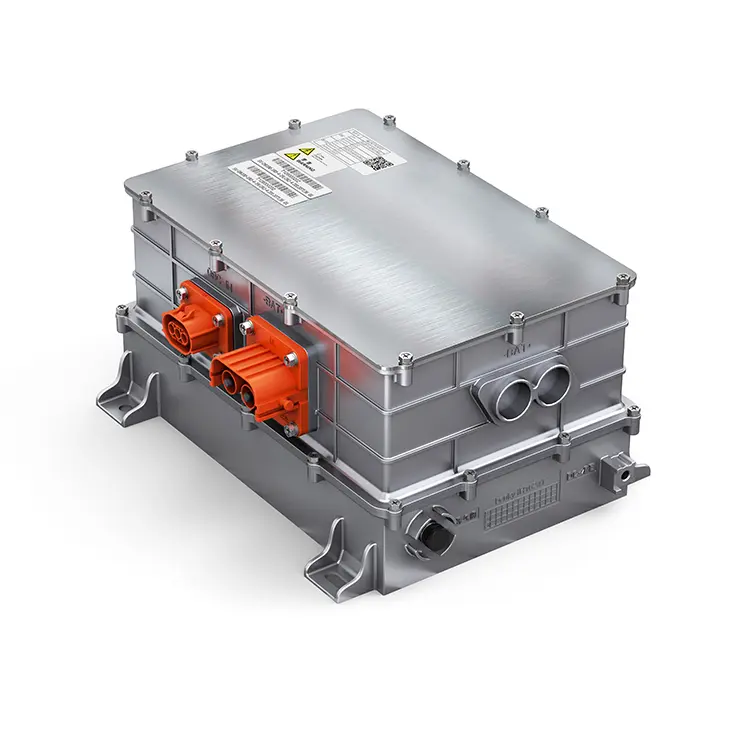
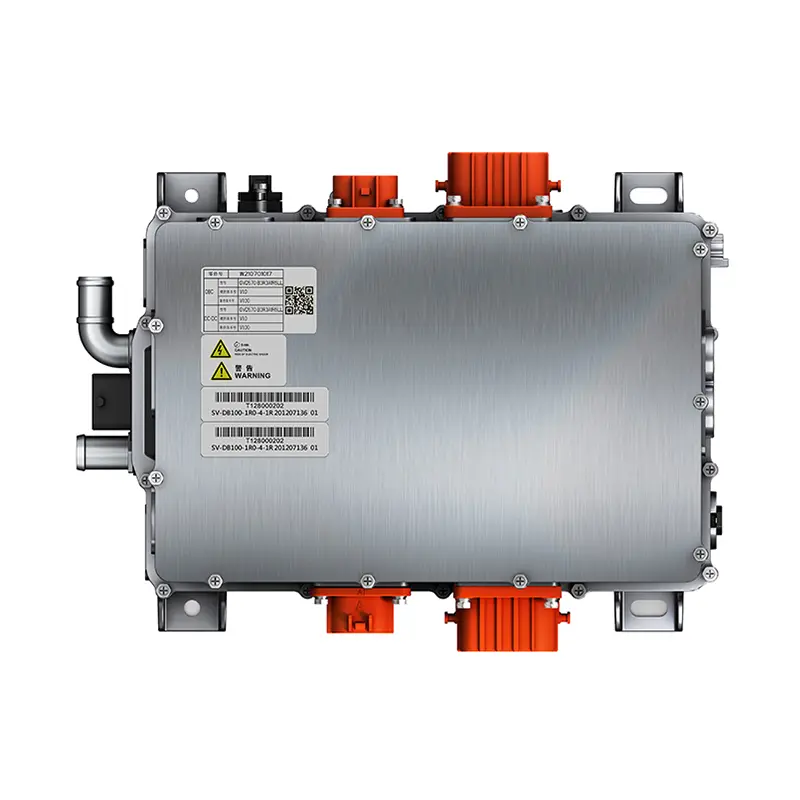
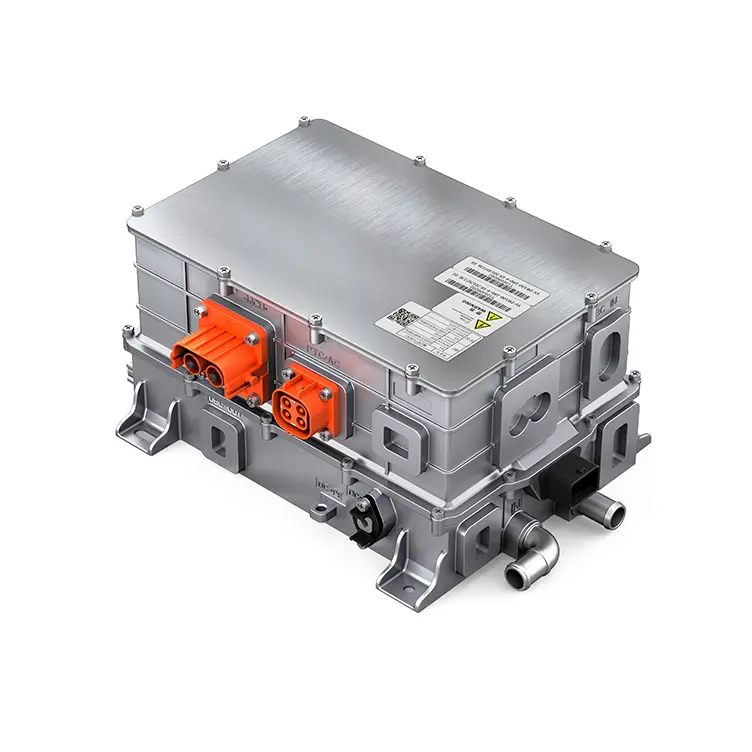
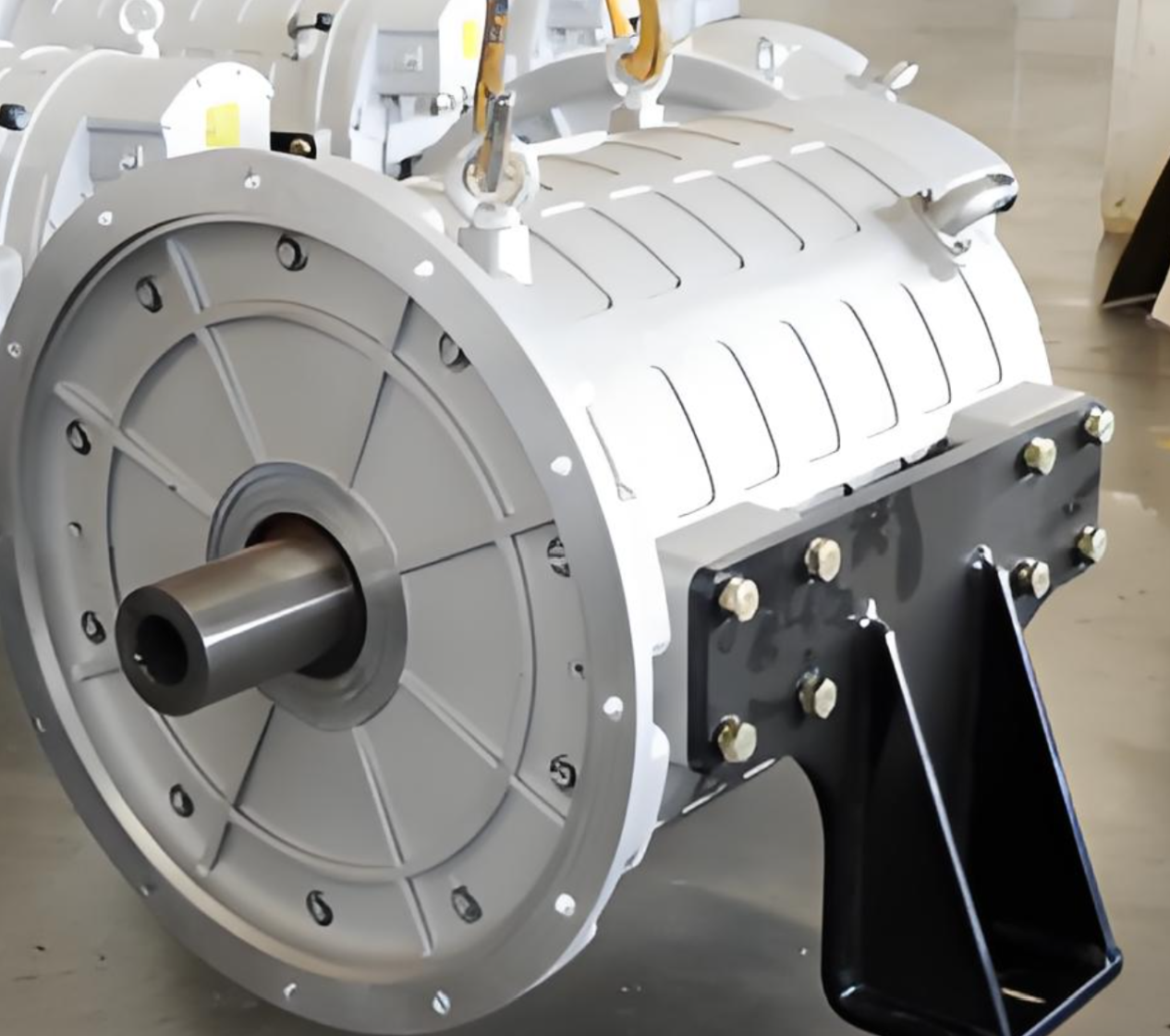
PUMBAA power conversion & distribution for electric vehicles PPS500
Features of PUMBAA Electric Vehicle power conversion & distribution 2*DCAC+DCDC+PDU 4-in-1 CDU Unit
1.Highly integrated electrical integration
2.Automotive grade design, ASIL compatible
3.Support V2L, V2G, V2V and other multi-scene requirements
4.Smaller and lighter design, stable technical performance and high efficiency
5.Liquid-cooled cooling method, fast heat dissipation, dustproof and low noise
6.Multiple protection functions such as EMC, voltage resistance, insulation, vibration and electrical protection
7.Allocation and control of high-voltage devices of the whole vehicle through the whole vehicle control unit to ensure the safety performance of each system
description2
Benefits of PUMBAA Electric Vehicle power conversion & distribution 2*DCAC+DCDC+PDU 4-in-1 CDU Unit
● Powerful hardware configuration
The main components adopt automotive components to improve product reliability;
● Efficient operation
Controller efficiency can be up to 98%, high power density, applications more flexible;
● Reliable protective design
The overall protection level is high and the working temperature range is wide, thus it can better adapt to all kinds of harsh application environment.
description2
Specification of PUMBAA Electric Vehicle power supply 2*DCAC+DCDC+PDU 4-in-1 CDU Unit
|
Model |
PPS500 |
|
|
Functional integration |
2*DCAC+DCDC+PDU |
|
|
Applicable models |
Logistics vehicles, sanitation vehicles |
|
|
Input characteristics |
High Voltage |
200-750V |
|
Low pressure |
24V |
|
|
Output characteristics |
Power |
Rating:5.5kW Peak:8.2kW |
|
Output Current |
Rating:13A Peak:19.5A(60S) |
|
|
Operating frequency |
0-400Hz |
|
|
System characteristics |
Operating temperature |
-40℃-85℃ |
|
Cooling mode |
Water cooling |
|
|
Size |
610W×430D×209H(mm) |
|
|
Weight |
About 20 kg |
|
|
Protection level |
IP67 |
|
description2
Application of EV OBC
Light truck, heavy truck, Bus, Mining trucks , pickup , van-type truck, Coach, Bus, City Sanitation vehicles

pick-up truck

van-type truck

Light truck

4.5T Electric Light truck

rubbish truck

sprinkler truck

bus

coach
The EV on-board Charger (OBC) is a device that converts alternating current (AC) power to direct current (DC) power in electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. It uses alternating current to charge the vehicle, and can also use the electrical outlet in the home to charge the electric vehicle. OBC electric vehicle has the ability to adjust voltage and current, can adapt to the needs of different electric vehicles.
description2
What's an EV OBC?
description2
How to charge an electric car
At present, electric vehicle charging stations can be broadly divided into two categories: AC charging stations and DC charging stations.

AC charging station
As the name implies is through the AC power grid to provide AC power to the electric vehicle, and then through the car charger will be converted from AC to DC power for the car charge. These charging stations are also known as Level 1 and 2 charging stations and are used in residential and commercial premises.
The advantage of the AC charging station is that the OBC (on board charger) can adjust the voltage and current according to the needs of the electric vehicle, so the charging station does not need to communicate with the electric vehicle. The disadvantage is low output power, long charge time. A typical AC charging system is shown. We can see that the AC power in the grid is fed directly to the OBC (on board charger) through the electric vehicle charging post (EVSE) , which then converts it to DC and charges the battery through the BMS.

DC charging station
Take AC power from the grid and convert it to DC voltage, then bypass the car charger (OBC) to charge the battery pack directly. These chargers typically deliver up to 600V of high voltage and up to 400A of current, and DC charging stations can charge an electric car in 30 minutes, compared with 8-16 hours for AC Chargers. These charging stations are also known as tertiary charging stations, and the Chargers used are often referred to as DC Fast Chargers (DCFC) or superchargers. The advantage of this type of charger is that the charging time is fast, the disadvantage is complex technology, the need to communicate with electric vehicles, in order to efficiently and safely charge electric vehicles. A typical DC charging system is shown below, where the EVSE bypasses the EV OBC to provide direct current to the battery pack.

The capacity of a standard DC charging station is 50-300 kilowatts, more than six times that of a single-phase vehicle charger. However, AC charging via the EV OBC has less impact on the battery and minimizes battery ageing.
description2
OBC (on board charger) features
▎The main function of the vehicle charger is to manage the charging process from the power grid to the power battery
The OBC (on board charger) aims to charge the battery faster while minimizing battery decay. AC chargers provide two types of charging: constant current and constant voltage. Constant current charges the battery faster, but does not charge the vehicle to full; constant voltage, also known as trickle charging, is slower, but has more control, and can charge the vehicle to full. To optimize the charging speed, the ev OBC uses a constant current at the beginning of the charging cycle and switches to constant-voltage charging mode at the end of the charging cycle.
▎Car Chargers also play an important role in the two-way charging mode of some models, which means they can also convert the DC power of high-voltage battery packs into AC power, to support ac Load (V2L: Vehicle to Load) , power Grid (V2G: Vehicle to Grid) , and even Home electricity (V2H: Vehicle to Home) .

description2
The hardware architecture of the OBC electric vehicle
The OBC electric vehicle consists mainly of the following hardware components:
Input voltage measuring circuit: this circuit measures the voltage used to control the conversion circuit.
Input Filter: this filter suppresses internal or peripheral equipment noise.
Full-wave rectifier circuit: this circuit will be AC voltage rectifier to DC voltage.
Power Factor Correction (PFC-RRB- circuit: this circuit improves power efficiency due to waveform phase shift deterioration.
Voltage conversion circuit: the circuit through the insulation transformer and FET switches for voltage conversion.
Output filter: this filter can suppress the internal noise generated.
Output voltage measuring circuit: this circuit is used to measure the voltage to control the conversion circuit.
DC/DC converter for electric vehicle: the converter supplies power to the control circuit.
Communication interface: this is the communication circuit that communicates with the peripheral equipment.
Typical hardware block diagrams are as follows:

description2
EV OBC trends and challenges
▎The EV OBC is an important component of BEV and PHEV. As the number of electric cars increases, so will the number of vehicles equipped with the OBC. At the same time, more and more electric vehicles will also be equipped with DC fast charging function.
▎The EV OBC will accommodate 800V high voltage platforms.
▎As 800V high-voltage platforms become more popular, and to charge larger batteries, we need to provide more power output OBC. The future OBC needs to have these features: “High Voltage (high voltage)”, “High current”, “Low loss”, “High heat resistance” and“Small size”.
▎The EV OBC requires the ability to charge in both directions.
▎The EV OBC converts the DC power of a high-voltage battery pack into AC power to support external AC loads.
▎Discrete high-voltage components will be widely used in OBC.
▎The trend toward fast charging will greatly increase the power required for the OBC topology.
The new OBC electric vehicle tends to be high power (11-22kW) . This trend, coupled with the need for low system costs, high efficiency and high power density.

In short, with the advancement of technology and the popularity of electric vehicles, more advanced OBC will facilitate everyone's travel and life.
description2